Guangzhouwan
| Kouang-Tchéou-Wan Guangzhouwan | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1898–1946 | |||||||||
 Flag
 Emblem
| |||||||||
|
| |||||||||
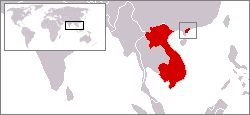 Location of Kwangchow Wan in French Indochina | |||||||||
| Status |
Constituent territory of French Indochina Leased territory of France | ||||||||
| Capital | Fort-Bayard | ||||||||
| Common languages | |||||||||
| Governor-General | |||||||||
| Historical era | New Imperialism | ||||||||
• Treaty of Kouang-Tchéou-Wan | 10 April 1898 | ||||||||
• Franco-Chinese Agreement | 28 February 1946 | ||||||||
| Area | |||||||||
| 1899 | 1,300 km2 (500 sq mi) | ||||||||
| Population | |||||||||
• 1911 | 189,000 | ||||||||
• 1935 | 209,000 | ||||||||
| Currency | French Indochinese piastre | ||||||||
| |||||||||
Guangzhouwan (officially Kouang-Tchéou-Wan; also spelled Kwangchow Wan, Kwangchow-wan, Kwang-Chou-Wan or Quang-Tchéou-Wan) (Chinese: 廣州灣; literally: "Guangzhou Bay") was a small enclave on the southern coast of China ceded by Qing China to France as a leased territory and administered as an outlier of French Indochina.[1] The territory did not experience the rapid growth in population that other parts of coastal China experienced, rising from 189,000 in the early 20th century[2] to just 209,000 in 1935.[3] Industries included shipping and coal mining.
Japan occupied the territory in February 1943. The French never regained it and retroceded it to the Republic of China by a convention signed 18 August 1945.
The capital of the territory was Fort-Bayard. The old spellings "Tsankiang", "Chankiang" and "Tsamkong" were replaced by the pinyin romanisation "Zhanjiang" by the Chinese government in 1958.
Geography
The leased territory was situated in Guangdong Province (Kwangtung Province) on the east side of the Leizhou Peninsula (French: Péninsule de Leitcheou), north of Hainan, around a bay then called Kwangchowan, now called the Port of Zhanjiang. The bay forms the estuary of the Maxie River (Chinese: Maxie He, French: Rivière Ma-The). The Maxie is navigable as far as 19 kilometres (12 mi) inland even by large warships. The territory ceded to France included the islands lying in the bay, which enclosed an area 29 km long by 10 km wide and a minimum water depth of 10 metres. The islands were recognized at the time as an admirable natural defense, the main islands being Donghai Dao. The limits of the concession inland were fixed in November 1899; on the left bank of the Maxie, France gained from Gaozhou prefecture (Kow Chow Fu) a strip of territory 18 km by 10 km, and on the right bank a strip 24 km by 18 km from Leizhou prefecture (Lei Chow Fu).[2] The total land area of the leased territory was 1,300 square kilometres (500 sq mi).[3] The city of Fort-Bayard (Zhanjiang) was developed as a port.
History
Establishment of French rule and early development

Kwangchow Wan was leased by China to France for 99 years, or until 1997 (as the British did in Hong Kong’s New Territories), according to the Treaty of 10 April 1898, on 27 May as the Territoire de Kouang-Tchéou-Wan. Their colony was described as "commercially unimportant but strategically located"; most of France's energies went into their administration of French Indochina, and their main concern in China was the protection of Roman Catholic missionaries, rather than the promotion of trade.[1] Kwangchow Wan was effectively placed under the authority of the French Resident Superior in Tonkin (itself under the Governor General of French Indochina, also in Hanoi); the French Resident was represented locally by Administrators.[4]
In addition to the territory acquired, France was given the right to connect the bay by railway with the city and harbour situated on the west side of the peninsula; however, when they attempted to take possession of the land to build the railway, forces of the provincial government offered armed resistance. As a result, France demanded and obtained exclusive mining rights in the three adjoining prefectures.[2] The return of the leased territory to China was promised by France at the Washington Naval Conference of 1921–1922 but this plan was in fact never realised.[5]
By 1931, the population of Kwangchow Wan had reached 206,000, giving the colony a population density of 245 persons per km²; virtually all were Chinese, and only 266 French citizens and four other Europeans were recorded as living there.[3] Industries included shipping and coal mining.[4] The port was also popular with smugglers; prior to the 1928 cancellation of the American ban on export of commercial airplanes, Kwangchow Wan was also used as a stop for Cantonese smugglers transporting military aircraft purchased in Manila to China,[6] and US records mention at least one drug smuggler who picked up opium and Chinese emigrants to be smuggled into the United States from there.[7]
World War II

