List of states with nuclear weapons
Eight sovereign states have publicly announced successful detonation of nuclear weapons.[1] Five are considered to be nuclear-weapon states (NWS) under the terms of the Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons (NPT). In order of acquisition of nuclear weapons these are the United States, Russia (the successor state to the Soviet Union), the United Kingdom, France, and China.

| Nuclear weapons |
|---|
 |
| Background |
| Nuclear-armed states |
|
Since the NPT entered into force in 1970, three states that were not parties to the Treaty have conducted overt nuclear tests, namely India, Pakistan, and North Korea. North Korea had been a party to the NPT but withdrew in 2003.
Israel is also generally understood to have nuclear weapons,[2][3][4][5][6] but does not acknowledge it, maintaining a policy of deliberate ambiguity, and is not known definitively to have conducted a nuclear test.[7] Israel is estimated to possess somewhere between 75 and 400 nuclear warheads.[8][9] One possible motivation for nuclear ambiguity is deterrence with minimum political cost.[10][11]
States that formerly possessed nuclear weapons are South Africa (developed nuclear weapons but then disassembled its arsenal before joining the NPT)[12] and the former Soviet republics of Belarus, Kazakhstan, and Ukraine, whose weapons were repatriated to Russia.
According to Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI), the worldwide total inventory of nuclear weapons as of 2019 stood at 13,865, of which 3,750 were deployed with operational forces.[13] In early 2019, more than 90% of the world's 13,865 nuclear weapons were owned by Russia and the United States.[14][15]
Statistics and force configuration
| Weapons of mass destruction |
|---|
 |
| By type |
| By country |
|
| Proliferation |
| Treaties |
|
The following is a list of states that have admitted the possession of nuclear weapons or are presumed to possess them, the approximate number of warheads under their control, and the year they tested their first weapon and their force configuration. This list is informally known in global politics as the "Nuclear Club".[16][17] With the exception of Russia and the United States (which have subjected their nuclear forces to independent verification under various treaties) these figures are estimates, in some cases quite unreliable estimates. In particular, under the Strategic Offensive Reductions Treaty thousands of Russian and U.S. nuclear warheads are inactive in stockpiles awaiting processing. The fissile material contained in the warheads can then be recycled for use in nuclear reactors.
From a high of 70,300 active weapons in 1986, as of 2019 there are approximately 3,750 active nuclear warheads and 13,890 total nuclear warheads in the world.[1] Many of the decommissioned weapons were simply stored or partially dismantled, not destroyed.[18]
It is also noteworthy that since the dawn of the Atomic Age, the delivery methods of most states with nuclear weapons has evolved with some achieving a nuclear triad, while others have consolidated away from land and air deterrents to submarine-based forces.
| Country | Warheads[lower-alpha 1] |
Date of first test |
Test site of first test |
CTBT status |
Delivery methods |
Tests |
Refs | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dep. | Tot. | |||||||
| The five nuclear-weapon states under the NPT | ||||||||
| 1,750 | 5,800 | 16 July 1945 (Trinity) | Alamogordo, New Mexico | Signatory[19] | Nuclear triad[20] | 1,054 | [1][21] | |
| 1,572 | 6,372 | 29 August 1949 (RDS-1) | Semipalatinsk, Kazakhstan | Ratifier[19] | Nuclear triad[22] | 715 | [1][21] | |
| 120 | 215 | 3 October 1952 (Hurricane) | Monte Bello Islands, Australia | Ratifier[19] | Sea-based[23][lower-alpha 2] | 45 | [1][21] | |
| 280 | 290 | 13 February 1960 (Gerboise Bleue) | Sahara, French Algeria | Ratifier[19] | Sea and air-based[24][lower-alpha 3] | 210 | [1][21] | |
| (?) | 320 | 16 October 1964 (596) | Lop Nur, Xinjiang | Signatory[19] | Nuclear triad[25][26] | 45 | [1][21] | |
| Non-NPT nuclear powers | ||||||||
| (?) | 150 | 18 May 1974 (Smiling Buddha) | Pokhran, Rajasthan | Non-signatory[19] | Nuclear triad[27][28][29][30] | 6 | [1][21] | |
| 0 | 160 | 28 May 1998 (Chagai-1) | Ras Koh Hills, Balochistan | Non-signatory[19] | Land and air-based[31][32][lower-alpha 4] | 6 | [1] | |
| 0 | 30–40 | 9 October 2006[34] | Kilju, North Hamgyong | Non-signatory[19] | Land and sea-based[35][36] | 6 | [1][21] | |
| Undeclared nuclear powers | ||||||||
| 0 | 90 | 1960–1979[37][lower-alpha 5] | Unknown | Signatory[19] | Suspected nuclear triad[39][40] | N/A | [1] | |
Recognized nuclear-weapon states
These five states are known to have detonated a nuclear explosive before 1 January 1967 and are thus nuclear weapons states under the Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons. They also happen to be the UN Security Council's permanent members with veto power on UNSC resolutions.
