Hyderabad Metro
 | |||
 Hyderabad Metro Rail | |||
| Overview | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Native name | హైదరాబాద్ మెట్రో | ||
| Owner | Government of Telangana, L&T | ||
| Locale | Hyderabad, Telangana, India | ||
| Transit type | Rapid transit | ||
| Number of lines | 2 | ||
| Number of stations | 40 | ||
| Daily ridership | 180,000 [1] | ||
| Chief executive | N. V. S. Reddy[2] | ||
| Headquarters | Metro Bhawan, Begumpet, Hyderabad | ||
| Website | |||
| Operation | |||
| Began operation | 29 November 2017[3] | ||
| Operator(s) | Hyderabad Metro Rail Ltd. (HMRL) | ||
| Technical | |||
| System length | 46.5 km (28.9 mi) | ||
| No. of tracks | 2 | ||
| Track gauge | 1,435 mm (4 ft 8 1⁄2 in) standard gauge | ||
| Electrification | 25 kV, 50 Hz AC through overhead catenary | ||
| Average speed | 35 km/h (22 mph) | ||
| Top speed | 80 km/h (50 mph) | ||
| |||
The Hyderabad Metro is a rapid transit system, serving the city of Hyderabad, Telangana, India.[4] It is in Secant Operational model. It is being implemented entirely on public-private partnership (PPP) basis,[5] with the state government holding a minority equity stake.[6] A 30 km stretch from Miyapur to Nagole, having 24 stations was inaugurated on 28 November 2017 by Prime Minister Narendra Modi.[7][8] No other rapid transit metro service in India opened for public operations on such a long stretch of 30 km.[9][10] As of October 2018, it is the second longest operational metro network in India after the Delhi Metro,[11] after a 16 km stretch between Ameerpet-LB Nagar Metro route was opened on 24 September 2018.[12] It is estimated to cost ₹18,800 crore (US$2.6 billion). As of August 2018, about 160,000 people use the Metro per day[13]. Trains are moderately crowded during the morning and evening hours, when employees travel to and from work.[14]. A ladies only coach was introduced on all the trains from 7 May 2018[15].
History
To respond the rising public transport needs and mitigate escalating vehicular traffic in the twin-cities of Hyderabad and Secunderabad, the State Government and the South Central Railway jointly launched the Multi Modal Transport System (MMTS) in [August] 2003.[16] The increase in population of Hyderabad made MMTS alone insufficient for public transport, which led to Union Ministry of Urban Development giving the nod for the Hyderabad Metro Rail Project and directed the DMRC to conduct a survey on the project.[17] this project was seen necessary in view that the population of Hyderabad was forecasted to reach 13.6 million by the year 2021.[17] According to the initial plan, the metro was to be connected with the already existing MMTS to provide commuters with alternate modes of transport. Simultaneously, the proposals for taking up the construction of MMTS Phase-II were also taken forward.[18]
On March 26, 2018, Telangana Govt announced that it would set up a SPV "Hyderabad Airport Metro Limited (HAML)", jointly promoted by HMRL and HMDA, to extend the Blue line from Raidurg to Rajiv Gandhi International Airport, Shamshabad.
Initial bidding
The bidding process was completed by July 2008 and awarded to Maytas which failed to achieve financial closure for the project as per schedule By March 2009. In July 2009, the State Government cancelled the contract and called for fresh bids for the project.
Re-bidding
In the July-2010 rebidding process, Larsen & Toubro (L&T) emerged as the lowest bidder for the ₹121.32 billion (US$1.7 billion) project. L&T came forward to take up the work for about ₹14.58 billion (US$200 million) as viability gap funding as against the sanctioned ₹48.53 billion (US$680 million).
