Inferior salivatory nucleus
| Inferior salivatory nucleus | |
|---|---|
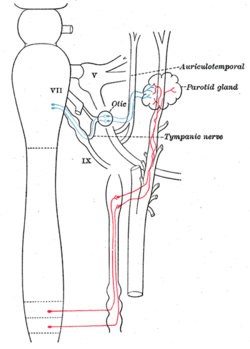 The inferior salivatory nucleus is one of the components of the glossopharyngeal nerve, which stimulates secretion from the parotid gland. | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | nucleus salivatorius inferior |
| NeuroNames | 764 |
| NeuroLex ID | birnlex_2645 |
| TA | A14.1.04.255 |
| FMA | 72601 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The inferior salivatory nucleus is a cluster of neurons in the pontine tegmentum (dorsal part of the pons), just above its junction with the medulla. It is the general visceral efferent (GVE) component of the glossopharyngeal nerve supplying the parasympathetic input to the parotid gland for salivation.
Structure
It is a small collection of nerve cells in the dorsal part of pons, just above its junction with the medulla. It lies immediately caudal to the superior salivatory nucleus and just above the upper end of the dorsal nucleus of the vagus nerve in the medulla.
The preganglionic parasympathetic fibres originate in the inferior salivatory nucleus of the glossopharyngeal nerve. They leave the glossopharngeal nerve by its tympanic branch and then pass via the tympanic plexus and the lesser petrosal nerve to the otic ganglion. Here, the fibres synapse, and the postganglionic fibers pass by communicating branches to the auriculotemporal nerve, which conveys them to the parotid gland. They produce vasodilator and secretomotor effects.
Function
Parasympathetic input from fibers of the inferior salivatory nucleus stimulates the parotid gland to produce vasodilation and secrete saliva.
See also
Additional images
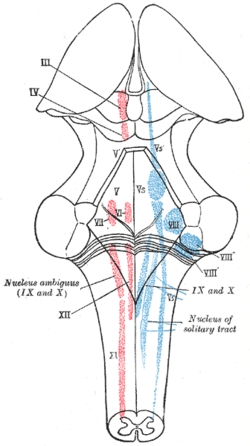 The cranial nerve nuclei schematically represented; dorsal view. Motor nuclei in red; sensory in blue.
The cranial nerve nuclei schematically represented; dorsal view. Motor nuclei in red; sensory in blue.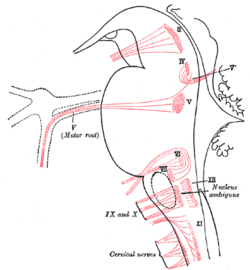 Nuclei of origin of cranial motor nerves schematically represented; lateral view.
Nuclei of origin of cranial motor nerves schematically represented; lateral view.
References
- Kiernan, John A. (2005). Barr's The Human Nervous System: An Anatomical Viewpoint. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 150. ISBN 0-7817-5154-3.