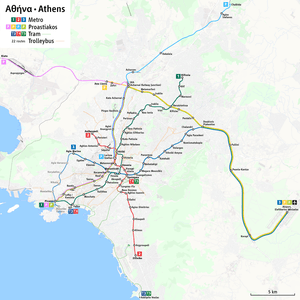
Athens Metro
The Athens Metro (Greek: Μετρό Αθήνας, Metró Athínas) is a rapid-transit system in Greece which serves the Athens conurbation and parts of East Attica. Line 1 opened as a conventional steam railway in 1869 and electrified in 1904. In 1991, Attiko Metro S.A. constructed and extended Lines 2 and 3.[3] It has significantly changed Athens by providing a much-needed solution to the city's traffic and air pollution problem, as well as revitalising many of the areas it serves. An extension of Line 3 is under construction towards Piraeus and also other extensions of existing lines, as well as a new Line 4, are under consideration. The Athens Metro is actively connected with the other means of public transport, such as buses, trolleys, the Athens Tram and the Proastiakos Athens suburban railway. The Athens Metro is hailed for its modernity and many of its stations feature works of art, exhibitions and displays of the archeological remains found during its construction. Photography and video-taking is permitted across the whole network[4] and street photographers often work in Athens Metro.
.svg.png) | |||
.jpg) Athens Metro train (3rd generation stock) | |||
| Overview | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Native name | Μετρό Αθήνας | ||
| Owner | Attiko Metro S.A. (Stasy S.A.) | ||
| Locale | Greater Athens and East Attica | ||
| Transit type | Rapid transit | ||
| Number of lines | 3 | ||
| Number of stations | 61 (6 under construction) | ||
| Daily ridership | 1,353,000[1] | ||
| Annual ridership | 493,800,000 (2013) | ||
| Website | STASY S.A. | ||
| Operation | |||
| Began operation | 1869 | ||
| Operator(s) | Statheres Sygkoinonies (Stasy) S.A. | ||
| Number of vehicles | 294 railcars | ||
| Technical | |||
| System length | 25.6 km (15.9 mi) (Line 1)[2] 58.9 km (36.6 mi) (Lines 2 & 3)[1] 84.5 km (52.5 mi) (Total; includes 20.7 km (12.9 mi) of mixed use suburban rail[1]) | ||
| Track gauge | 1,435 mm (4 ft 8 1⁄2 in) standard gauge | ||
| Electrification | |||
| Top speed | 80 km/h (50 mph) | ||
| |||
History
Piraeus-Kifissia Railway
Until 28 January 2000, Line 1 was the only rapid-transit line in Athens. The Athens and Piraeus Railway Company (SAP) opened the line on 27 February 1869 as a steam railway between Piraeus and Thiseio. It was electrified in 1904, and extended in stages to Kifisia in 1957.
From 1869 to 1926 the line operated by SAP.
From 1926 to 1976 the line operated by Hellenic Electric Railways (E.I.S.). In 1976 the Hellenic Electric Railways was nationalized and renamed Athens-Piraeus Electric Railways S.A.
From 1976 to 16 June 2011, the Athens-Piraeus Electric Railway Company (ISAP) operated Line 1.[5] Unlike Lines 2 and 3, it runs almost entirely above ground.
1990s projects
Since the current Line 1 opened, the government has proposed many expansions to the subway network, including a 1963 plan for a fourteen-line subway network.[6] Construction of Lines 2 and 3 began in November 1992 to decrease traffic congestion and improve Athens' air quality by reducing its smog level.[3] Both lines were constructed underground. Lines 2 and 3, built by Attiko Metro S.A. and operated until 2011 by Attiko Metro Operations Company, are known respectively as the red and blue lines and were inaugurated in January 2000. Line 3 was extended to the Eleftherios Venizelos International Airport in summer 2004, and Line 2 was extended to Anthoupoli and Helliniko in 2013.