Construction history
Groundbreaking (Bhoomi Puja) for the project was conducted on 26 April 2012[19] the concessionaire started the pillar erection on the same day for Stage-I and on 6 June 2012 for Stage-II.[20] The work for Corridor 2 has been delayed due to traders in Koti and Sultan Bazar demanding realignment of the route to safeguard traders and old age heritage markets.[21] If the recent bill proposed in Parliament which allows construction within a 100 metre radius of heritage structures and sites of historical or archaeological importance is passed, Metro might receive a chance as it helps to connect the Old city with IT corridor.[22]
The construction of the entire 71.16 km has been split into 6 stages with the first stage originally scheduled to be completed by March 2015[23][24]
In November 2013, L&T Hyderabad Metro started laying of rails on the metro viaduct between Nagole and Mettuguda, a stretch of 8 km.[25]
The first highly sophisticated train of the Hyderabad Metro Rail (HMR) came from Korea during the third week of May 2014. Stringent trial runs commenced from June 2014 till February 2015.[26] The trial runs started on the Miyapur to Sanjeeva Reddy Nagar stretch in October 2015.
CMRS inspection for Stage-II (Miyapur and S.R.Nagar Section) was done on 9, 10 August 2016.[27] Three interchanges are planned at Mahatma Gandhi Bus Terminus, Parade Grounds and Ameerpet.[28]
The steel bridge of the HMR was successfully placed over the Oliphant bridge in August 2017.[29][30]
In November 2017, Commissioner of Railway Safety (CMRS) granted safety approval for 12 km stretch from Miyapur to SR Nagar, 10 km stretch from SR Nagar to Mettuguda and 8 km stretch from Nagole to Mettuguda.[31]
Ameerpet-LB Nagar Metro stretch is open for commercial operations from 24 September 2018.[14]
Construction phases
The construction work will be undertaken in two phases. There are six stages of completion in Phase I[32].
Phase I
The Phase I of the project includes 3 lines covering a distance of around 72 km. The metro rail stretches between Nagole and Secunderabad 11 km originally scheduled to be operational by December 2015, is now partially operational since 29 November 2017. The entire 72 km 57-station first phase is due to be completed by December 2019 with Hitech City - Raidurg line and MGBS - Falaknuma line is scheduled to be completed by December 2019.
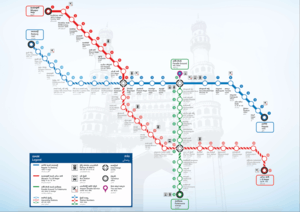
- Line 1 - Red Line - Miyapur – L B Nagar - 29.2 km (18.1 mi)
- Line 2 - Green Line - JBS - Falaknuma 15 km (9.3 mi)
- Line 3 - Blue Line - Nagole – Raidurg - 28 km (17 mi)
Construction schedule
| Stage | Target Section | Distance | Line | Line Colour | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stage 1 | Nagole–Mettuguda | 8.01 km (4.98 mi) | Line III | Blue | Operational |
| Stage 2 | Miyapur–Ameerpet | 11.9 km (7.4 mi) | Line I | Red | Operational |
| Stage 3 | Mettuguda–Ameerpet | 9.4 km (5.8 mi) | Line III | Blue | Operational |
| Stage 4/1 | Ameerpet–Hitec City | 9.43 km (5.86 mi) | Line III | Blue | Operational likely by December 31 2018 |
| Stage 4/2 | Hitec City–Raidurg | 1.3 km (0.81 mi) | Line III | Blue | Under Construction |
| Stage 5 | Ameerpet–LB Nagar | 17.31 km (10.76 mi) | Line I | Red | Operational |
| Stage 6/1 | JBS–MGBS | 9.66 km (6.00 mi) | Line II | Green | Under Construction |
| Stage 6/2 | MGBS–Falaknuma | 5.36 km (3.33 mi) | Line II | Green | Under Construction |
| Total | 72 km (45 mi) |
Note: Stage 6/2 MGBS - Falaknuma section (5.36 km) is also part of the initial phase - I stage 6, but has been rumored that the state government might take up this section instead of L&T, but will be completed along with the phase - I work. The Stage 4/2 Hitech City - Raidurg section (1.3 km) of Corridor III was not initial part of phase - I, it was later on added by the newly elected state government. This section is scheduled to open by end of 2019.