United States

The United States developed the first nuclear weapons during World War II in cooperation with the United Kingdom and Canada as part of the Manhattan Project, out of the fear that Nazi Germany would develop them first. It tested the first nuclear weapon on July 16, 1945 ("Trinity") at 5:30 am, and remains the only country to have used nuclear weapons in war, devastating the Japanese cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki. It was the first nation to develop the hydrogen bomb, testing an experimental prototype in 1952 ("Ivy Mike") and a deployable weapon in 1954 ("Castle Bravo"). Throughout the Cold War it continued to modernize and enlarge its nuclear arsenal, but from 1992 on has been involved primarily in a program of Stockpile stewardship.[41][42][43][44] The U.S. nuclear arsenal contained 31,175 warheads at its Cold War height (in 1966).[45] During the Cold War, the United States built approximately 70,000 nuclear warheads, more than all other nuclear-weapon states combined.[46][47]
Russia (successor to the Soviet Union)
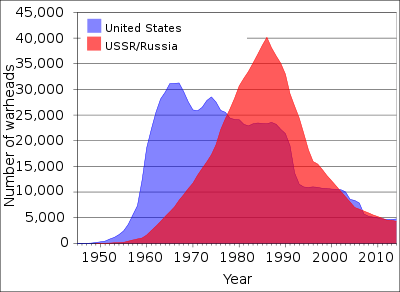
The Soviet Union tested its first nuclear weapon ("RDS-1") in 1949. This crash project was developed partially with information obtained via espionage during and after World War II. The Soviet Union was the second nation to have developed and tested a nuclear weapon. The direct motivation for Soviet weapons development was to achieve a balance of power during the Cold War. It tested its first megaton-range hydrogen bomb ("RDS-37") in 1955. The Soviet Union also tested the most powerful explosive ever detonated by humans, ("Tsar Bomba"), with a theoretical yield of 100 megatons, intentionally reduced to 50 when detonated. After its dissolution in 1991, the Soviet weapons entered officially into the possession of the Russian Federation.[48] The Soviet nuclear arsenal contained some 45,000 warheads at its peak (in 1986); the Soviet Union built about 55,000 nuclear warheads since 1949.[47]
United Kingdom

The United Kingdom tested its first nuclear weapon ("Hurricane") in 1952. The UK had provided considerable impetus and initial research for the early conception of the atomic bomb, aided by Austrian, German and Polish physicists working at British universities who had either fled or decided not to return to Nazi Germany or Nazi controlled territories. The UK collaborated closely with the United States and Canada during the Manhattan Project, but had to develop its own method for manufacturing and detonating a bomb as U.S. secrecy grew after 1945. The United Kingdom was the third country in the world, after the United States and the Soviet Union, to develop and test a nuclear weapon. Its programme was motivated to have an independent deterrent against the Soviet Union, while also maintaining its status as a great power. It tested its first hydrogen bomb in 1957 (Operation Grapple), making it the third country to do so after the United States and Soviet Union.[49][50] The UK maintained a fleet of V bomber strategic bombers and ballistic missile submarines (SSBNs) equipped with nuclear weapons during the Cold War. It currently maintains a fleet of four Vanguard-class ballistic missile submarines equipped with Trident II missiles. In 2016, the UK House of Commons voted to renew the British nuclear weapons system with the Dreadnought-class submarine, without setting a date for the commencement of service of a replacement to the current system.
France

France tested its first nuclear weapon in 1960 ("Gerboise Bleue"), based mostly on its own research. It was motivated by the Suez Crisis diplomatic tension vis-à-vis both the Soviet Union and its allies, the United States and United Kingdom. It was also relevant to retain great power status, alongside the United Kingdom, during the post-colonial Cold War (see: Force de frappe). France tested its first hydrogen bomb in 1968 ("Opération Canopus"). After the Cold War, France has disarmed 175 warheads with the reduction and modernization of its arsenal that has now evolved to a dual system based on submarine-launched ballistic missiles (SLBMs) and medium-range air-to-surface missiles (Rafale fighter-bombers). However new nuclear weapons are in development and reformed nuclear squadrons were trained during Enduring Freedom operations in Afghanistan. France signed the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty in 1992.[51] In January 2006, President Jacques Chirac stated a terrorist act or the use of weapons of mass destruction against France would result in a nuclear counterattack.[52] In February 2015, President Francois Hollande stressed the need for a nuclear deterrent in "a dangerous world". He also detailed the French deterrent as "fewer than 300" nuclear warheads, three sets of 16 submarine-launched ballistic missiles and 54 medium-range air-to-surface missiles" and urged other states to show similar transparency.[53]
China
China tested its first nuclear weapon device ("596") in 1964 at the Lop Nur test site. The weapon was developed as a deterrent against both the United States and the Soviet Union. Two years later, China had a fission bomb capable of being put onto a nuclear missile. It tested its first hydrogen bomb ("Test No. 6") in 1967, a mere 32 months after testing its first nuclear weapon (the shortest fission-to-fusion development known in history).[54] China is the only NPT nuclear-weapon state to give an unqualified negative security assurance with its "no first use" policy.[55][56] China signed the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty in 1992.[51] As of 2016, China fielded SLBMs onboard its JL-2 submarines.[57] As of July 2019, China has an estimated total inventory of 290 warheads.[1]
States declaring possession of nuclear weapons
India
