Dimenoxadol
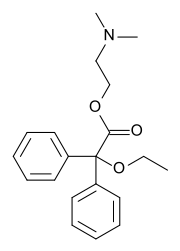
Dimenoxadol (INN) (brand name Estocin (in Russia)), or dimenoxadole (BAN), is an opioid analgesic which is a benzilic acid derivative, closely related to benactyzine (an anticholinergic). Further, the structure is similar to methadone and related compounds like dextropropoxyphene.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Dimenoxadol, Estocin |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C20H25NO3 |
| Molar mass | 327.424 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
It was invented in Germany in the 1950s,[1] and produces similar effects to other opioids, including analgesia, sedation, dizziness and nausea.[2][3][4]
In the United States it is a Schedule I Narcotic controlled substance with an ACSCN of 9617 and a 2013 annual aggregate manufacturing quota of zero.
References
- GB 716700, Boehringer A, et al., "A new and improved analgesic and process for its production", published 10/13/1954
- Gorbatova EN (1967). "[The pharmacology of estocin, an new analgesic]". Stomatologiia. 46 (2): 22–5. PMID 5232927.
- Kingisepp GI, Kurvits K, Nurmand LB (1969). "[Pharmacology of dimethylaminoethyl ester of diphenylethoxyacetic acid hydrochloride--estocin]". Farmakologiia I Toksikologiia. 32 (6): 710–2. PMID 5381602.
- Liberman SS (1968). "[Analgesic action of estocin (dimethylaminoethyl ester hydrochloride of alpha, alpha-diphenylethoxyacetic acid)]". Farmakologiia I Toksikologiia. 31 (6): 668–71. PMID 5729519.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.