Phase II
The Government is planning second phase of metro rail extending further.[33] The construction of Phase II will be taken up solely by the state government, instead of public private partnership (PPP) mode in Phase I.[34] Delhi Metro Rail Corporation (DMRC) was entrusted to give a detailed project report (DPR) for Phase II.[35] Metro Rail Phase II expansion plan is for about 60 km, which includes providing link to Shamshabad RGI Airport.[36] The proposed routes are as following:
| Target Section | Distance (in km) | Line |
|---|---|---|
| Raidurg–Gachibowli –Shamshabad RGI Airport | 30 km (19 mi) | Line IV |
| Nagole–LB Nagar–Falaknuma–Shamshabad RGI Airport | 28 km (17 mi) | Line III extension |
| Miyapur– Gachibowli–Tolichowki–Lakdi ka pul | 20 km (12 mi) | Line V |
| Miyapur–BHEL-Patancheru | 15 km (9.3 mi) | Line I extension |
| LB Nagar–Hayath Nagar | 7 km (4.3 mi) | Line I extension |
| JBS–Alwal | 8 km (5.0 mi) | Line II extension |
| Tarnaka–ECIL 'X' Roads | 7 km (4.3 mi) | Line VI |
Mascot
The mascot of Hyderabad Metro Rail is Niz. It was derived from the word Nizam, who ruled the princely state of Hyderabad.[37]
Awards and nominations
HMR project was showcased as one of the top 100 strategic global infrastructure projects at the Global Infrastructure Leadership Forum held in New York during February–March 2013.[38] [39]
L&T Metro Rail Hyderabad Limited (LTMRHL) has been conferred the SAP ACE Award 2015 in the 'Strategic HR and Talent Management[40]' category.
Current status
| Line | First operational | Last extension | Stations | Length | Terminals | Rolling stock | Track gauge (mm) |
Power | Average Frequency (Minutes) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Red | 29 November 2017 | 24 September 2018 | 27 | 29.2 km (18.1 mi) | Miyapur | LB Nagar | 1435 | 25 kV OHE | 7.5 | |
| Green | 1435 | 25 kV OHE | ||||||||
| Blue | 29 November 2017 | 14 | 17.3 km (10.7 mi) | Ameerpet | Nagole | 1435 | 25 kV OHE | 7.5 | ||
| 41 | 46.5 km (28.9 mi) | |||||||||
Lines
Hyderabad Metro Phase I | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Red Line: Miyapur — LB Nagar [29.21 km] Green Line: JBS — Falaknuma [10.06 km] Blue Line: Nagole — Raidurg [29 km] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Since the first version of the plans, the three corridors mostly remained the same, but minor changes were introduced. These include the lack of stop at Lalaguda, or a stop at Lakdikapul instead of Secretariat. Also, the lines have been marked with several different combination of color.[41] Ameerpet-LB Nagar metro stretch is scheduled to open on 24 September 2018.[42] Hi-Tec City to Raidurg, 1.5-kilometre stretch on Corridor Three - Nagole to Shilparmamam/Raidurg, is scheduled to be completed in November 2019, as it involves construction of 49 pillars and the Raidurg terminal station. Efforts are being made to complete the 8.5-km stretch from Ameerpet to Hi-Tec City by June 2018.[43]
Red Line: Miyapur – L.B. Nagar
Route Length — 29.21 km (18.15 mi)
Number of Stations (All elevated) — 27
Link to other Corridors
- At Ameerpet – Connecting Corridors 1 and 3
