List of German flags
This is a list of flags used by and in Germany between 1848 and now. For more information about the current national flag, see flag of Germany.
National flags
| Flag | Date | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 | 1949–present | National and merchant flag (Bundes- und Handelsflagge) | A tricolour, made of three equal horizontal bands coloured black (top), red, and gold (bottom). |
.svg.png) | 1950–present | State flag and ensign (Bundesdienstflagge) and military flag (Kriegsflagge). This flag may only be used by federal government authorities. | The national flag with the Bundesschild (a variant of the coat of arms of Germany) in the centre. The flag was originally used 1921–1933 in the Weimar Republic. While identical in heraldic terms to the original Weimar era flag, the modern exact design is slightly simplified. |
.svg.png) | National flag with coat of arms (Bundesflagge mit Bundeswappen). Unofficial version, the private use of which is not penalized. | ||
| 1996–present | Hanging national flag (Bannerflagge) | ||
| 1996–present | Hanging state flag |
Presidential standard
| Flag | Date | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 | 1921–1926; since 1950 | Standard of the President of Germany | The standard depicts the elements of the coat of arms. A version of the standard that is identical in heraldic terms, but with a slightly different exact design, was used 1926–1933. |
Military and state flags
| Flag | Date | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 | 1956– | War ensign and jack (Seekriegsflagge und Gösch) of the German Navy | A swallowtail variant of the state flag |
 | 1957– | Standard of Inspector General of the Bundeswehr | |
 | 1964– | Troop colour (Truppenfahne) of the Bundeswehr | |
.svg.png) | 1950–1994 | Flag of Deutsche Bundespost | |
 | 1950–1994 | Flag of the Minister of Deutsche Bundespost | |
 | 1950–1994 | Flag of the President of Deutsche Bundespost | A swallowtail variant of the postal flag |
 | 1950–1994 | Flag of the State Secretary of Deutsche Bundespost |
Flags of German states
Civil flags
| Flag | Date | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 | Civil flag of Baden-Württemberg | ||
.svg.png) | Civil flag of Bavaria (striped variant) | ||
.svg.png) | Civil flag of Bavaria (lozengy variant) | ||
 | Civil flag of Berlin | ||
 | Civil flag of Brandenburg | ||
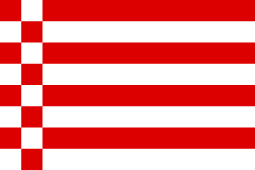 | Civil flag of Bremen | ||
.svg.png) | Civil flag of Bremen (with middle arms) | ||
 | Civil flag of Bremen (with flag arms) | ||
 | Civil flag of Hamburg | ||
 | Civil flag of Hesse | ||
 | Civil flag of Lower Saxony | ||
 | Civil flag of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern | ||
 | Civil flag of North Rhine-Westphalia | ||
 | Civil flag of Rhineland-Palatinate | ||
 | Civil flag of Saarland | ||
 | Civil flag of Saxony | ||
 | Civil flag of Saxony-Anhalt | ||
 | Civil flag of Schleswig-Holstein | ||
 | Civil flag of Thuringia |
State flags
| Flag | Date | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
.svg.png) | State flag of Baden-Württemberg (lesser arms) | ||
.svg.png) | State flag of Baden-Württemberg (greater arms) | ||
.svg.png) | State flag of Bavaria (striped variant) | ||
.svg.png) | State flag of Bavaria (lozengy variant) | ||
.svg.png) | 1954–2007 | State flag of Berlin | |
 | State flag of Brandenburg | ||
.svg.png) | State flag of Bremen (with lesser arms) | ||
 | State flag of Bremen (with flag arms) | ||
 | State flag of Hamburg | ||
 | Admiralty flag of Hamburg (used by state ships)[1] | ||
.svg.png) | State flag of Hesse | ||
 | Flag of Lower Saxony (on land) | ||
.svg.png) | State ensign of Lower Saxony (at sea) | ||
.svg.png) | State flag of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern | ||
.svg.png) | State flag of North Rhine-Westphalia | ||
 | State flag of Rhineland-Palatinate | ||
 | Flag of Saarland | ||
.svg.png) | State flag of Saxony | ||
.svg.png) | State flag of Saxony-Anhalt | ||
.svg.png) | State flag of Schleswig-Holstein | ||
.svg.png) | State flag of Thuringia |