India is not a party to the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty. India adopted "no first use" policy in 1998. India tested what it called a "peaceful nuclear explosive" in 1974 (which became known as "Smiling Buddha"). The test was the first test developed after the creation of the NPT, and created new questions about how civilian nuclear technology could be diverted secretly to weapons purposes (dual-use technology). India's secret development caused great concern and anger particularly from nations that had supplied its nuclear reactors for peaceful and power generating needs, such as Canada.[58]
Indian officials rejected the NPT in the 1960s on the grounds that it created a world of nuclear "haves" and "have-nots", arguing that it unnecessarily restricted "peaceful activity" (including "peaceful nuclear explosives"), and that India would not accede to international control of their nuclear facilities unless all other countries engaged in unilateral disarmament of their own nuclear weapons. The Indian position has also asserted that the NPT is in many ways a neo-colonial regime designed to deny security to post-colonial powers.[59] Even after its 1974 test, India maintained that its nuclear capability was primarily "peaceful", but between 1988 and 1990 it apparently weaponized two dozen nuclear weapons for delivery by air.[60] In 1998 India tested weaponized nuclear warheads ("Operation Shakti"), including a thermonuclear device.[61]
In July 2005, U.S. President George W. Bush and Indian Prime Minister Manmohan Singh announced plans to conclude an Indo-US civilian nuclear agreement.[62] This came to fruition through a series of steps that included India's announced plan to separate its civil and military nuclear programs in March 2006,[63] the passage of the India–United States Civil Nuclear Agreement by the U.S. Congress in December 2006, the conclusion of a U.S.–India nuclear cooperation agreement in July 2007,[64] approval by the IAEA of an India-specific safeguards agreement,[65] agreement by the Nuclear Suppliers Group to a waiver of export restrictions for India,[66] approval by the U.S. Congress[67] and culminating in the signature of U.S.–India agreement for civil nuclear cooperation[68] in October 2008. The U.S. State Department said it made it "very clear that we will not recognize India as a nuclear-weapon state".[69] The United States is bound by the Hyde Act with India and may cease all cooperation with India if India detonates a nuclear explosive device. The US had further said it is not its intention to assist India in the design, construction or operation of sensitive nuclear technologies through the transfer of dual-use items.[70] In establishing an exemption for India, the Nuclear Suppliers Group reserved the right to consult on any future issues which might trouble it.[71] As of January 2020, India was estimated to have a stockpile of around 150 warheads.[1]
Pakistan
Pakistan also is not a party to the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty. Pakistan covertly developed nuclear weapons over decades, beginning in the late 1970s. Pakistan first delved into nuclear power after the establishment of its first nuclear power plant near Karachi with equipment and materials supplied mainly by western nations in the early 1970s. Pakistani President Zulfiqar Ali Bhutto promised in 1971 that if India could build nuclear weapons then Pakistan would too, according to him: "We will develop Nuclear stockpiles, even if we have to eat grass."[72]
It is believed that Pakistan has possessed nuclear weapons since the mid-1980s.[73] The United States continued to certify that Pakistan did not possess such weapons until 1990, when sanctions were imposed under the Pressler Amendment, requiring a cutoff of U.S. economic and military assistance to Pakistan.[74] In 1998, Pakistan conducted its first six nuclear tests at the Ras Koh Hills in response to the five tests conducted by India a few weeks before.
In 2004, the Pakistani metallurgist Abdul Qadeer Khan, a key figure in Pakistan's nuclear weapons program, confessed to heading an international black market ring involved in selling nuclear weapons technology. In particular, Khan had been selling gas centrifuge technology to North Korea, Iran, and Libya. Khan denied complicity by the Pakistani government or Army, but this has been called into question by journalists and IAEA officials, and was later contradicted by statements from Khan himself.[75]
As of early 2013, Pakistan was estimated to have had a stockpile of around 140 warheads,[76] and in November 2014 it was projected that by 2020 Pakistan would have enough fissile material for 200 warheads.[77]
North Korea

North Korea was a party to the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty, but announced a withdrawal on January 10, 2003, after the United States accused it of having a secret uranium enrichment program and cut off energy assistance under the 1994 Agreed Framework. In February 2005, North Korea claimed to possess functional nuclear weapons, though their lack of a test at the time led many experts to doubt the claim. In October 2006, North Korea stated that, in response to growing intimidation by the United States, it would conduct a nuclear test to confirm its nuclear status. North Korea reported a successful nuclear test on October 9, 2006 (see 2006 North Korean nuclear test). Most U.S. intelligence officials believed that the test was probably only partially successful with a yield of less than a kiloton.[78] North Korea conducted a second, higher yield test on 25 May 2009 (see 2009 North Korean nuclear test) and a third test with still higher yield on 12 February 2013 (see 2013 North Korean nuclear test). North Korea claimed to have conducted its first hydrogen-bomb test on 5 January 2016, though measurements of seismic disturbances indicate that the detonation was not consistent with a hydrogen bomb.[79] On 3 September 2017, North Korea detonated a device which caused a magnitude 6.1 tremor, consistent with a low-powered thermonuclear detonation; NORSAR estimates the yield at 250 kilotons[80] of TNT. In 2018, North Korea announced a halt in nuclear weapons tests and made a conditional commitment to denuclearisation of the Korean Peninsula[81][82]; however in December 2019 it indicated it no longer considered itself bound by the moratorium[83].