- At Mahatma Gandhi Bus Station – Connecting Corridors 1 and 2
| # | Station Name | Telugu Name | Operational | Connections |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Miyapur | మియాపూర్ | Yes | None |
| 2 | J.N.T.U College | జె.ఎన్.టి.యూ కాలేజి | Yes | None |
| 3 | K.P.H.B. Colony | కె.పి.హెచ్.బి కాలనీ | Yes | None |
| 4 | Kukatpally | కూక్కట్పల్లి | Yes | None |
| 5 | Balanagar | బాలానగర్ | Yes | None |
| 6 | Moosapet | మూసాపేట్ | Yes | None |
| 7 | Bharatnagar | భరత్ నగర్ | Yes | None |
| 8 | Erragadda | ఎర్రగడ్డ | Yes | None |
| 9 | ESI Hospital | ఈ.ఎస్.ఐ ఆస్పత్రి | Yes | None |
| 10 | S.R Nagar | ఎస్.ఆర్. నగర్ | Yes | None |
| 11 | Ameerpet | అమీర్పేట్ | Yes | Blue Line |
| 12 | Punjagutta | పంజాగుట్ట | Yes | None |
| 13 | Erra Manzil | ఎర్రా మంజిల్ | Yes | None |
| 14 | Khairatabad | ఖైరతాబాద్ | Yes | None |
| 15 | Lakdi-ka-pul | లక్డి-కా-పుల్ | Yes | None |
| 16 | Assembly | అసెంబ్లీ | Yes | None |
| 17 | Nampally | నాంపల్లి | Yes | None |
| 18 | Gandhi Bhavan | గాంధీ భవన్ | Yes | None |
| 19 | Osmania Medical College | ఉస్మానియా వైద్య కళాశాల | Yes | None |
| 20 | MG Bus Station | ఎం.జి. బస్. స్టేషన్ | Yes | Green Line |
| 21 | Malakpet | మలక్పేట్ | Yes | None |
| 22 | New Market | కొత్త మార్కెట్ | Yes | None |
| 23 | Musarambagh | మూసారంబాగ్ | Yes | None |
| 24 | DilsukhNagar | దిల్సుఖ్నగర్ | Yes | None |
| 25 | Chaitanyapuri | ఛైతన్యపురి | Yes | None |
| 26 | Victoria Memorial | విక్టోరియా మెమోరియల్ | Yes | None |
| 27 | L.B. Nagar | ఎల్.బి. నగర్ | Yes | None |
Green Line: JBS – Falaknuma
Route Length — 15 km (9.3 mi)
Number of Stations (All elevated) — 14
Link to other Corridors
- At Parade Grounds – Connecting Corridors 2 and 3
- At Mahatma Gandhi Bus Station – Connecting Corridors 2 and 1
| # | Station Name | Telugu Name | Operational | Connections |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | JBS | జె.బి.ఎస్ | Pending | None |
| 2 | Parade Grounds | పెరేడ్ గ్రౌండ్స్ | Pending | Blue Line |
| 3 | Secunderabad West | సికింద్రాబాద్ పడమర | Pending | None |
| 4 | Gandhi Hospital | గాంధీ ఆస్పత్రి | Pending | None |
| 5 | Musheerabad | ముషీరాబాద్ | Pending | None |
| 6 | R.T.C. Cross Roads | ఆర్.టీ.సి. క్రాస్ రోడ్స్ | Pending | None |
| 7 | Chikkadpally | చిక్కడ్పల్లి | Pending | None |
| 8 | Narayanguda | నారాయణ్గూడ | Pending | None |
| 9 | Sultan Bazaar | సుల్తాన్ బజార్ | Pending | None |
| 10 | M.G. Bus Station | ఎం. జి. బస్ స్టేషన్ | Pending | Red Line |
| 11 | Salarjung Museum | సాలార్ జంగ్ మ్యూజియం | Pending | None |
| 12 | Charminar | చార్మినార్ | Pending | None |
| 13 | Shalibanda | శాలిబండ | Pending | None |
| 14 | Shamsherganj | శంశేర్గంజ్ | Pending | None |
| 15 | Falaknuma | ఫలక్నుమా | Pending | None |
Blue Line: Nagole - Raidurg[44]
Route Length — 27 km (17 mi)
Number of Stations (All elevated) — 23
Link to other Corridors
- At Ameerpet – Connecting Corridors 3 and 1
- At Parade Grounds – Connecting Corridors 3 and 2
| # | Station Name | Telugu Name | Operational | Connections |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Nagole | నాగోల్ | Yes | None |
| 2 | Uppal | ఉప్పల్ | Yes | None |
