New Hebrides
| New Hebrides Condominium Condominium des Nouvelles-Hébrides | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1906–1980 | |||||||||
.svg.png) Flag
 Emblem (1969)
| |||||||||
 New Hebrides | |||||||||
| Capital | Port Vila | ||||||||
| Common languages | English, French, Bislama | ||||||||
| History | |||||||||
• Established | 1906 | ||||||||
| 30 July 1980 | |||||||||
| Area | |||||||||
| 1976 | 12,189 km2 (4,706 sq mi) | ||||||||
| Population | |||||||||
• 1976 | 100000 | ||||||||
| Currency | New Hebrides franc | ||||||||
| |||||||||
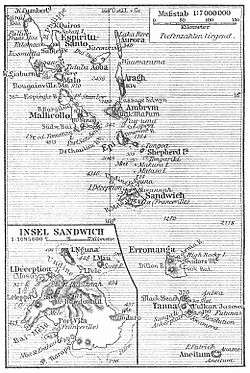
New Hebrides, officially the New Hebrides Condominium (French: Condominium des Nouvelles-Hébrides, lit. "Condominium of the New Hebrides") and named for the Hebrides Scottish archipelago, was the colonial name for the island group in the South Pacific Ocean that is now Vanuatu. Native people had inhabited the islands for three thousand years before the first Europeans arrived in 1606 from a Spanish expedition led by Pedro Fernandes de Queirós. The islands were colonised by both the British and French in the 18th century, shortly after Captain James Cook visited.
The two countries eventually signed an agreement making the islands an Anglo-French condominium that divided the New Hebrides into two separate communities: one Anglophone and one Francophone. This divide continues even after independence, with schools teaching in either one language or the other, and with different political parties. The condominium lasted from 1906 until 1980, when the New Hebrides gained their independence as the Republic of Vanuatu.
Politics and economy
The New Hebrides was a rare form of colonial territory in which sovereignty was shared by two powers, Britain and France, instead of just one. Under the Condominium there were three separate governments – one French, one British, and one joint administration that was partially elected after 1975.
The French and British governments were called residencies, each headed by a resident appointed by the metropolitan government. The residency structure greatly emphasised dualism, with both consisting of an equal number of French and British representatives, bureaucrats and administrators. Every member of one residency always had an exact mirror opposite number on the other side who they could consult. The symmetry between the two residencies was almost exact.
The joint government consisted of both local and European officials. It had jurisdiction over the postal service, public radio station, public works, infrastructure, and censuses, among other things. The two main cities of Luganville and Port Vila also had city councils, but these did not have a great deal of authority.
While initial settlers were predominantly British living in Australia, the late 19th century saw an influx of French. Within a few decades, there were twice as many French on the islands as there were British, prompting a multitude of petitions to cede power to either the French or the British. Despite this, the two nations came together to form a condominium, a specialised form of government where both nations would have all of their own administrations and jointly rule the islands. The only place they came together was in the Joint Court. As Mander describes, "The Joint Court was the key to the situation and much was to depend upon it….Three judges–one British, one French, and the third nominated by the King of Spain–were to comprise the court."[1] This meant convictions in court were chosen based on either British or French law, depending on the circumstances.
Other than the Joint Court, everything existed in pairs. "Cynics called the Condominium 'the Pandemonium', as the dual administration produced amazing duplication. There were two police forces with their own laws, including road laws, two health services, two education systems, two currencies, and two prison systems."[2] Additionally, there were separate British and French governments, which meant two immigration policies, two courts (outside of the Joint Court), two corporation laws, and inhabitants of the islands were given the choice as to which government they wanted to go under. For instance, if you were convicted, you could choose whether to be convicted under British or French law. As Miles put it, "The result was an inevitable clash of foreign policy and colonial mentality."[3]
The Condominium was not beneficial for Ni-Vanuatus, as they were "...officially stateless. [For instance,] To travel abroad, they needed an identifying document signed by both the British and the French resident commissioners."[2] Inevitably, this led to revolt across the islands, with a multitude of revolutionary groups forming to attempt to create agency and self-government for themselves.
Local people could choose whether to be tried under the British common law or the French civil law. Visitors could choose which immigration rules to enter under. Nationals of one country could set up corporations under the laws of the other. In addition to these two legal systems, a third Native Court existed to handle cases involving Melanesian customary law. There was also a Joint Court, composed of British and French judges. The President of the Joint Court was appointed by the King of Spain until 1939 when the post was abolished after the retirement of the last President, partly due to the abolition of the Spanish monarchy in 1931.[4]
There were two prison systems to complement the two court systems. The police force was technically unified but consisted of two chiefs and two equal groups of officers wearing two different uniforms. Each group alternated duties and assignments.
Language was a serious barrier to the operation of this naturally inefficient system, as all documents had to be translated once to be understood by one side, then the response translated again to be understood by the other, though Bislama creole represented an informal bridge between the British and the French camps.
See also
References
- Notes
- ↑ Mander 1944, p. 152
- 1 2 Harewood et al. 2006
- ↑ Miles 1994, p. 201
- ↑ Woodward, Keith. "A Political Memoir of the Anglo-French Condominium of the New Hebrides". Australian National University. Retrieved 15 March 2015.
- Sources
- Harewood, J.; Chinula, T.; Talbot, V.; Carillet, J.-B.; Sorokin, M. (2006). Vanuatu and New Caledonia (1st ed.). Singapore: Lonely Planet.
- Mander, L. A. (1944). "The New Hebrides Condominium". Pacific Historical Review. 13 (2): 151–167. doi:10.2307/3634610. JSTOR 3634610.
- Miles, W. F. (1994). "Anachronistic Antagonisms: France Versus Britain in the New Hebrides, 1966-1977". Proceedings of the Meeting of the French Colonial Historical Society. Michigan State University Press. 19: 200–215. JSTOR 43007776.
- Peck, John G.; Gregory, Robert J. (2005). "A Brief Overview of the Old New Hebrides" (PDF). Palmerston North, New Zealand: School of Psychology, Massey University. Retrieved 5 February 2008.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to History of Vanuatu. |
| Wikisource has the text of The New Student's Reference Work article New Hebrides. |