States indicated to possess nuclear weapons
Israel
Israel is widely believed to have been the sixth country in the world to develop nuclear weapons, but has not acknowledged its nuclear forces. It had "rudimentary, but deliverable," nuclear weapons available as early as 1966.[84][85][86][87][88][89][90][10] Israel is not a party to the NPT. Israel engages in strategic ambiguity, saying it would not be the first country to "introduce" nuclear weapons into the region, but refusing to otherwise confirm or deny a nuclear weapons program or arsenal. This policy of "nuclear opacity" has been interpreted as an attempt to get the benefits of deterrence with a minimal political cost.[10][11]
According to the Natural Resources Defense Council and the Federation of American Scientists, Israel likely possesses around 75–200 nuclear weapons.[91][92] The Stockholm International Peace Research Institute estimates that Israel has approximately 80 intact nuclear weapons, of which 50 are for delivery by Jericho II medium-range ballistic missiles and 30 are gravity bombs for delivery by aircraft. SIPRI also reports that there was renewed speculation in 2012 that Israel may also have developed nuclear-capable submarine-launched cruise missiles.[93]
Nuclear weapons sharing
| Country | Air base | Custodian | Warheads |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kleine Brogel | 52nd Fighter Wing | 20 | |
| Büchel | 52nd Fighter Wing | 20 | |
| Ghedi Torre | 52nd Fighter Wing | 40 | |
| Aviano | 31st Fighter Wing | ||
| Volkel | 52nd Fighter Wing | 20 | |
| Incirlik | 39th Air Base Wing | 50 | |
| Total | 150 | ||
Under NATO nuclear weapons sharing, the United States has provided nuclear weapons for Belgium, Germany, Italy, the Netherlands, and Turkey to deploy and store.[95] This involves pilots and other staff of the "non-nuclear" NATO states practicing, handling, and delivering the U.S. nuclear bombs, and adapting non-U.S. warplanes to deliver U.S. nuclear bombs. However, since all U.S. nuclear weapons are protected with Permissive Action Links, the host states cannot easily arm the bombs without authorization codes from the U.S. Department of Defense.[96] Former Italian President Francesco Cossiga acknowledged the presence of U.S. nuclear weapons in Italy.[97] U.S. nuclear weapons were also deployed in Canada as well as Greece from 1963 to 1984. However, Canada withdrew three of the four nuclear-capable weapons systems by 1972. The single system retained, the AIR-2 Genie, had a yield of 1.5 kilotons, was designed to strike enemy aircraft as opposed to ground targets, and might not have qualified as a weapon of mass destruction given its limited yield.[98]
Members of the Non-Aligned Movement have called on all countries to "refrain from nuclear sharing for military purposes under any kind of security arrangements."[99] The Institute of Strategic Studies Islamabad (ISSI) has criticized the arrangement for allegedly violating Articles I and II of the NPT, arguing that "these Articles do not permit the NWS to delegate the control of their nuclear weapons directly or indirectly to others."[100] NATO has argued that the weapons' sharing is compliant with the NPT because "the U.S. nuclear weapons based in Europe are in the sole possession and under constant and complete custody and control of the United States."[101]
As of April 2019, the United States maintained around 150 nuclear weapons in Europe, as reflected in the table to the right.[94]
States formerly possessing nuclear weapons
Nuclear weapons have been present in many nations, often as staging grounds under control of other powers. However, in only one instance has a nation given up nuclear weapons after being in full control of them. The fall of the Soviet Union left several former Soviet republics in physical possession of nuclear weapons, though not operational control which was dependent on Russian-controlled electronic Permissive Action Links and the Russian command and control system.[102][103]

South Africa
South Africa produced six nuclear weapons in the 1980s, but dismantled them in the early 1990s.
In 1979, there was a detection of a putative covert nuclear test in the Indian Ocean, called the Vela incident. It has long been speculated that it was a test by Israel, in collaboration with and support of South Africa, though this has never been confirmed. South Africa could not have constructed such a nuclear bomb until November 1979, two months after the "double flash" incident. South Africa signed the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty in 1991.[105][106]
Former Soviet Republics
- Belarus had 81 single warhead missiles stationed on its territory after the Soviet Union collapsed in 1991. They were all transferred to Russia by 1996. In May 1992, Belarus acceded to the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty.[107]
- Kazakhstan inherited 1,400 nuclear weapons from the Soviet Union, and transferred them all to Russia by 1995. Kazakhstan has since acceded to the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty.[108]
- Ukraine has acceded to the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty. Ukraine inherited "as many as 3,000" nuclear weapons when it became independent from the Soviet Union in 1991, making its nuclear arsenal the third-largest in the world.[109] By 1994, Ukraine had agreed to dispose of all nuclear weapons within its territory, with the condition that its borders were respected, as part of the Budapest Memorandum on Security Assurances. The warheads were removed from Ukraine by 1996 and disassembled in Russia.[110] Despite Russia's subsequent and internationally disputed annexation of Crimea in 2014, Ukraine reaffirmed its 1994 decision to accede to the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty as a non-nuclear-weapon state.[111]
See also
- Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty
- Doomsday Clock
- Historical nuclear weapons stockpiles and nuclear tests by country
- International Campaign to Abolish Nuclear Weapons
- No first use
- Nuclear disarmament
- Nuclear latency
- Nuclear power
- Nuclear proliferation
- Nuclear terrorism
- Nuclear war
- Nuclear-weapon-free zone
Notes
- All numbers are estimates from the Federation of American Scientists. The latest update was in November 2018. "Deployed" indicates the total of deployed strategic and non-strategic warheads. Because the number of non-strategic warheads is unknown for many countries, this number should be taken as a minimum. When a range of weapons is given (e.g., 0–10), it generally indicates that the estimate is being made on the amount of fissile material that has likely been produced, and the amount of fissile material needed per warhead depends on estimates of a country's proficiency at nuclear weapon design.