| 3 | Stadium | స్టేడియం | Yes | None |
| 4 | NGRI | ఎన్.జి.ఆర్.ఐ | Yes | None |
| 5 | Habsiguda | హబ్సీగూడ | Yes | None |
| 6 | Tarnaka | తార్నాక | Yes | None |
| 7 | Mettuguda | మెట్టుగూడ | Yes | None |
| 8 | Secunderabad East | సికింద్రాబాద్ తూర్పు | Yes | None |
| 9 | Parade Grounds | పెరేడ్ గ్రౌండ్స్ | Yes | Green Line |
| 10 | Paradise | ప్యారడైజ్ | Yes | None |
| 11 | Rasoolpura | రసూల్పుర | Yes | None |
| 12 | Prakash Nagar | ప్రకాశ్నగర్ | Yes | None |
| 13 | Begumpet | బేగంపేట్ | Yes | None |
| 14 | Ameerpet | అమీర్పేట్ | Yes | Red Line |
| 15 | MadhuraNagar | మధురానగర్ | Pending | None |
| 16 | Yousufguda | యూసఫ్గూడ | Pending | None |
| 17 | Jubilee Hills Road No. 5 | జూబ్లీ హిల్ల్స్ రోడ్డు నం: 5 | Pending | None |
| 18 | Jubilee Hills Checkpost | జూబ్లీ హిల్ల్స్ చెక్పోస్ట్ | Pending | None |
| 19 | Peddamma Temple | పెద్దమ్మ గుడి | Pending | None |
| 20 | Madhapur | మాదాపూర్ | Pending | None |
| 21 | Durgam Cheruvu | దుర్గం చెఱువు | Pending | None |
| 22 | Hitec City | హైటెక్ సిటీ మెట్రో స్టేషన్ | Pending | None |
| 23 | Cyber Gateway | సైబర్ గేట్వే | Pending | None |
| 24 | Raidurg | రాయదుర్గం | Pending | None |
Reception
The Metro has opened to overwhelming response, with over 200,000 people using it on Day 1.[45] On the first Sunday of operations, the Metro was used by 240,000 people.[46]. As of September 2018, the daily ridership was about 1,60,000[47].
Trains are initially being operated at a frequency of 6.5 minutes (between Miyapur-Ameerpet) and (between Ameerpet-Nagole),[48], though maximum achievable frequency is every 90 seconds. Similarly, three-car trains are being used currently, though it is planned to use six-car trains in the future.[49]
In December 2017, Hyderabad Metro Rail launched its mobile app, TSavaari.[50][51] Ola Cabs tied up its services with app.[52]
Cost
The initial official estimated cost of the 72 km long Metro project stood at ₹14,132 crore (US$2.0 billion). The Central Government decided to bear 10% of it, while L&T was to bear the remaining 90% of the cost.[53][54] The construction work which was supposed to commence on 3 March 2011 commenced in 2012. In March 2012, the cost of the project was revised upwards to ₹15,957 crore (US$2.2 billion).[55]. This has been further revised upwards to ₹18,800 crore (US$2.6 billion) (as of November 2017).[56]
Infrastructure
The 71.3 km standard-gauge network will feature ballastless track throughout and will be electrified at 25kV ac 50 Hz. An operations control centre and depot are constructed at Uppal. At some places, a flyover, underpass and metro has been constructed at the same place, as part of Strategic road development plan (SRDP).[57]
CBTC Technology
At the end of 2012, L&T Metro Rail awarded Thales a Rs 7.4bn ($US 134m) contract to provide CBTC and integrated telecommunications and supervision systems on all three lines. Thales will supply its SelTrac CBTC technology, and trains will initially run in automatic train operation mode with minimum headways of 90 seconds, although the system will support eventual migration to unattended train operation (UTO)[58].
