Gresik Regency
| Gresik Regency Kabupaten Gresik | ||
|---|---|---|
| Regency | ||
|
Duduk Train Station | ||
| ||
| Motto(s): Gresik Berhias Iman | ||
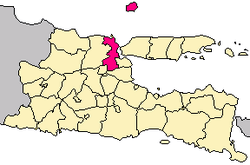 Location within East Java | ||
| Coordinates: 7°9′14″S 112°39′22″E / 7.15389°S 112.65611°ECoordinates: 7°9′14″S 112°39′22″E / 7.15389°S 112.65611°E | ||
| Country |
| |
| Province | East Java | |
| Capital | Gresik | |
| Government | ||
| • Regent | Sambari Halim Radianto | |
| • Vice Regent | Mohammad Qosim | |
| Area | ||
| • Total | 1,137.05 km2 (439.02 sq mi) | |
| Population (2010) | ||
| • Total | 1,177,201 | |
| • Density | 1,000/km2 (2,700/sq mi) | |
| Time zone | UTC+7 (IWST) | |
| Area code | (+62) 31 | |
| Website | www.gresikkab.go.id | |

Gresik Regency (older spelling Grissee) (Javanese:Nggersik) is a regency within East Java Province of Indonesia. It includes the offshore Bawean Island, some 125 km to the north of Java and Madura. The regency's administrative centre is the town of Gresik, about 25 km to the northwest of Surabaya; Gresik is also the capital of the sub-region of Gerbangkartasusilo, the metropolitan region of the city of Surabaya.
History


The port of Gresik-Djaratan has functioned as an important commercial center since the eleventh century, trading with merchants from as far away as China, India, and Arabia. Some of these traders helped spread Islam in the area. In 1487 Sunan Giri, also known as Sultan Ainul Yaqin, began to rule Gresik. In his 1515 book, Suma Oriental, the Portuguese apothecary and traveller Tomé Pires described Gresik as "the jewel of Java in trading ports".[1] Sunan Giri's descendants ruled the area for the following two centuries.
In 1974 the Indonesian government made Gresik, now a suburb of the regional capital of Surabaya, the capital of Gerbankartasusilo.
Administration
The Gresik Regency was divided at 2010 into eighteen kecamatan (district), tabulated below with their 2010 Census population.[2]
- Wringinanom (65,411)
- Driyorejo (120,149)
- Kedamean (66,715)
- Menganti (119,278)
- Cerme (69,217)
- Benjeng (57,336)
- Balongpanggang (49,035)
- Duduksampeyan (43,783)
- Kebomas (106,259)
- Gresik (76,594)
- Manyar (109,949)
- Bungah (57,689)
- Sidayu (40,650)
- Dukun (54,384)
- Panceng (39,535)
- Ujungpangkah (41,828)
- Sangkapura (45,755)
- Tambak (24,475)
Sangkapura and Tambak districts together constitute the island of Bawean, lying to the north of Madura but administratively a part of Gresik Regency.
Industry
A large number of industries have established themselves in Gresik, mainly supporting agriculture and agricultural machinery. A lot of home-based industry exists, making caps (songkoks), bags, etc.
One of the largest factories in Gresik are PT. Semen Gresik (Gresik Portland Cement) and PT Petrokimia Gresik. PT. Semen Gresik, the largest cement factory in Indonesia, supplies 41% of the Indonesian market. While PT Petrokimia Gresik, the most complete fertilizer producer in Indonesia, supplies 50% of national subsidized fertilizers.
21st-century Gresik
The city has a reputation for its many coffee shops, called warkop (from warung kopi). In 2002, Petrokimia Putra (owned by PT Petrokimia Gresik), a soccer club from Gresik, won their first national league title in Jakarta.
Climate
Gresik has 44-88% of humidity. The maximum humidity is 88% and the average humidity is 58%. The wind velocity of Gresik is within the range of 0–18 km/hour. The maximum wind velocity is 18 km/hour and the average is 12.6 km/hour. The temperature of this City is within the range of 23 °C-35 °C with the average temperature is 28.5 °C.
| Month | January | February | March | April | May | June | July | August | September | October | November | December |
| Max Temperature (°C) | 32 | 32 | 32 | 33 | 33 | 32 | 32 | 32 | 34 | 35 | 34 | 33 |
| Minimum Temperature (°C) | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 24 | 24 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
References
Further reading
- Turner, Peter (1997). Java (1st edition). Melbourne: Lonely Planet. p. 341. ISBN 0-86442-314-4.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Gresik Regency. |