- See also UK Trident programme. From the 1960s until the 1990s, the United Kingdom's Royal Air Force maintained the independent capability to deliver nuclear weapons via its V bomber fleet.
- See also Force de dissuasion. France formerly possessed a nuclear triad until 1996 and the retirement of its land-based arsenal.
- Sea-based tested but not yet operational.[33]
- Data include the suspected Vela incident of 22 September 1979.[38]
References
- "World Nuclear Forces, SIPRI yearbook 2020". Stockholm International Peace Research Institute. Stockholm International Peace Research Institute. January 2020. Retrieved 18 June 2020.
- Hersh, Seymour (Oct 27, 1991). "Authors Note". The Samson Option. Random House. ISBN 978-0394570068."This is a book about how Israel became a nuclear power in secret." (First sentence, Authors' Note/Introduction, The Samson Option: Israel's Nuclear Arsenal and American Foreign Policy, Hersh)
- "Nuclear Weapons: Who Has What at a Glance". Arms Control Association. October 2016. Archived from the original on January 24, 2018. Retrieved Jan 16, 2017.
India, Israel, and Pakistan never signed the NPT and possess nuclear arsenals.
- Rosen, Armin (Nov 10, 2014). "Israel's Nuclear Arsenal Might Be Smaller And More Strategic Than Everyone Thinks". Business Insider. Archived from the original on December 6, 2016. Retrieved January 16, 2017.
The country possesses some of the most powerful weaponry on earth, along with delivery systems that give it the ability to strike far beyond its borders.
- "Israel". Nuclear Threat Initiative. May 2015. Archived from the original on January 16, 2017. Retrieved Jan 16, 2017.
While experts generally agree that Israel possesses nuclear weapons, no such current open source consensus exists on the status of Israel's offensive chemical or biological weapons programs.
- Stover, Dawn (Sep 16, 2016). "Does Israel really have 200 nuclear weapons, or was Colin Powell exaggerating?". Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists. Archived from the original on January 18, 2017. Retrieved Jan 16, 2017.
The boys in Tehran know Israel has 200, all targeted on Tehran, and we have thousands.
citing primary source private email from Colin Powell to Jeffrey Leeds Archived 2017-02-16 at the Wayback Machine - Harding, Luke (2006-12-12). "Calls for Olmert to resign after nuclear gaffe Israel and the Middle East | Guardian Unlimited". Guardian. London. Retrieved 2009-05-15.
- Nuclear Forces Archived 2015-01-07 at the Wayback Machine, Stockholm International Peace Research Institute, sipri.org
- There are a wide range of estimates as to the size of the Israeli nuclear arsenal. For a compiled list of estimates, see Avner Cohen, The Worst-Kept Secret: Israel's bargain with the Bomb (Columbia University Press, 2010), Table 1, page xxvii and page 82.
- NTI Israel Profile Archived 2011-07-28 at the Wayback Machine Retrieved July 12, 2007.
- Avner Cohen (2010). The Worst-Kept Secret: Israel's bargain with the Bomb. Columbia University Press.
- Arms Control and Global Security, Paul R. Viotti - 2010, p 312
- "SIPRI YEARBOOK 2019 Armaments, Disarmament and International Security" (PDF). SIPRI: 10. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2019-06-24. Retrieved 2019-08-05.
- Reichmann, Kelsey (16 June 2019). "Here's how many nuclear warheads exist, and which countries own them". Defense News.
- "Global Nuclear Arsenal Declines, But Future Cuts Uncertain Amid U.S.-Russia Tensions". Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty (RFE/RL). 17 June 2019. Archived from the original on 2 July 2019. Retrieved 23 July 2019.
- "Nuclear club", Oxford English Dictionary: "nuclear club n. the nations that possess nuclear weapons." The term's first cited usage is from 1957.
- Jane Onyanga-Omara, "The Nuclear Club: Who are the 9 members?" Archived 2017-09-04 at the Wayback Machine, USA TODAY, 6 January 2016
- Webster, Paul (July/August 2003). "Nuclear weapons: how many are there in 2009 and who has them? Archived 2017-01-08 at the Wayback Machine" The Guardian, 6 September 2009.
- "Status of Signature and Ratification of the Comprehensive Test Ban Treaty". Archived from the original on 25 September 2011. Retrieved 13 January 2012.
- IISS 2012, pp. 54–55
- "FAS World Nuclear Forces". Federation of American Scientists. April 2020. Retrieved 18 June 2020.
- IISS 2012, p. 192
- IISS 2012, p. 169
- IISS 2012, p. 111
- The Long Shadow: Nuclear Weapons and Security in 21st Century Asia by Muthiah Alagappa (NUS Press, 2009), page 169: "China has developed strategic nuclear forces made up of land-based missiles, submarine-launched missiles, and bombers. Within this triad, China has also developed weapons of different ranges, capabilities, and survivability."
