State of Syria (1924–1930)
| State of Syria État de Syrie دولة سورية | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1924–1930 | |||||||||||
 | |||||||||||
| Status | French Mandate | ||||||||||
| Capital | Damascus | ||||||||||
| Common languages |
French Arabic Syriac Armenian Kurdish Turkish | ||||||||||
| Religion |
Islam Christianity Judaism Druzism Yezidism | ||||||||||
• 1922–1925 | Subhi Barakat | ||||||||||
• 1926 | François Pierre-Alype | ||||||||||
• 1926–1928 | Ahmad Nami | ||||||||||
• 1928–1930/1931 | Taj al-Din al-Hasani | ||||||||||
| Historical era | Interwar period | ||||||||||
• Federation declared | 1922 | ||||||||||
• State declared | 1924 | ||||||||||
| 1925–1927 | |||||||||||
• Republic declared | 1930 | ||||||||||
| Currency | Syrian pound | ||||||||||
| ISO 3166 code | SY | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| Today part of |
| ||||||||||
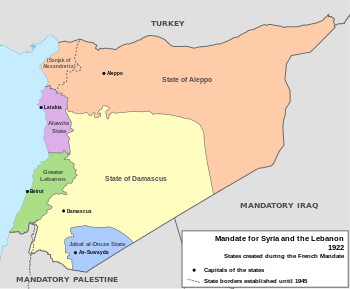
The State of Syria (French: État de Syrie, Arabic: دولة سوريا Dawlat Sūriyā) was a French Mandate state declared on 1 December 1924 from the union of the State of Aleppo and the State of Damascus. It was the successor of the Syrian Federation (French: Fédération syrienne, Arabic: الاتحاد السوري al-Ittiḥād as-Sūrī) which had been created by providing a central assembly for the State of Aleppo, the State of Damascus and the Alawite State. The Alawite State did not join the State of Syria.
Background
In 1920, an independent Arab Kingdom of Syria was established under King Faisal of the Hashemite family, who later became the King of Iraq. However, his rule over Syria ended after only a few months, following the clash between his Syrian Arab forces and regular French forces at the Battle of Maysalun. French troops occupied Syria later that year after the League of Nations put Syria under French mandate.
History of Syria under the Mandate
Initial civil administration
Following the San Remo conference and the defeat of King Faisal's short-lived monarchy in Syria at the Battle of Maysalun, the French general Henri Gouraud established civil administration in the territory. The mandate region was subdivided into six states. The drawing of those states was based in part on the sectarian make up on the ground in Syria. However, nearly all the Syrian sects were hostile to the French mandate and to the division it created.
The primarily Sunni population of Aleppo and Damascus were strongly opposed to the division of Syria.
Syrian Federation (1922–24)

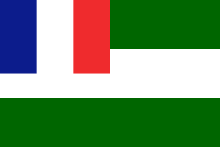
In July 1922, France established a loose federation between three of the states: the State of Damascus, the State of Aleppo and the Alawite State under the name of the Syrian Federation. Jabal Druze and Greater Lebanon were not parts of this federation. The autonomous Sanjak of Alexandretta was added to the state of Aleppo in 1923. The Federation adopted a new federal flag (green-white-green with French canton), which later became the flag of the State of Syria.
State of Syria

On January 1, 1925, the Alawite state seceded from the federation when the states of Aleppo and Damascus were united into the State of Syria.
General revolt
In 1925, Syrian resistance to French colonial rule broke out in full scale revolt, led by Sultan Pasha el Atrash.
The revolt broke out in Jabal Druze but quickly spread to other Syrian states and became a general rebellion in Syria. France tried to retaliate by having the parliament of Aleppo declare secession from the union with Damascus, but the voting was foiled by Syrian patriots.
Despite French attempts to maintain control by encouraging sectarian divisions and isolating urban and rural areas, the revolt spread from the countryside and united Syrian Druze, Sunnis, Shiites, Alawis, and Christians. Once the rebel forces had besieged Damascus, the French military responded with brutal counter-insurgency techniques that prefigured those that would be used later in Algeria and Indo-China. These techniques included house demolitions, collective punishments of towns, executions, population transfers, and the use of heavy armor in urban neighborhoods. The revolt was eventually subdued in 1926-27 via French aerial bombardment of civilian areas, including Damascus.[1]
Republic of Syria
On May 14, 1930, the State of Syria was declared the Republic of Syria and a new constitution was drafted.
Government
While the State enjoyed a certain degree of autonomy as a Mandate, France exercised significant authority over the government. The revolt that began in Jabal Druze led to France easing their hold on Syria and a constitution was drafted but not ratified by the French Chamber of Duties, and the coming of World War II stopped any progress in Syrian self-determination.[2]
Education
Under French administration, the University of Damascus, known then as Syrian University was established in 1923, teaching in Arabic. It was the first university to be founded in Syria, being established through the merger of the School of Medicine and the Institute of Law, founded 1903 and 1913 respectively during the Ottoman era.
See also
References
Bibliography
- David Kenneth Fieldhouse (2006). Western Imperialism in the Middle East 1914-1958.
- Sami M. Moubayed (2006). Steel & silk: men and women who shaped Syria 1900-2000.
- Derek Hopwood (1988). Syria 1945-1986: politics and society.
External links
- Timeline of the French Mandate period
- (in French) Mandat Syrie-Liban ... (1920-1946)
- (in French) La Syrie et le mandat français (1920-1946)
- (in French) Les Relations franco-libanaises dans le cadre des relations Internationales
- (in French) Mandat français au Proche-Orient
- "No Yo-Yo!". Time. January 30, 1933. Retrieved August 19, 2009.