Subconjunctival bleeding
| Subconjunctival bleeding | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Subconjunctival hemorrhage, subconjunctival haemorrhage, hyposphagma |
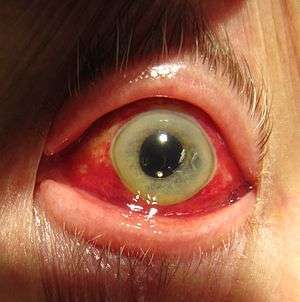 | |
| Subconjunctival hemorrhage causing red coloration as result of ruptured blood vessel in the eye. | |
| Specialty | Ophthalmology |
Subconjunctival bleeding, also known as subconjunctival hemorrhage, is bleeding underneath the conjunctiva. The conjunctiva contains many small, fragile blood vessels that are easily ruptured or broken. When this happens, blood leaks into the space between the conjunctiva and sclera.
Such a hemorrhage may be caused by a sudden or severe sneeze or cough, or due to high blood pressure or as a side effect of blood thinners such as aspirin or warfarin.[1] It may also be caused by heavy lifting, vomiting, or even rubbing one's eyes too roughly.[2] In other cases, it may result from being choked or from straining due to constipation. Also, it can result as a minor post-operative complication in eye surgeries such as LASIK.
Signs and symptoms
Whereas a bruise typically appears black or blue underneath the skin, a subconjunctival bleeding initially appears bright-red underneath the transparent conjunctiva. Later, the hemorrhage may spread and become green or yellow, like a bruise. Usually this disappears within 2 weeks.[3]
Although its appearance may be alarming, in general a subconjunctival bleeding is a painless and harmless condition; however, it may be associated with high blood pressure, trauma to the eye, or a base of skull fracture if there is no posterior border of the hemorrhage visible.
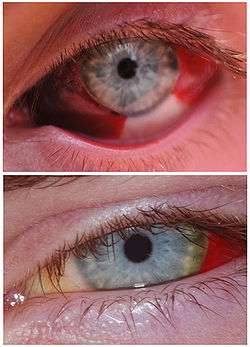 (Top) A stress induced subconjunctival bleeding in the left eye one week after hemorrhaging.
(Top) A stress induced subconjunctival bleeding in the left eye one week after hemorrhaging.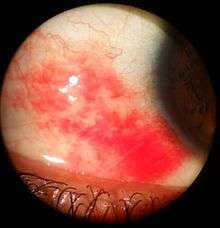 Subconjunctival hemorrhage viewed through slit lamp biomicroscope
Subconjunctival hemorrhage viewed through slit lamp biomicroscope- Subconjunctival hemorrhage in the left eye 48 hours after hemorrhaging.
Causes
- It may result from being choked
- Certain infections of the outside of the eye (conjunctivitis) where a virus or a bacteria weaken the walls of small blood vessels under the conjunctiva
- Mask squeeze from diving and not equalizing mask pressure during descent
- Eye trauma
- Coagulation disorder (congenital or acquired)
- Head injury
- Whooping cough or other extreme sneezing or coughing[1]
- Severe hypertension
- LASIK
- Acute hemorrhagic conjunctivitis (caused by Enterovirus 70 or Coxsackie A virus)
- Leptospirosis
- Ebola
- Increased venous pressure (e.g., extreme g-force, straining, vomiting, choking, or coughing)[1][2] or from straining due to constipation
- Zygoma fracture (results in lateral subconjunctival hemorrhage)
Subconjunctival hemorrhages in infants may be associated with scurvy (a vitamin C deficiency),[4][5] abuse or traumatic asphyxia syndrome.[6]
Management
A subconjunctival hemorrhage is typically a self-limiting condition that requires no treatment in the absence of infection or significant trauma. The elective use of aspirin and NSAIDs is typically discouraged. Artificial tears may be applied four to six times a day.[7]
References
- 1 2 3 "Subconjunctival hemorrhage". PubMed Health on the National Institutes of Health website. May 1, 2011. Retrieved October 15, 2012.
- 1 2 "Subconjunctival hemorrhage". Disease.com. n.d. Retrieved October 15, 2012.
- ↑ Robert H. Grahamn (February 2009). "Subconjunctival Hemorrhage". emedicine.com. Retrieved 23 November 2010.
- ↑ "Möller-Barlow disease". whonamedit.com. Retrieved 23 November 2010.
- ↑ Bruce M. Rothschild (December 17, 2008). "Scurvy". eMedicine.com. Retrieved 23 November 2010.
- ↑ Spitzer S. G; Luorno J.; Noël L. P. "Isolated subconjunctival hemorrhages in nonaccidental trauma". ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 23 November 2010.
- ↑ Robert H. Grahamn (February 2009). "Subconjunctival Hemorrhage". emedicine.com. Retrieved 23 November 2010.
External links
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Conjunctival hemorrhage. |