Rolling stock
On 12 September 2012, Larsen and Toubro Metro Rail Hyderabad Ltd (LTMRHL) announced that it has awarded tender for supply of rolling stock to Hyundai Rotem.[59][60] The ₹18 billion (US$250 million) tender is for 57 trains consisting of 171 cars which will be delivered in phases at least 9 months before the commencement of each stage.[61][62] On 2 October 2013, LTMRHL unveiled its train car for Hyderabad Metro. A model coach which is half the size of the actual coach, was on public display at Necklace Road on the banks of Hussain Sagar in the heart of Hyderabad.[63] The trains will be 3.2m wide and 4m high.[64] There will be 4 doors on each side of each coach.[64]
On 10 April 2014, the first metro train for HMR rolled out of Hyundai Rotem factory at Changwon in South Korea and reached Hyderabad in May 2014.[65] On 31 December 2014, Hyderabad Metro Rail successfully conducted a training run in Automatic Train Operation (ATO) mode for the first time between Nagole and Mettuguda.[66]
Ticketing
The L&T Hyderabad project will have an automated ticketing system with features such as contactless smart card based ticketing, slim automatic gates, payment by cash and credit/debit card, passenger operated ticket vending machine and provision of common ticketing system. It will also have a provision of NFC-based technology to enable usage of mobile phones as fare media and high performance machine to avoid long queues.[67] Samsung Data Systems India, a subsidiary of South Korean firm Samsung, has been awarded the automatic fare collection system package for the L&T metro rail project. The package involves design, manufacture, supply, installation, testing and commissioning of the system.[67][68]
Official ticket prices were announced on 25 November 2017. The base fare is ₹10 for up to 2 km.
| Slab | Distance (km) | Metro Fare (₹) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 - 2 | 10 |
| 2 | 2 - 4 | 15 |
| 3 | 4 - 6 | 25 |
| 4 | 6 - 8 | 30 |
| 5 | 8 - 10 | 35 |
| 6 | 10 - 14 | 40 |
| 7 | 14 - 18 | 45 |
| 8 | 18 - 22 | 50 |
| 9 | 22 - 26 | 55 |
| 10 | > 26 | 60 |
Stations
Hyderabad metro will have 64 stations in phase I. They will be provided with amenities such as escalators and elevators to reach the stations, announcement boards, electronic display systems among others for passengers. Commercial will also be provided on stations. Hyderabad metro stations will also have service roads underneath them to provide last mile connectivity by allowing other public transportation systems use it for dropping/picking passengers right in front of the stations and ensure uninterrupted traffic. Currently the service lane works are currently on at Nagole and Uppal stations.[69] The signboards of Hyderabad Metro are displayed in Telugu, English, Hindi and Urdu at metro stations.[70]
Otis Elevator Company of United States won the contract to supply and maintain 670 elevators.[71]
In May 2018, L&T Metro Rail announced that it had signed a contract with Powergrid Corporation of India to install electric vehicle charging facilities at all metro stations beginning with Miyapur and Dr. B R Ambedkar Balanagar stations.[72] L&THMRL has setup free wifi access units for commuters at Miyapur, Ameerpet and Nagole metro stations, in association with ACT Fibernet, as part of a pilot project.[73]
See also
References
- ↑ "Hyderabad metro footfalls".
- ↑ "N. V. S. REDDY".
- ↑ "Hyderabad Metro rail flagged off today: See fares, timings, routes and other features". The Indian Express. 28 November 2017. Retrieved 28 November 2017.
- ↑ "Project Description". Archived from the original on 11 June 2012. Retrieved 19 June 2012.
- ↑ "How metro rail networks are spreading across India".
- ↑ "EPC vs PPP in metro rail". Projectsmonitor.com. 2 December 2007. Archived from the original on 2 December 2007. Retrieved 18 April 2013.