- IISS 2012, pp. 223-224
- IISS 2012, p. 243
- "Now, India has a nuclear triad". The Hindu. 18 October 2016. Archived from the original on 21 December 2016. Retrieved 24 December 2016.
- Peri, Dinakar (12 June 2014). "India's Nuclear Triad Finally Coming of Age". The Diplomat. Archived from the original on 9 April 2015. Retrieved 10 March 2015.
- "Nuclear triad weapons ready for deployment: DRDO". 2014-07-07. Archived from the original on 2015-04-02. Retrieved 2015-03-10.
- IISS 2012, p. 272
- Pakistan's Nuclear Weapons. Bhumitra Chakma (Routledge 2012), page 61: "Pakistan possesses two types of nuclear delivery vehicles: aircraft and missiles. Initially in the pre-tests era, Islamabad depended solely on aircraft as its chief means of delivering nuclear weapons. In the early 1990s, Pakistan acquired a few dozen ballistic missiles from China, and subsequently, it developed a number of missile systems which became its mainstay of nuclear delivery."
- "Pakistan fires 'first submarine-launched nuclear-capable missile'". Reuters. 2017-01-10. Retrieved 2020-05-13.
- "U.S.: Test Points to N. Korea Nuke Blast". The Washington Post. October 13, 2006. Archived from the original on December 27, 2016. Retrieved September 3, 2017.
- Kristensen, Hans M.; Norris, Robert S. (2018-01-02). "North Korean nuclear capabilities, 2018". Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists. 74 (1): 41–51. doi:10.1080/00963402.2017.1413062. ISSN 0096-3402.
- "New North Korean submarine capable of carrying three SLBMs: South Korean MND | NK News - North Korea News". 2019-07-31. Archived from the original on 2019-08-04. Retrieved 2019-08-05.
- Farr, Warner D (September 1999), The Third Temple's holy of holies: Israel's nuclear weapons, The Counterproliferation Papers, Future Warfare Series 2, USAF Counterproliferation Center, Air War College, Air University, Maxwell Air Force Base, retrieved July 2, 2006.
-
- Hersh, Seymour (1991). The Samson option: Israel's Nuclear Arsenal and American Foreign Policy. Random House. ISBN 978-0-394-57006-8.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link), page 271
- An Atlas of Middle Eastern Affairs By Ewan W. Anderson, Liam D. Anderson, (Routledge 2013), page 233: "In terms of delivery systems, there is strong evidence that Israel now possesses all three elements of the nuclear triad."
- IISS 2012, p. 328
- Hansen, Chuck (1988). U.S. nuclear weapons: The secret history. Arlington, TX: Aerofax. ISBN 978-0-517-56740-1.
- Hansen, Chuck (1995). The Swords of Armageddon: U.S. nuclear weapons development since 1945. Sunnyvale, CA: Chukelea Publications. Archived from the original on 2016-12-30. Retrieved 2016-02-20.
- Stephen I. Schwartz, ed., Atomic Audit: The Costs and Consequences of U.S. Nuclear Weapons Since 1940 (Washington, D.C.: Brookings Institution Press, 1998).
- Gross, Daniel A. (2016). "An Aging Army". Distillations. Vol. 2 no. 1. pp. 26–36. Archived from the original on 20 March 2018. Retrieved 22 March 2018.
- "Fact Sheet: Increasing Transparency in the U.S. Nuclear Weapons Stockpile" (PDF). U.S. Department of Defense. 3 May 2010. Archived from the original (PDF) on 11 August 2015. Retrieved 31 August 2013.
- "Policy Library". Archived from the original on 2016-08-22. Retrieved 2016-08-23.
- Robert S. Norris and Hans M. Kristensen, "Global nuclear stockpiles, 1945-2006," Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists 62, no. 4 (July/August 2006), 64-66...
- Holloway, David (1994). Stalin and the bomb: The Soviet Union and atomic energy, 1939-1956. New Haven, CT: Yale University Press. ISBN 978-0-300-06056-0.
- Gowing, Margaret (1974). Independence and deterrence: Britain and atomic energy, 1945-1952. London: Macmillan. ISBN 978-0-333-15781-7.
- Arnold, Lorna (2001). Britain and the H-bomb. Basingstoke: Palgrave. ISBN 978-0-312-23518-5.
- Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons Archived 2014-12-17 at the Wayback Machine, United Nations Office for Disarmament Affairs.
- France 'would use nuclear arms' Archived 2006-12-19 at the Wayback Machine (BBC, January 2006)
- "Nuclear deterrent important in 'dangerous world', says Hollande". spacedaily.com. Archived from the original on 2016-03-04. Retrieved 2016-02-20.
- John Wilson Lewis and Xue Litai, China Builds the Bomb (Stanford, Calif.: Stanford University Press, 1988). ISBN 0-8047-1452-5
- "No-First-Use (NFU)". Nuclear Threat Initiative. Archived from the original on 2010-01-25.
