Spinothalamic tract
| Spinothalamic tract | |
|---|---|
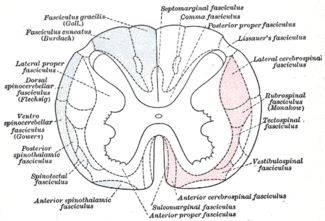 Diagram of the main tracts within the spinal cord - spinothalamic fasciculus is labelled at bottom left | |
| Details | |
| Part of | Spinal cord |
| System | Somatosensory system |
| Decussation | Anterior white commissure |
| Parts | Anterior and lateral tracts |
| From | Skin |
| To | Thalamus |
| Artery | Anterior spinal artery |
| Function | Gross touch and temperature |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Tractus spinothalamicus |
| MeSH | D013133 |
| NeuroNames | 2058, 810 |
| TA | A14.1.04.138 |
| FMA | 72644 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The spinothalamic tract (also known as anterolateral system or the ventrolateral system) is a sensory pathway from the skin to the thalamus. From the ventral posterolateral nucleus in the thalamus, sensory information is relayed upward to the somatosensory cortex of the postcentral gyrus.
The spinothalamic tract consists of two adjacent pathways: anterior and lateral. The anterior spinothalamic tract carries information about crude touch. The lateral spinothalamic tract conveys pain and temperature.
In the spinal cord, the spinothalamic tract has somatotopic organization. This is the segmental organization of its cervical, thoracic, lumbar, and sacral components, which is arranged from most medial to most lateral respectively.
The pathway crosses over (decussates) at the level of the spinal cord, rather than in the brainstem like the dorsal column-medial lemniscus pathway and lateral corticospinal tract.
Structure
There are two main parts of the spinothalamic tract:
- The lateral spinothalamic tract transmits pain and temperature.
- The anterior spinothalamic tract (or ventral spinothalamic tract) transmits crude touch and firm pressure.
The spinothalamic tract, like the dorsal column-medial lemniscus pathway, uses three neurons to convey sensory information from the periphery to conscious level at the cerebral cortex.
Pseudounipolar neurons in the dorsal root ganglion have axons that lead from the skin into the dorsal spinal cord where they ascend or descend one or two vertebral levels via Lissauer's tract and then synapse with secondary neurons in either the substantia gelatinosa of Rolando or the nucleus proprius. These secondary neurons are called tract cells.
The axons of the tract cells cross over (decussate) to the other side of the spinal cord via the anterior white commissure, and to the anterolateral corner of the spinal cord (hence the spinothalamic tract being part of the anterolateral system). Decussation usually occurs 1-2 spinal nerve segments above the point of entry. The axons travel up the length of the spinal cord into the brainstem, specifically the rostral ventromedial medulla.
Traveling up the brainstem, the tract moves dorsally. The neurons ultimately synapse with third-order neurons in several nuclei of the thalamus—including the medial dorsal, ventral posterior lateral, and ventral posterior medial nuclei. From there, signals go to the cingulate cortex, the primary somatosensory cortex, and insular cortex respectively.
Function
The types of sensory information transmitted via the spinothalamic tract are described as affective sensation. This means that the sensation is accompanied by a compulsion to act. For instance, an itch is accompanied by a need to scratch, and a painful stimulus makes us want to withdraw from the pain.
There are two sub-systems identified:
- Direct (for direct conscious appreciation of pain)
- Indirect (for affective and arousal impact of pain). Indirect projections include
- Spino-Reticulo-Thalamo-Cortical (part of the ascending reticular arousal system, aka ARAS)
- Spino-Mesencephalic-Limbic (for affective impact of pain).
Anterolateral system
In the nervous system, the anterolateral system is an ascending pathway that conveys pain,[1] temperature (protopathic sensation), and crude touch from the periphery to the brain. It comprises three main pathways:
| Name | Destination | Function |
| spinothalamic tract (lateral and anterior) | thalamus | important in the localization of painful or thermal stimuli |
| spinoreticular tract | reticular formation | causes alertness and arousal in response to painful stimuli |
| spinotectal tract | tectum | orients the eyes and head towards the stimuli |
Clinical significance
In contrast to the axons of second-order neurons in dorsal column-medial lemniscus pathway, the axons of second-order neurons in the spinothalamic tracts cross at every segmental level in the spinal cord. This fact aids in determining whether a lesion is in the brain or the spinal cord. With lesions in the brain stem or higher, deficits of pain perception, touch sensation, and proprioception are all contralateral to the lesion. With spinal cord lesions, however, the deficit in pain perception is contralateral to the lesion, whereas the other deficits are ipsilateral. See Brown-Séquard syndrome.
Unilateral lesions usually cause contralateral anaesthesia (loss of pain and temperature). Anaesthesia will normally begin 1-2 segments below the level of lesion, due to the sensory fibers being carried by dorsal-lateral tract of Lissauer up several levels upon entry into the spinal cord, and will affect all caudal body areas. This is clinically tested by using pin pricks.
See also
References
- ↑ "Chapter 25:Neural Mechanisms of Cardiac Pain: The Anterolateral System". Archived from the original on 2010-08-11. Retrieved 2009-11-26.