Consolidation
Until 17 June 2011,[5] the operational management of the Athens Metro network was similar to that of the London Underground network before the creation of the London Passenger Transport Board and the absorption of the Metropolitan Railway on 1 July 1933. The Greek government attempted to absorb ISAP into Attiko Metro under Law 2669/1998 so the latter would be responsible for the whole network,[7] but this initiative failed. Athens Metro operations were consolidated when the Greek government enacted Law 3920/2011,[8] replacing AMEL, ISAP and Tram S.A. with Urban Rail Transport S.A. (STASY S.A.) (Greek: ΣΤΑΣΥ Α.Ε.), a subsidiary of OASA S.A. (Athens Urban Transport Organisation S.A.).[9]
Infrastructure
Lines and stations
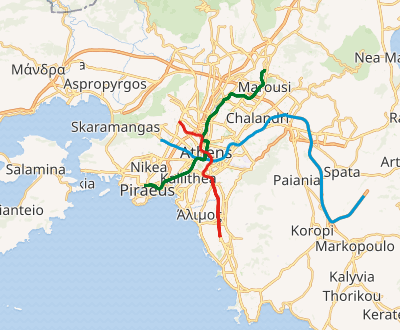
The Line 1 is 25.6-kilometre (15.9 mi) long,[2] and serves 24 stations. Together, Lines 2 and 3 are 58.9-kilometre (36.6 mi) long (including 20.7 kilometres (12.9 mi) of suburban rail line from Doukissis Plakentias station to the Airport on Line 3), and serve 41 stations.[1][10]
| Line | Map colour[I][11] | First section opened |
Elec. | Latest section opened |
Latest station opened | Route | Length (km, mi) | Sta. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Green | February 27, 1869 | 1904 | August 10, 1957 | August 6, 2004 (Nerantziotissa) |
Piraeus – Kifisia | 25.6 km (15.9 mi)[2] | 24 | |||||
| Red | January 28, 2000 | 2000 | July 26, 2013 | July 26, 2013 (Elliniko)[12] |
Anthoupoli – Elliniko | 17.9 km (11.1 mi) | 20 | |||||
| Light Blue[*] | January 28, 2000 | 2000 | December 14, 2013 | December 14, 2013 (Agia Marina) |
Agia Marina – Doukissis Plakentias/Airport | 18.1 km (11.2 mi) / 39 km (24.2 mi) | 21 | |||||
| * Dark blue on signage. | ||||||||||||
.svg.png)

The three-line Athens Metro network serves 61 stations. It owns and operates 57 of them, and OSE owns the remainder on the airport section. The network has four metro interchanges, enabling the lines to interchange with each other at least once. Each line also has at least one station connecting with the Proastiakos Suburban Railway and Athens Tram.
Line 2 and the Attiko Metro portion of Line 3 is entirely underground. Line 1 is primarily overground, with a tunnel section in central Athens. The airport section of Line 3, east of the tunnel portal near Doukissis Plakentias, is open. In the tunnel sections up and down lines share a common tunnel, except for approaches to stations with an island platform (such as Egaleo).
The network uses standard gauge electric trains which in most places run on 750 V DC third rail, but the section of Line 3 running to the airport requires trains which can use overhead lines of 25 kV AC, 50 Hz. There are rail connections between Lines 1 and 2 near Attiki and between Lines 2 and 3 near Syntagma. Train maintenance facilities are located at Attiki, Faliro, Irini, Piraeus, Kifissia and Thissio for Line 1, and Doukissis Plakentias, Eleonas and Sepolia for Lines 2 and 3.
The overall length of the green, red and blue lines to approximately 74 km. The Athens Metro's three lines carry approximately 1,353,000 passengers daily.[1]
Rolling stock
The Athens Metro classifies rolling stock by "batch" for Line 1 and "generation" for Lines 2 and 3 because ISAP and AMEL used different classification systems for rolling stock before consolidation. Six types of rolling stock operate on the network, all equipped with third rail current collection systems; however, only seven second-generation trains have the necessary overhead line equipment to serve Line 3 from Doukissis Plakentias to Airport. Differing signalling systems prevent batch stock from running on Lines 2 and 3 and generation stock from running on Line 1.
The eighth batch (introduced in 1983) is the oldest rolling stock in passenger service, while the third generation (introduced in 2013) is the latest rolling stock in passenger service. The eighth- and tenth-batch stock is externally similar, but the former has split-flap headsigns in Johnston typeface and a cream-and-green interior colour scheme.
| Line | Stock | Image | Introduced |
|---|---|---|---|
| 8th-batch stock |  |
1983 | |
| 10th-batch stock |  |
1993 | |
| 11th-batch stock |  |
2000 | |
| 1st-generation stock |  |
2000 | |
| 2nd-generation stock | 2003 & 2004 | ||
| 3rd-generation stock | .jpg) |
2014 |
- First series (delivery): 28 six-car electric multiple units made by Alstom–Siemens–Adtranz (2000); maximum speed 80 km/h[13]
- Second series (delivery): 21 six-car EMU made by Hanwha-Rotem-Mitsubishi (2004).[14] Seven of these trains can also operate on OSE lines with 25 kV AC −50 Hz overhead electrification system and are used for airport service. All second-series trains are air-conditioned. Maximum speed 80 km/h
- Third series: Athens Metro ordered 17 additional trains made by Hyundai Rotem.