- "Statement on security assurances issued on 5 April 1995 by the People's Republic of China". United Nations. 6 April 1995. S/1995/265. Archived from the original on 2007-08-24. Retrieved 20 September 2012. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - Kristensen, Hans M.; Korda, Matt (2019-07-04). "Chinese nuclear forces, 2019". Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists. 75 (4): 171–178. doi:10.1080/00963402.2019.1628511. ISSN 0096-3402.
- "18 MAY 1974 - SMILING BUDDAH". CTBTO. Retrieved 24 January 2018.
- George Perkovich, India's Nuclear Bomb: The Impact on Global Proliferation (Berkeley: University of California Press, 1999), 120-121, and 7.
- George Perkovich, India's Nuclear Bomb: The Impact on Global Proliferation (Berkeley: University of California Press, 1999), 293–297.
- "India's Nuclear Weapons Program: Operation Shakti". 1998. Archived from the original on 2006-10-03. Retrieved 2006-10-10.
- "Joint Statement Between President George W. Bush and Prime Minister Manmohan Singh". Whitehouse.gov. Archived from the original on 2009-12-27. Retrieved 2009-05-15.
- "Wayback Machine" (PDF). 3 September 2006. Archived from the original (PDF) on 3 September 2006.
- "U.S.- India Civil Nuclear Cooperation Initiative – Bilateral Agreement on Peaceful Nuclear Cooperation". Archived from the original on 2017-11-17. Retrieved 2019-05-22.
- "IAEA Board Approves India-Safeguards Agreement". Iaea.org. 2008-07-31. Archived from the original on 2009-05-05. Retrieved 2009-05-15.
- "Statement on Civil Nuclear Cooperation with India" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2008-10-19. Retrieved 2008-10-18.
- "Congressional Approval of the U.S.-India Agreement for Cooperation Concerning Peaceful Uses of Nuclear Energy (123 Agreement)". Archived from the original on 2017-11-17. Retrieved 2019-05-22.
- "Secretary of State Condoleezza Rice and Indian Minister of External Affairs Pranab Mukherjee At the Signing of the U.S.-India Civilian Nuclear Cooperation Agreement". Archived from the original on 2017-11-17. Retrieved 2019-05-22.
- Interview With Undersecretary of State for Arms Control and International Security Robert Joseph Archived 2008-10-23 at the Wayback Machine, Arms Control Today, May 2006.
- Was India misled by America on nuclear deal? Archived 2008-09-10 at the Wayback Machine, Indian Express.
- "ACA: Final NSG Statement" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2010-11-20. Retrieved 2008-10-18.
- Sublettle, Carey (15 October 1965). "Historical Background: Zulfikar Ali Bhutto". Nuclear weapons archives. Federation of American Scientists (FAS). Archived from the original on 16 December 2013. Retrieved 19 August 2018.
- NTI Pakistan Profile Archived 2012-04-16 at the Wayback Machine, retrieved 22 April 2012.
- "Case Studies in Sanctions and Terrorism: Pakistan". Iie.com. Archived from the original on 2009-05-12. Retrieved 2009-05-15.
- See A.Q. Khan: Investigation, dismissal, confession, pardon and aftermath, for citations and details.
- "Status of World Nuclear Forces". Federation of American Scientists. Archived from the original on 24 January 2018. Retrieved 24 January 2018.
- "Pakistan to Have 200 Nuke Weapons by 2020: US Think Tank". The Times of india. November 2014. Archived from the original on 2014-11-27. Retrieved 2014-11-28.
- "CIA's Hayden: North Korea Nuke Test 'Was a Failure'". Newsmax.com. 2007-03-28. Archived from the original on 2012-09-04. Retrieved 2009-05-15.
- "North Korea Test Shows Technical Advance". The Wall Street Journal. CCLXVII (5). January 7, 2016. p. A6.
- "The nuclear explosion in North Korea on 3 September 2017: A revised magnitude assessment". NORSAR.no. Archived from the original on 2017-09-13. Retrieved 2017-09-15.
- "North Korea has Begun Dismantlement of the Punggye-ri Nuclear Test Site'". 38north.org. Archived from the original on August 3, 2018. Retrieved Aug 3, 2018.
- "'Destruction at North Korea's Nuclear Test Site: A Review in Photos'". 38north.org. Archived from the original on August 14, 2018. Retrieved Aug 3, 2018.
- Sang-Hun, Choe (2019-12-31). "North Korea Is No Longer Bound by Nuclear Test Moratorium, Kim Says". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved 2020-06-18.
- Cohen 1998a, p. 349.
- ElBaradei, Mohamed (July 27, 2004). "Transcript of the Director General's Interview with Al-Ahram News". International Atomic Energy Agency. Archived from the original on April 18, 2012. Retrieved June 3, 2007.
- "Nuclear Overview". Israel. NTI. Archived from the original (profile) on 2009-01-02. Retrieved June 23, 2009.
- My Promised Land, by Ari Shavit, (London 2014), page 188
- Nuclear Proliferation International History Project (2013-06-28). "Israel's Quest for Yellowcake: The Secret Argentina-Israel Connection, 1963–1966". Woodrow Wilson International Center for Scholars. Archived from the original on 2017-08-14. Retrieved 2017-11-22.
- John Pike. "Nuclear Weapons". globalsecurity.org. Archived from the original on 2017-11-17. Retrieved 2017-11-22.