- ↑ "PM Modi inaugurates Hyderabad Metro Rail".
- ↑ "PM Narendra Modi flags off Hyderabad Metro".
- ↑ "SR Nagar-Mettuguda was missing link in 30-km Metro rail corridor".
- ↑ "Metro Rail to get lease of life in November".
- ↑ "Tryst with Metro history as 2nd longest corridor opens".
- ↑ "Hyderabad Metro chugs on Ameerpet-LB Nagar route".
- ↑ "Hyderabad Metro touches1 lakh ridership". Deccan Chronicle. 2018-08-18. Retrieved 2018-08-21.
- ↑ "Hyderabad Metro project delay by L&T pushes up cost by over 30 per cent". India Today. 26 November 2017.
- ↑ ""Ladies only" coach in Hyderabad metro rail". Deccan Chronicle. 2018-05-06. Retrieved 2018-06-10.
- ↑ "Advani flags off first MMTS train". The Hindu. Hyderabad. 10 August 2003. Retrieved 18 April 2015.
- 1 2 "Nod for metro rail project". The Hindu. Hyderabad. 27 October 2003. Retrieved 18 May 2015.
- ↑ "Rs 4,500-crore MMTS project report under way". Business Standard. Hyderabad. 15 February 2004. Retrieved 18 May 2015.
- ↑ "L&T performs Bhoomi Puja for Hyderabad metro". The Hindu. 26 April 2012.
- ↑ "L&T metro rail schedule on track". The Hindu. Chennai, India. 7 June 2012.
- ↑ "Metro Rail works picking up speed". The Deccan Chronicle. 31 August 2011. Archived from the original on 12 October 2012. Retrieved 31 August 2011.
- ↑ "Monument law amendment buoys Metro dream in Old City, but political will needed".
- ↑ "Hyderabad Metro Rail phase-I to be completed by 2014". NDTV.com. 21 January 2013. Retrieved 18 April 2013.
- ↑ Our Bureau. "Hyderabad Metro rail stage I to be flagged off by June 2014 - Business Line". Thehindubusinessline.com. Retrieved 18 April 2013.
- ↑ Kumar, V. Rishi (20 November 2013). "L&T Hyderabad Metro begins laying of rails". Retrieved 29 November 2017.
- ↑ Kumar, V.Rishi (7 November 2013). "L&T Hyderabad Metro phase I to be ready by March 2015". Retrieved 29 November 2017.
- ↑ "CMRS completes 1 day inspection for Hyderabad Metro Stage-II, Miyapur to S.R. Nagar". metrorailnews.info. Archived from the original on 15 September 2016.
- ↑ Kumar, S. Sandeep (5 February 2014). "MGBS land sought for Metro Rail interchange station". The Hindu. Chennai, India.
- ↑ "Hyderabad Metro ROB placed at Oliphant Bridge". telanganatoday.com.
- ↑ "Metro steel bridge crosses Oliphenta railway bridge". thehindu.com.
- ↑ "L&T Hyderabad Metro Rail gets safety approval".
- ↑ http://hmrl.telangana.gov.in/project-description.html
- ↑ "State to seek Japanese help for Phase II works of Metro Rail Project". 9 August 2017. Retrieved 9 August 2017.
- ↑ "Metro corridors to crisscross Hyderabad for airport link".
- ↑ "SPV formed to extend Metro from Raidurg to Hyderabad airport".
- ↑ "Metro line to RGIA under study".
- ↑ "Niz is Hyderabad Metro Rail's mascot". The Hindu. 12 September 2014. Retrieved 3 October 2016.
- ↑ "TheHindu.com Metro in best 100 global projects". www.thehindubusinessline.com.
- ↑ "DeccanChronicle.com metro-among-100-global-projects". metro-among-100-global-projects. Archived from the original on 17 December 2012.
- ↑ "L&T Metro Rail Hyd bags SAP award". 10 December 2015. Retrieved 29 November 2017 – via www.thehindu.com.