- Four service hybrid locomotives made by Kaelble-Gmeinder-Siemens. They can operate from a third-rail 750 V DC system or their own diesel generators. They have a B-B configuration, with a maximum power of 550 kW under diesel traction and 600 kW under electric traction.[15]
- One road-rail Unimog
| Batch | Year | Configuration | Type | Numbering | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st | 2000 | DT-M-MD+MD-M-DT | DT | A01-A56 | 56 EMU-3 "half-trains" operating as 28 EMU-6 trains. Made by Alsthom-Siemens-ADtranz. MD railcars have an auxiliary driving facility used only for shunting. |
| M | B01-B56 | ||||
| MD | C01-C56 | ||||
| 2nd (DC) |
2003–2004 | D-T-M+M-T-D | D | D201-D228 | 28 EMU-3 "half-trains" operating as 14 EMU-6 trains. Made by Hanwha-Rotem-Mitsubishi. |
| T | T201-T228 | ||||
| M | M201-M228 | ||||
| 2nd (DC/AC) |
2003–2004 | D-T-M+M-T-D | D | D251-D264 | 14 EMU-3 "half-trains" operating as 7 EMU-6 trains. Made by Hanwha-Rotem-Mitsubishi, can also operate on 25 kV AC, 50 Hz lines. |
| T | T251-T264 | ||||
| M | M251-M264 | ||||
| 3rd | 2012–2013 | D-T-M+M-T-D | D | D301-D334 | A contract for 17 air conditioned EMU-6 trains was signed on 2009-09-16 with Hanwha-Rotem.[16] 34 EMU-3 "half-trains" entered service as 17 EMU-6 trains in June 2014. |
| T | T301-T334 | ||||
| M | M301-M334 |
Railcar codes: DM: driving motor car, DT: driving trailer, M: motor car, T: trailer, MD: motor car with auxiliary driving facility.
Signalling
Line 1 uses two-aspect red/green home signals, yellow/green distant signals and a passenger information system (PIS). The current system replaced 1950s-era semaphore signals.
Lines 2 and 3 use the Alstom automatic train supervision system (ATS) and a passenger information system (PIS). Two-aspect red/white colour signals are used at points and junctions only.
Network map
Fares

Fares are prepaid, either as short term tickets valid for 90 minutes, 24 hours, 5 days, or as long term tickets. As of February 2017, there are two types of fare products, the ATH.ENA Ticket and ATH.ENA Card, both of which are validated using a contactless system (by scanning the ticket or card at the electronic validating machines). The tickets is valid on all modes of public transport in Athens except on trains and buses to the airport, and airport tickets.[17] Long term tickets are available in 30, 90, 180, and 365 day periods and are available only with a personalized ATH.ENA Card. Reduced fares are available for university students, seniors, disabled and persons under 18.[18] On buses, trolleys and trams the ticket or card must be validated only when entering the vehicle/car by scanning the ticket at the electronic validating machines. At metro or suburban railway stations, the ticket or card must be validated at the electronic gates when entering and exiting the station.
Archaeological excavations and exhibits

During construction of the metro tunnels, artifacts of archaeological interest were discovered and rescue archaeology was employed. Teams of archaeologists worked ahead of, then with, engineers for six years, protecting and recording archaeological finds (streets, houses, cemeteries, sanctuaries, public workshops, foundry pits, kilns, aqueducts, wells, cisterns, drains and sewage tunnels). This afforded new insight into the city's ancient topography, through unprecedented infrastructure development combined with the study and preservation of archaeological data. Exhibitions of ancient artifacts or replicas are found at a number of metro stations, including Monastiraki and Syntagma.
Future Plans
Line 4
A fourth line is planned for the Athens Metro and it has been incorporated in the roadmap of Athens's mass transit system since 2005. The new line in its totality will extend over a length of 38.2 km, adding thirty five (35) new stations to the Athens Metro system. The cost of the entire project is estimated at 3.3 billion EUR.[19] The recommendation is for lighter rolling stock than the type used in existing lines of Athens Metro which would operate automatically without a driver.
The first phase of Line 4 will be between Alsos Veikou and Goudi stations, predicting fifteen (15) new stations and a length of 12.8 km of new track. An invitation to tender for the construction of the first phase of Line 4 was issued in September 2018. The construction is expected to start by mid-2020 and the opening of the line by circa 2028. The estimated cost for constructing the first phase of the new line is 1.51 billion EUR. Currently, the project of the first phase is considered to follow a PPP scheme which might be extended for constructing the whole new line. An alternative solution is a mixed funding between the EIB and the Greek State. It is also a high-profile candidate project to be included in the Juncker Plan of EU that will include also the second phase of Line 4 of Athens Metro.
