KvLQT3
Kv7.3 (KvLQT3) is a potassium channel protein coded for by the gene KCNQ3.[5]
It is associated with benign familial neonatal epilepsy.
The M channel is a slowly activating and deactivating potassium channel that plays a critical role in the regulation of neuronal excitability. The M channel is formed by the association of the protein encoded by this gene and one of two related proteins encoded by the KCNQ2 and KCNQ5 genes, both integral membrane proteins. M channel currents are inhibited by M1 muscarinic acetylcholine receptors and activated by retigabine, a novel anti-convulsant drug. Defects in this gene are a cause of benign familial neonatal convulsions type 2 (BFNC2), also known as epilepsy, benign neonatal type 2 (EBN2).[5]
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000184156 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000056258 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Entrez Gene: KCNQ3 potassium voltage-gated channel, KQT-like subfamily, member 3".
- Yus-Nájera, E; Muñoz A; Salvador N; Jensen B S; Rasmussen H B; Defelipe J; Villarroel A (2003). "Localization of KCNQ5 in the normal and epileptic human temporal neocortex and hippocampal formation". Neuroscience. 120 (2): 353–64. doi:10.1016/S0306-4522(03)00321-X. ISSN 0306-4522. PMID 12890507.
Further reading
- Gutman GA, Chandy KG, Grissmer S, et al. (2006). "International Union of Pharmacology. LIII. Nomenclature and molecular relationships of voltage-gated potassium channels". Pharmacol. Rev. 57 (4): 473–508. doi:10.1124/pr.57.4.10. PMID 16382104.
- Ryan SG, Wiznitzer M, Hollman C, et al. (1991). "Benign familial neonatal convulsions: evidence for clinical and genetic heterogeneity". Ann. Neurol. 29 (5): 469–73. doi:10.1002/ana.410290504. PMID 1859177.
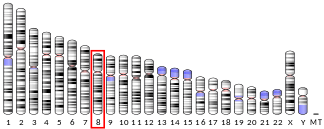
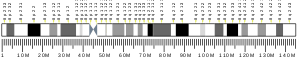
- Lewis TB, Leach RJ, Ward K, et al. (1993). "Genetic heterogeneity in benign familial neonatal convulsions: identification of a new locus on chromosome 8q". Am. J. Hum. Genet. 53 (3): 670–5. PMC 1682419. PMID 8102508.
- Charlier C, Singh NA, Ryan SG, et al. (1998). "A pore mutation in a novel KQT-like potassium channel gene in an idiopathic epilepsy family". Nat. Genet. 18 (1): 53–5. doi:10.1038/ng0198-53. PMID 9425900.
- Yang WP, Levesque PC, Little WA, et al. (1998). "Functional expression of two KvLQT1-related potassium channels responsible for an inherited idiopathic epilepsy". J. Biol. Chem. 273 (31): 19419–23. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.31.19419. PMID 9677360.
- Wang HS, Pan Z, Shi W, et al. (1998). "KCNQ2 and KCNQ3 potassium channel subunits: molecular correlates of the M-channel". Science. 282 (5395): 1890–3. Bibcode:1998Sci...282.1890W. doi:10.1126/science.282.5395.1890. PMID 9836639.
- Schroeder BC, Kubisch C, Stein V, Jentsch TJ (1999). "Moderate loss of function of cyclic-AMP-modulated KCNQ2/KCNQ3 K+ channels causes epilepsy". Nature. 396 (6712): 687–90. Bibcode:1998Natur.396..687S. doi:10.1038/25367. PMID 9872318.
- Kubisch C, Schroeder BC, Friedrich T, et al. (1999). "KCNQ4, a novel potassium channel expressed in sensory outer hair cells, is mutated in dominant deafness". Cell. 96 (3): 437–46. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80556-5. PMID 10025409.
- Selyanko AA, Hadley JK, Wood IC, et al. (1999). "Two types of K(+) channel subunit, Erg1 and KCNQ2/3, contribute to the M-like current in a mammalian neuronal cell" (PDF). J. Neurosci. 19 (18): 7742–56. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-18-07742.1999. PMID 10479678.
- Shapiro MS, Roche JP, Kaftan EJ, et al. (2000). "Reconstitution of muscarinic modulation of the KCNQ2/KCNQ3 K(+) channels that underlie the neuronal M current". J. Neurosci. 20 (5): 1710–21. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-05-01710.2000. PMID 10684873.
- Rundfeldt C, Netzer R (2000). "The novel anticonvulsant retigabine activates M-currents in Chinese hamster ovary-cells tranfected with human KCNQ2/3 subunits". Neurosci. Lett. 282 (1–2): 73–6. doi:10.1016/S0304-3940(00)00866-1. PMID 10713399.
- Selyanko AA, Hadley JK, Wood IC, et al. (2000). "Inhibition of KCNQ1-4 potassium channels expressed in mammalian cells via M1 muscarinic acetylcholine receptors". J. Physiol. 522 Pt 3 (3): 349–55. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7793.2000.t01-2-00349.x. PMC 2269765. PMID 10713961.
- Cooper EC, Aldape KD, Abosch A, et al. (2000). "Colocalization and coassembly of two human brain M-type potassium channel subunits that are mutated in epilepsy". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 97 (9): 4914–9. Bibcode:2000PNAS...97.4914C. doi:10.1073/pnas.090092797. PMC 18332. PMID 10781098.
- Schwake M, Pusch M, Kharkovets T, Jentsch TJ (2000). "Surface expression and single channel properties of KCNQ2/KCNQ3, M-type K+ channels involved in epilepsy". J. Biol. Chem. 275 (18): 13343–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.275.18.13343. PMID 10788442.
- Hirose S, Zenri F, Akiyoshi H, et al. (2000). "A novel mutation of KCNQ3 (c.925T-->C) in a Japanese family with benign familial neonatal convulsions". Ann. Neurol. 47 (6): 822–6. doi:10.1002/1531-8249(200006)47:6<822::AID-ANA19>3.0.CO;2-X. PMID 10852552.
- Main MJ, Cryan JE, Dupere JR, et al. (2000). "Modulation of KCNQ2/3 potassium channels by the novel anticonvulsant retigabine". Mol. Pharmacol. 58 (2): 253–62. doi:10.1124/mol.58.2.253. PMID 10908292.
- Wickenden AD, Yu W, Zou A, et al. (2000). "Retigabine, a novel anti-convulsant, enhances activation of KCNQ2/Q3 potassium channels". Mol. Pharmacol. 58 (3): 591–600. doi:10.1124/mol.58.3.591. PMID 10953053.
- Tinel N, Diochot S, Lauritzen I, et al. (2000). "M-type KCNQ2-KCNQ3 potassium channels are modulated by the KCNE2 subunit". FEBS Lett. 480 (2–3): 137–41. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(00)01918-9. PMID 11034315.
- Wickenden AD, Zou A, Wagoner PK, Jegla T (2001). "Characterization of KCNQ5/Q3 potassium channels expressed in mammalian cells". Br. J. Pharmacol. 132 (2): 381–4. doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0703861. PMC 1572592. PMID 11159685.
- Yus-Najera E, Santana-Castro I, Villarroel A (2002). "The identification and characterization of a noncontinuous calmodulin-binding site in noninactivating voltage-dependent KCNQ potassium channels". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (32): 28545–53. doi:10.1074/jbc.M204130200. PMID 12032157.
External links
- KCNQ3+Potassium+Channel at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.