Minority flags
| Flag | Date | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
.png) | Flag of Silesians | Official in Saxony. | |
 | Flag of Silesians | Official in Saxony. | |
 | Flag of Sorbs | Official in Saxony. |
Historical flags
German Confederation (1815–1866)
| Flag | Date | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
.svg.png) | 1848–1866 | Flag of the German Confederation, used in 1848/1849 and again in 1863–1866 First appeared within the Fürstentum Reuß-Greiz after 12 May 1778 (4:5 aspect ratio) | Also German Empire (1848/1849) |
.svg.png) | 1848–1852 | War ensign of the Reichsflotte | |
 | 1848–1852 | Marine jack of the Reichsflotte |
North German Confederation (1866–1871)
| Flag | Date | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
.svg.png) | 1867–1871 | National and merchant flag (National- und Handelsflagge) | A tricolour, made of three equal horizontal bands coloured black (top), white, and red (bottom) |
.svg.png) | 1867–1871 | War flag (Kriegsflagge) | |
.svg.png) | 1867–1871 | Marine jack (Kriegsschiffgösch) |
German Empire (1871–1918)
| Flag | Date | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
.svg.png) | 1871–1918 | National and merchant flag (National- und Handelsflagge) | |
.svg.png) | 1896–1918 | Merchant flag variant with the Iron Cross (Eisernes Kreuz) | |
 | 1884–1918 | Colonial flag | |
.svg.png) | 1871–1892 | Imperial Navy war ensign (Kriegsflagge) | |
.svg.png) | 1892–1903 | Reich war flag (Reichskriegsflagge) | |
.svg.png) | 1903–1918 (1921) | Reich war flag | |
.svg.png) | 1871–1903 | Marine jack (Kriegsschiffgösch) | |
.svg.png) | 1903–1918 (1921) | Marine jack |
Imperial family standards
| Flag | Date | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 | 1871 | The King in Prussia's Standard | |
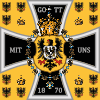 | 1871–1888 | German Emperor's Standard | |
 | 1888–1918 | German Emperor's Standard | |
 | 1871–1901 | Empress Augusta and Empress Frederick's Standard | |
 | 1888–1918 | Empress Augusta Viktoria's Standard | |
 | 1871–1888 | Standard of the Crown Prince | |
 | 1888–1918 | Standard of the Crown Prince |
Weimar Republic (1919–1933)
| Flag | Date | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
.svg.png) | 1919–1933 | National flag (Nationalflagge) | |
.svg.png) | 1921–1933 | State flag (Dienstflagge zu Land) | |
.svg.png) | 1919–1933 | Merchant flag (Handelsflagge) | |
.svg.png) | 1921–1933 | Merchant flag variant with the Iron Cross (Eisernes Kreuz) | |
.svg.png) | 1921–1926 | State ensign (Dienstflagge zur See) | |
 | 1926–1933 | State ensign (Dienstflagge zur See) | |
.svg.png) | 1919–1921 (de jure) | Reich war flag (Reichskriegsflagge) | |
.svg.png) | 1921–1933 | Reich war flag | |
.svg.png) | 1921–1933 | Marine jack (Kriegsgösch) | |
 | 1921–1926 | Standard of the President | |
.svg.png) | 1926–1933 | Standard of the President | |
.svg.png) | 1919–1921 | Flag of the President | |
.svg.png) | 1919–1921 | Flag of Defence Minister | |
.svg.png) | 1921–1933 | Flag of Defence Minister | |
 | 1924–1933; since 1953 | Flag of the Reichsbanner Schwarz-Rot-Gold | The Reichsbanner Schwarz-Rot-Gold was an unofficial republican paramilitary organization dominated by social democrats, liberals, and members of the Catholic Centre Party, to defend the Weimar Republic against National Socialists, communists, and monarchists. Refounded in 1953 as an association for political education. |
Nazi Germany (1933–1945)
The flag with the Hakenkreuz and white disc centered was used throughout (1920–1945) as the NSDAP party flag (Parteiflagge).[2] Between 1933 and 1935, it was used as the national flag (Nationalflagge) and merchant flag (Handelsflagge) – interchangeably with the black-white-red horizontal tricolour last used (up to 1918) by the German Empire. In 1935, the black-white-red horizontal tricolour was scrapped again, and the flag with the off-center Hakenkreuz and disc was instituted as the only national flag (and was to remain as such until 1945). The flag with the centered disc only continued to be used as the Parteiflagge after 1935.