As of March 2020, the planned stations for the first phase of Line 4 are:[20]
| Name | Location | Opening date |
Transfers | Platform type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Athens Metro Line 4 [I] | ||||
| Alsos Veikou | Omorfoklissias (Veikou) Ave. & Tralleon St. | 2028 | none | Side |
| Galatsi | Omorfoklissias (Veikou) Ave. & Galatsiou Ave. | |||
| Elikonos | Aghias Glykerias St. & Parnithos St. | |||
| Kypseli | Kanari (Kypselis) Square | |||
| Dikastiria | Evelpidon St. & Moustoxidi St. | |||
| Alexandras | Alexandras Ave. & Moustoxidi St. | |||
| Exarcheia | Exarcheia Square | |||
| Akadimia | Akadimias St. | |||
| Kolonaki | Filikis Etaireias (Kolonaki) Square | none | ||
| Evangelismos | Rizari Park | |||
| Kaisariani | Ethnikis Antistaseos Ave. & Vass. Alexandrou Ave. | none | ||
| Panepistimioupoli | within the campus of the National and Kapodistrian University of Athens | |||
| Ilisia | Indou St. & Aornou Square & Kyprou Square | |||
| Zografou | Alexandri (Gardenia) Square | |||
| Goudi | Eleftherias Square | |||
Notes
References
- "Homepage - The Company - Attiko Metro S.A." Attiko Metro S.A. Archived from the original on 3 December 2010. Retrieved 2 June 2014.
- "Homepage - The Company - Historic Data - Transit in Athens". Attiko Metro S.A. Archived from the original on 8 July 2014. Retrieved 2 June 2014.
- "AttikoMetro Inside – Base Project". Attiko Metro S.A. 9 September 2012. Retrieved 3 October 2012.
- "synigoros.gr" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 14 March 2016.
- "Urban Rail Transport SA (STASY SA): Urban Rail Transport S.A". Urban Rail Transport S.A. Retrieved 2 October 2012.
- Hekimoglou, Achilleas (24 August 2013). Οραμα για 14 γραμμές Μετρό στην Αττική από το 2000 (in Greek). Το Βήμα (To Vima). Retrieved 25 September 2013.
- "Law 2669/1998". Εφημερίδας της Κυβερνήσεως (in Greek). Athens: Government of Greece. A (283). 18 December 1998. Retrieved 24 September 2013.
- Law 3920, Government Gazette issue A-33, 3 March 2011.
- Ministerial Decision 28737/2637, Government Gazette issue B-1454, 17 June 2011
- "Homepage - Construction of the Athens Metro - Projects in Operation - Base Project". Attiko Metro S.A. Retrieved 2 June 2014.
- "Athens Metro Regulatory Plan" (PDF). Attiko Metro S.A. Retrieved 17 March 2020.
- "Urban rail news in brief – May 2013". Railway Gazette International. 3 May 2013. Retrieved 21 June 2013.
- G. Nathenas; A. Kourbelis; T. Vlastos; S. Kourouzidis; V. Katsareas; P. Karamanis; A. Klonos; N. Kokkinos (2007). Από τα Παμφορεία στο Μετρό (in Greek). 2. Athens: Μίλητος (Militos). pp. 703–708. ISBN 978-960-8460-91-1.
- "New Athens metro trains are ready to roll". Ekathimerini. 5 June 2014. Retrieved 17 March 2020.
- N. Sbarounis (December 2002). "Hybrid locomotives of Athens Metropolitan Network (Greek: Υβριδικές Ηλεκτράμαξες του Μητροπολιτικού Δικτύου Αθηνών)". Sidirotrohia (Greek: Σιδηροτροχιά) (in Greek) (23): 30–31.
- ATHENS METRO – Completion of the tender for the supply of 17 new trainsets for the Athens Metro (16/09/2009)
- "Tickets" (PDF). OASA S.A. Retrieved 22 September 2015.
- "Travel Cards (Greek - English not available)". STASY S.A./OASA S.A. Retrieved 23 September 2015.
- "Attiko Metro Γραμμή 4 (Line 4)". Attiko Metro S.A. Retrieved 17 March 2020.
- "Attiko Metro Line 4 Stations". Attiko Metro S.A. Retrieved 17 March 2020.
- "Athens Public Transportation Map". Athens Urban Transport Organisation. Retrieved 17 March 2020.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Athens Metro. |
- Athens Metro Map on Google earth with geolocation
- Urban Rail Transport Company (STASY S.A.)
- Attiko Metro Company (Construction and Infrastructure)
- Athens Urban Transport Organisation (OASA S.A.)
- Hellenic Ministry of Public Works page on the Attiko Metro
- UrbanRail.Net – Athens Metro
- CityRailTransit – Athens railway map (real distance)