As an adjunct of French Indochina, Kwangchow Wan generally endured the same fate as Indochina proper during World War II. Even before the signing of the 30 August 1940 accord with Japan in which France recognized the “privileged status of Japanese interests in the Far East” and which constituted the first step of the Japanese military occupation of Indochina, a small detachment of Japanese marines had landed at Fort-Bayard without opposition in early July and set up a control and observation post in the harbor.[8] However, as in French Indochina proper, the civilian administration of the territory was to remain in the hands of official of the France State, commonly known as Vichy France following the Fall of France; in November 1941, Governor General Jean Decoux, newly appointed by Marshal Pétain, made an official visit to Kwangchow Wan.[9] In mid-February 1943, the Japanese, after having informed the Vichy government that they needed to strengthen the defence of Kwangchow Wan Bay, unilaterally landed more troops and occupied the airport and all other strategic locations in the Territory. From then on, Kwanchow Wan was de facto under full military Japanese occupation and the French civilian administration was gradually reduced to a mere façade. The Administrator resigned in disgust and Adrien Roques, a local pro-Vichy militant, was appointed to replace him.[10] In May of the same year, Roques signed a convention with the local Japanese military authorities in which the French authorities promised to cooperate fully with the Japanese. On 10 March 1945, the Japanese, following up on their sudden attack on French garrisons throughout Indochina the night before, disarmed and imprisoned the small French colonial garrison in Fort-Bayard.[11]
Just prior to the Japanese surrender which ended World War II, the National Revolutionary Army, having recaptured Liuzhou, Guilin, and Taizhou, as well as Lashio and Mandalay in Burma, was planning to launch a large-scale assault on Kwangchow Wan; however, due to the end of the war, the assault never materialised.[12]
On 18 August 1945 in Chongqing, while the Japanese were still occupying Kwangchow Wan following the surrender, a French diplomat and Kuo Chang Wu, Vice-Minister of Foreign Affairs of the Republic of China, signed the Convention between the Provisional Government of the French Republic and the National Government of China for the retrocession of the Leased Territory of Kouang-Tchéou-Wan. Almost immediately after the last Japanese occupation troops had left the territory in late September, representatives of the French and the Chinese governments went to Fort-Bayard to proceed to the transfer of authority; the French flag was lowered for the last time on 20 November 1945.[13]
During the Japanese occupation of Hong Kong, Kwangchow Wan was often used as a stopover on an escape route for civilians fleeing Hong Kong and trying to make their way to Free China; Patrick Yu, a prominent trial lawyer, recalled in his memoirs how a Japanese civilian in Hong Kong helped him to escape in this way.[14] However, the escape route was closed when the Japanese occupied the area in February 1943.[15]
French cultural and economic influence
A French-language school, École Franco-Chinoise de Kouang-Tchéou-Wan, as well as a branch of the Banque de l'Indochine, were set up in Fort-Bayard.[16] In addition, a Roman Catholic church constructed during the colonial period is still preserved today.[17]
Gallery
 Kwangchow Wan pavilion at the Marseille Colonial Exhibition
Kwangchow Wan pavilion at the Marseille Colonial Exhibition Post and Telegraph building in Poteou, Kwangchow Wan.
Post and Telegraph building in Poteou, Kwangchow Wan. Colonial militia with French officers.
Colonial militia with French officers. Pupils and teachers of the École Franco-Chinoise de Kouang-Tchéou-Wan
Pupils and teachers of the École Franco-Chinoise de Kouang-Tchéou-Wan
See also
References
Citations
- 1 2 Gale 1970: 201
- 1 2 3 Chisholm 1911.
- 1 2 3 Priestly 1967: 441
- 1 2 Olson 1991: 349
- ↑ Escarra 1929: 9
- ↑ Xu 2001: 21
- ↑ Anslinger 1953: 141
- ↑ Matot, p. 193.
- ↑ Matot, p. 194.
- ↑ Matot, p. 204.
- ↑ Matot, p. 209-210.
- ↑ Handel 1990: 242
- ↑ Matot, p. 214-217.
- ↑ Yu 2000: 38
- ↑ Olson 1991: 349–350
- ↑ Le Papier Colonial
- ↑ Li 2001
Sources
- Anslinger, H.J.; Tompkins, William F. (1953), The Traffic in Narcotics, Funk and Wagnalls

- Escarra, Jean (1929), Le régime des concessions étrangères en Chine, Académie de droit international
- Gale, Esson M. (1970), "International Relations: The Twentieth Century", China, Ayer Publishing, pp. 200–221, ISBN 0-8369-1987-4
- A. Choveaux, "Situation économique du territoire de Kouang-Tchéou-Wan en 1923". Annales de Géographie, Volume 34, Nr. 187, pp. 74–77, 1925.
- Handel, Michael (1990), Intelligence and Military Operations, United Kingdom: Routledge
- Li, Chuanyi; Ou, Jie (2001), "湛江维多尔天主教堂考察" [Research on the Victor Catholic Church of Zhanjiang], Study and preservation of Chinese modern architecture series, Tsinghua University, 1, archived from the original on 2014-10-21
- Luong, Hy Van (1992), Revolution in the Village: tradition and transformation in North Vietnam, 1925–1988, Hawaii: University of Hawaii Press
- Matot, Bertrand. Fort Bayard. Quand la France vendait son opium. Éditions François Bourin, 2013, Paris, p. 193.
- Olson, James S., ed. (1991), Historical Dictionary of European Imperialism, Westport, Connecticut: Greenwood Press
- Priestly, Herbert Ingram (1967), France Overseas: Study of Modern Imperialism, United Kingdom: Routledge
- Xu, Guangqiu (2001), War Wings: The United States and Chinese Military Aviation, 1929–1949, Greenwood Press, ISBN 0-313-32004-7
- Yu, Patrick Shuk-Siu (2000), A Seventh Child and the Law, Hong Kong, China: Hong Kong University Press
- lettres > par pays > Chine > Kouang-Tcheou-Wan, Le Papier Colonial: la France d'outre-mer et ses anciennes colonies, retrieved 2007-01-01 Includes images of letters sent to and from the territory.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Kouang-tchéou Wan. |
- WorldStatesmen - China
- Historic pictures of Fort Bayard at the Wayback Machine (archived October 12, 2007)
- Map of French Guangzhouwan
- Map of French Indochina and Guangzhouwan
- Other map about Guangzhouwan and Indochina
- Map of Kwang Tchou Wan
- "French Colonial Zhanjiang"
Coordinates: 21°10′38.2″N 110°25′4.76″E / 21.177278°N 110.4179889°E