- ↑ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 11 January 2014. Retrieved 18 August 2013.
- ↑ "Telangana Governor To Flag Off New Metro Line On September 24".
- ↑ "Where's my Metro to cyber city, ask techies".
- ↑ "Metro rail line to Raidurg another two years away". The Hindu. Retrieved 29 November 2017.
- ↑ "Over 2 lakh passengers travel by Hyderabad metro rail on day 1". The Indian Express. 30 October 2017. Retrieved 30 November 2017.
- ↑ http://www.zeebiz.com/india/news-record-24-lakh-commuters-travel-by-hyderabad-metro-on-sunday-32847
- ↑ "LB Nagar- Ameerpet Metro in August: NVS Reddy". Siasat Daily. 2018-06-09. Retrieved 2018-06-10.
- ↑ https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/city/hyderabad/mania-peaks-2-1-lakh-riders-send-metro-in-tizzy/articleshow/61898886.cms
- ↑ http://www.thehindu.com/news/cities/Hyderabad/full-metro-service-from-launch-day/article19652407.ece
- ↑ "'TSavaari' app for Hyderabad metro rail passengers".
- ↑ "Hyderabad Metro Rail app update includes latest timings".
- ↑ "Ola integrates services with Hyderabad Metro Rail's TSavaari app".
- ↑ "Hyderabad Metro Rail Project will be completed by 2017: Andhra Pradesh government". NDTV.com. 8 August 2012. Retrieved 18 April 2013.
- ↑ "Hyd Metro Rail Project will be completed on schedule: AP govt, IBN Live News". Ibnlive.in.com. 8 August 2012. Retrieved 18 April 2013.
- ↑ "Metro rail cost overshoots estimates". The Times Of India. 8 March 2012.
- ↑ "Hyderabad Metro project delay by L&T pushes up cost by over 30 per cent". India Today. 26 November 2017.
- ↑ "Hyderabad: Women safety is key objective for metro".
- ↑ "L&T Hyderabad Metro awards contracts to Thales". thehindubusinessline.com. 16 November 2012. Retrieved 28 November 2017.
- ↑ "L&T Metro Rail grants Rs 1,800 cr contract to Hyundai Rotem". Zeenews.india.com. Retrieved 18 April 2013.
- ↑
- ↑ "Hyundai Rotem cars to run on metro tracks". The Times Of India. 12 September 2012. Retrieved 15 September 2012.
- ↑ "L&T awards rolling stock contract to Hyundai Rotem". Ibnlive.in.com. 14 September 2012. Retrieved 18 April 2013.
- ↑ "Larsen and Tourbo Hyderabad Metro unveils train car". Retrieved 29 November 2017.
- 1 2 "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 20 August 2013. Retrieved 23 October 2013.
- ↑ "First train for Hyderabad Metro rolls out of Korean factory". IANS. news.biharprabha.com. Retrieved 10 April 2014.
- ↑ "Metro rail goes on first automatic trial run". 31 December 2014. Retrieved 29 November 2017 – via www.thehindu.com.
- 1 2 Our Bureau (18 February 2013). "Samsung bags fare collection system contract for Hyderabad Metro | Business Line". Thehindubusinessline.com. Retrieved 28 September 2013.
- ↑ Udgirkar, Trushna. "Hyderabad Metro in ticketing deal with Samsung". mydigitalfc.com. Retrieved 28 September 2013.
- ↑ "Hyderabad Metro to get service lanes". 22 May 2015. Retrieved 29 November 2017.
- ↑ "No Language Wars Here, Hyderabad Metro to Use 4 Languages".
- ↑ Bureau, Our (14 April 2011). "Fare structure for Hyderabad metro notified". Retrieved 29 November 2017.
- ↑ "Hyderabad Metro stations to have electric vehicle charging points". The Economic Times. 19 May 2018. Retrieved 20 May 2018.
- ↑ "Watch videos with free Wi-Fi at Hyderabad metro".
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Hyderabad Metro Rail. |