- "Nuclear Weapons". fas.org. Archived from the original on 2010-12-07. Retrieved 2015-11-07.
- There are a wide range of estimates as to the size of the Israeli nuclear arsenal. For a compiled list of estimates, see Avner Cohen, The Worst-Kept Secret: Israel's bargain with the Bomb (Columbia University Press, 2010), Table 1, page xxvii and page 82.
- Israel's Nuclear Weapons Archived 2010-12-07 at the Wayback Machine, Federation of American Scientists (August 17, 2000)
- "Israel". Archived from the original on 2014-12-17. Retrieved 2015-01-19.
- Kristensen, Hans M.; Korda, Matt (2019-05-04). "United States nuclear forces, 2019". Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists. 75 (3): 122–134. doi:10.1080/00963402.2019.1606503. ISSN 0096-3402.
- "Berlin Information-center for Transatlantic Security: NATO Nuclear Sharing and the N.PT - Questions to be Answered". Bits.de. Archived from the original on 2009-05-19. Retrieved 2009-05-15.
- "Nuclear Command and Control" (PDF). Security Engineering: A Guide to Building Dependable Distributed Systems. Ross Anderson, University of Cambridge Computing Laboratory. Retrieved April 29, 2010.
- "Cossiga: "In Italia ci sono bombe atomiche Usa"". Archived from the original on 2015-09-28. Retrieved 2015-09-16.
- Hans M. Kristensen (February 2005). "U.S. Nuclear Weapons in Europe" (PDF). Natural Resources Defense Council. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2014-07-23. Retrieved 2006-05-23. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - Statement on behalf of the non-aligned state parties to the Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons, 2 May 2005
- ISSI - NPT in 2000: Challenges ahead, Zafar Nawaz Jaspal, The Institute of Strategic Studies, Islamabad Archived January 9, 2009, at the Wayback Machine
- "NATO's Positions Regarding Nuclear Non-Proliferation, Arms Control and Disarmament and Related Issues" (PDF). NATO. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2013-09-11. Retrieved 2013-09-08.
- William C. Martel (1998). "Why Ukraine gave up nuclear weapons : nonproliferation incentives and disincentives". In Barry R. Schneider, William L. Dowdy (ed.). Pulling Back from the Nuclear Brink: Reducing and Countering Nuclear Threats. Psychology Press. pp. 88–104. ISBN 9780714648569. Retrieved 6 August 2014.
- Alexander A. Pikayev (Spring–Summer 1994). "Post-Soviet Russia and Ukraine: Who can push the Button?" (PDF). The Nonproliferation Review. 1 (3): 31–46. doi:10.1080/10736709408436550. Archived (PDF) from the original on 21 May 2014. Retrieved 6 August 2014.
- Lewis, Jeffrey (3 December 2015). "Revisiting South Africa's Bomb". Arms Control Wonk. Leading Voice on Arms Control, Disarmament and Non-Proliferation. Archived from the original on 6 December 2015. Retrieved 6 December 2015.
- Nuclear Weapons Program (South Africa) Archived 2015-10-16 at the Wayback Machine, Federation of American Scientists (May 29, 2000).
- Von Wielligh, N. & von Wielligh-Steyn, L. (2015). The Bomb – South Africa's Nuclear Weapons Programme. Pretoria: Litera.
- "Belarus Special Weapons". Federation of American Scientists. Archived from the original on 2015-11-17. Retrieved 2015-11-07.
- "Kazakhstan Special Weapons". Federation of American Scientists. Archived from the original on 2015-11-17. Retrieved 2015-11-07.
- Ukraine Special Weapons Archived 2005-04-01 at the Wayback Machine, GlobalSecurity.org
- "Ukraine Special Weapons". Federation of American Scientists. Archived from the original on 2015-10-16. Retrieved 2015-11-07.
- Joint Statement by the United States and Ukraine Archived 2016-05-17 at the Wayback Machine, March 25, 2014.
Bibliography
- International Institute for Strategic Studies (7 March 2012). Hackett, James (ed.). The Military Balance 2012. London, England: Routledge. ISBN 978-1857436426.
- Farr, Warner D. (September 1999), The Third Temple's holy of holies: Israel's nuclear weapons, The Counterproliferation Papers, Future Warfare Series, 2, USAF Counterproliferation Center, Air War College, Air University, Maxwell Air Force Base, retrieved July 2, 2006.
- Philipp C. Bleek, “When Did (and Didn’t) States Proliferate? Chronicling the Spread of Nuclear Weapons,” Discussion Paper (Cambridge, MA: Project on Managing the Atom, Belfer Center for Science and International Affairs, June 2017).
External links
- Globalsecurity.org – World Special Weapons Guide
- The Nuclear Weapon Archive
- Nuclear Notebook from Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists
- U.S. Nuclear Weapons in Europe: A review of post-Cold War policy, force levels, and war planning NRDC, February 2005
- Tracking Nuclear Proliferation Online NewsHour with Jim Lehrer
- Stockholm International Peace Research Institute's data on world nuclear forces
- Nuclear Proliferation International History Project For more on the history of nuclear proliferation see the Woodrow Wilson Center's Nuclear Proliferation International History Project website.
- Proliferation Watch: US Intelligence Assessments of Potential Nuclear Powers, 1977–2001