| Flag | Date | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flags used 1933–1935 | |||
.svg.png) |
|
|
A red field, with a white disc with a black swastika, or hakenkreuz, at a 45 degree angle. Disc and swastika are exactly in the centre. |
.svg.png) |
1933–1935 |
|
Black, white, and red horizontal tricolour. Used in conjunction with the Parteiflagge. |
 | 1933–1935 | Merchant flag variant with the Iron Cross (Eisernes Kreuz) | |
.svg.png) | 1933–1935 | Reich war flag (Reichskriegsflagge) and marine jack | |
 | 1933 | Reich service flag (Reichsdienstflagge) of the Wehrmacht | |
 | 1933–1935 | Reich service flag | |
 | 1933–1935 (de facto up to 1934) | Standard of the President | |
 | 1933–1935 | Flag of the Minister of Defence | |
| Flags used 1935–1945 | |||
.svg.png) |
|
|
A red field, with a white disc with a black swastika, or hakenkreuz, at a 45 degree angle. Disk and swastika are slightly off-centre. |
.svg.png) | 1920–1945 | Nazi Party flag (Parteiflagge)[2] | A red field, with a white disc with a black swastika, or hakenkreuz, at a 45 degree angle. Disk and swastika are exactly in the centre. |
| 1933–1945 | Banner (Bannerflagge) of Germany | Banners were of various lengths, which were hung vertically on public buildings. | |
 | 1935–1945 | Merchant flag variant with the Iron Cross | |
.svg.png) | 1935–1938 | Kriegsmarine, Heer, Luftwaffe | |
.svg.png) | 1938–1945 | Kriegsmarine, Heer, Luftwaffe | |
 | 1935–1945 | Reich service flag | |
 | 1935–1945 | Standard of Adolf Hitler | |
 | 1935–1938 | Flag of the Wehrmacht Commander in Chief (replaced the Minister of Defence) | |
 | 1935–1945 | Flag of the Schutzstaffel (SS) | |
 | 1936–1945 | Flag of the Ordnungspolizei (OrPo) ("Order Police", the national regular police organization of Nazi Germany) | |
 | 1933–1945 | Flag of the Hitler Youth, a youth organization in the Nazi Party | |
World War II aftermath in Germany
Allied Control Council (1945–1949) and Saar Protectorate
| Flag | Date | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
.svg.png) | 1946–1950 | "C-Pennant" (C-Doppelstander) (provisional civil ensign) | Used during the Occupation Period to identify German ships according to international law. |
.svg.png) | 1947–1957 | Flag of Saar Protectorate | Flag of Saarland which was given by French Government. at this time period Saar was satellite state of France. |
East Germany (1949–1990)
| Flag | Date | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 | 1949–1959 | State flag (Staatsflagge) | |
 | 1959–1990 | State flag (Staatsflagge) 1959–1990 Merchant flag (Handelsflagge) 1973–1990 | Tricolour of black, red, and yellow (same as West German colours), but bears the coat of arms of East Germany, consisting of a compass and a hammer encircled with rye |
.svg.png) | 1959–1973 | Merchant flag (Handelsflagge) | |
| 1963–1990 | Hanging state flag (Bannerflagge) | ||
.svg.png) | 1955–1973 | Flag of East German Post | |
.svg.png) | 1975–1990 | Flag of East German Post | |
.svg.png) | 1955–1990 | Standard of the President | |
 | 1960–1990 | Standard of President of State Council | |
.svg.png) | 1960–1990 | Flag of the National People's Army (Nationale Volksarmee or NVA) | |
.svg.png) | 1960–1990 | Regimental colours (Truppenfahne) of Nationale Volksarmee | |
.svg.png) | 1960–1990 | Naval ensign (Seekriegsflagge) | |
.svg.png) | 1962–1990 | Flag of boats of border troops | |
 | 1989–1990 | Defaced state flag | Used by supporters of German reunification in East Germany after the fall of the Berlin Wall. |
Historic flag proposals
Note: Ottfried Neubecker's proposal of 1919 and those of Josef Wirmer in 1944 and of his brother Ernst in 1948 are clearly modeled on the Nordic Cross flags used in all Nordic countries – the flags of Denmark, Norway, Sweden, Finland and Iceland all having the same horizontal cross, though differing in color.
| Flag | Date | Description |
|---|---|---|
 | 1817 | German unification flag at Wartburg Festival |
 | 1832 | German unification flag at Hambach Festival |
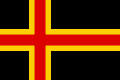 | 1919 | Proposal for the flag for Germany by Ottfried Neubecker |
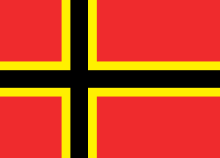 | 1944 | Proposal for the flag of Germany after 1944 military coup d'état by Josef Wirmer |
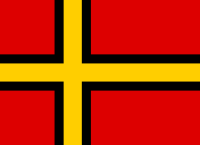 | 1948 | Proposal for the flag for West Germany, based on Josef Wirmer's 1944 design, created by his brother, Ernst |
.svg.png) | 1948 | Proposal for the flag for West Germany by Paul Wentzcke, based on 1848 republican designs |
.svg.png) | 1948 | Proposal for a national flag, by Robert Lehr |
German colonial empire (1884–1918)
The flags of the German overseas colonies were first proposed in 1914, but were never implemented due to the breakout of World War I.
| Flag | Date | Description |
|---|---|---|
 | 1914 | Proposal for German East Africa |
 | 1914 | Proposal for German Kamerun |
 | 1914 | Proposal for German New Guinea |
 | 1914 | Proposal for German Samoa |
 | 1914 | Proposal for German South-West Africa |
 | 1914 | Proposal for German Togoland |
References
- "The flags of Hamburg". Retrieved 2017-11-02.
- (in German) Herzfeld, Andreas (June 2001). "Einige unbekannte Flaggenänderungen 1933–1945". Der Flaggenkurier (in German). Hennigsdorf: Deutsche Gesellschaft für Flaggenkunde (13): 17–23. Archived from the original on 2011-07-17.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Flags of Germany. |