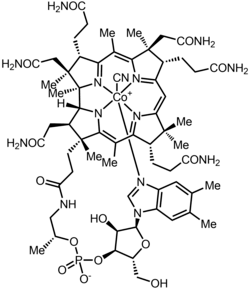
Cyanocobalamin
 | |
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.618 |
| EC Number | 200-680-0 V09XX01 (WHO) (57Co) V09XX02 (WHO) (58Co) |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C63H88CoN14O14P | |
| Molar mass | 1355.38 g/mol |
| Appearance | Dark red solid |
| Melting point | > 300 °C |
| Boiling point | > 300 °C |
| 1g/80ml | |
| Solubility | soluble in alcohol, insoluble in acetone and chloroform |
| Pharmacology | |
| B03BA01 (WHO) | |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | External MSDS from Fisher Scientific |
| GHS pictograms |  |
| GHS signal word | Warning |
| H315, H319 | |
| P264, P280, P302+352, P305+351+338, P321, P332+313, P337+313, P362 | |
| NFPA 704 | |
| Flash point | N/A |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Cyanocobalamin is a synthetic form of vitamin B
12. Vitamin B
12 is the "generic descriptor" name for any vitamers of vitamin B
12. Because humans and animals can convert cyanocobalamin to any one of the active vitamin B
12 compounds,[1] by definition this makes cyanocobalamin itself a form (or vitamer) of B
12.
Medical use
Cyanocobalamin is usually prescribed after surgical removal of part or all of the stomach or intestine to ensure adequate serum levels of vitamin B
12. It is also used to treat pernicious anemia, vitamin B
12 deficiency (due to low intake from food), thyrotoxicosis, hemorrhage, malignancy, liver disease and kidney disease. Cyanocobalamin injections are often prescribed to gastric bypass patients who have had part of their small intestine bypassed, making it difficult for B
12 to be acquired via food or vitamins. Cyanocobamide is also used to perform the Schilling test to check ability to absorb vitamin B
12.[2]
Side effects
Possible side effects of cyanocobalamin injection include allergic reactions such as hives, difficult breathing; redness of the face; swelling of the arms, hands, feet, ankles or lower legs; extreme thirst; and diarrhoea. Less-serious side effects may include headache, dizziness, leg pain, itching, or rash.[3]
Treatment of megaloblastic anemia with concurrent vitamin B
12 deficiency using B
12 vitamers (including cyanocobalamin), creates the possibility of hypokalemia due to increased erythropoiesis (red blood cell production) and consequent cellular uptake of potassium upon anemia resolution.[4] When treated with vitamin B
12, patients with Leber's disease may suffer serious optic atrophy, possibly leading to blindness.[5]
Chemistry
Cyanocobalamin is one of the most widely manufactured vitamers in the vitamin B
12 family (the family of chemicals that function as B
12 when put into the body), because cyanocobalamin is the most air-stable of the B
12 forms. It is the easiest to crystallize and therefore easiest to purify after it is produced by bacterial fermentation, or synthesized in vitro. It can be obtained as dark red crystals or as an amorphous red powder. Cyanocobalamin is hygroscopic in the anhydrous form, and sparingly soluble in water (1:80). It is stable to autoclaving for short periods at 121 °C (250 °F). The vitamin B
12 coenzymes are unstable in light. After consumption the cyanide ligand is replaced by other groups (adenosyl, methyl), which are the biologically active forms. The cyanide is converted to thiocyanate and excreted by the kidney..
Chemical reactions
In the cobalamins, cobalt normally exists in the trivalent state, Co(III). However, under reducing conditions, the cobalt center is reduced to Co(II) or even Co(I), which are usually denoted as B
12rand B
12s, for reduced and super reduced, respectively.
B
12r and B
12s can be prepared from cyanocobalamin by controlled potential reduction, or chemical reduction using sodium borohydride in alkaline solution, zinc in acetic acid, or by the action of thiols. Both B
12r and B
12sare stable indefinitely under oxygen-free conditions. B
12r appears orange-brown in solution, while B
12sappears bluish-green under natural daylight, and purple under artificial light.[6]
B
12sis one of the most nucleophilic species known in aqueous solution. This property allows the convenient preparation of cobalamin analogs with different substituents, via nucleophilic attack on alkyl halides and vinyl halides.[6]
For example, cyanocobalamin can be converted to its analog cobalamins via reduction to B
12s, followed by the addition of the corresponding alkyl halides, acyl halides, alkene or alkyne. Steric hindrance is the major limiting factor in the synthesis of the B
12 coenzyme analogs. For example, no reaction occurs between neopentyl chloride and B
12s, whereas the secondary alkyl halide analogs are too unstable to be isolated.[6] This effect may be due to the strong coordination between benzimidazole and the central cobalt atom, pulling it down into the plane of corrin ring. The trans effect determines the polarizability of the Co-C bond so formed. However, once the benzimidazole is detached from cobalt by quaternization with methyl iodide, it is replaced by H
2O or hydroxyl ions. Various secondary alkyl halides are then readily attacked by the modified B
12sto give the corresponding stable cobalamin analogs.[7] The products are usually extracted and purified by phenol-methylene chloride extraction or by column chromatography.[6]
Cobalamin analogs prepared by this method include the naturally occurring coenzymes methylcobalamin and cobamamide, and other cobalamins that do not occur naturally, such as vinylcobalamin, carboxymethylcobalamin and cyclohexylcobalamin.[6] This reaction is under review for use as a catalyst for chemical dehalogenation, organic reagent and photosensitized catalyst systems.[8]

Production
Cyanocobalamin is commercially prepared by bacterial fermentation. Fermentation by a variety of microorganisms yields a mixture of methyl-, hydroxo- and adenosylcobalamin. These compounds are converted to cyanocobalamin by addition of potassium cyanide in the presence of sodium nitrite and heat. Since multiple species of Propionibacterium produce no exotoxins or endotoxins and have been granted GRAS status (generally regarded as safe) by the United States Food and Drug Administration, they are the preferred bacterial fermentation organisms for vitamin B
12 production.[9]
Historically, a form of vitamin B
12 called hydroxocobalamin is often produced by bacteria and was then changed to cyanocobalamin during purification in activated charcoal columns after separation from the bacterial cultures. This change was not immediately realized when vitamin B
12 was first extracted for characterization. Cyanide is naturally present in activated charcoal. Hydroxocobalamin, which has affinity for cyanide, picks it up and changes to cyanocobalamin. Cyanocobalamin is the form in most pharmaceutical preparations because adding cyanide stabilizes the molecule.[10]
As of 2000 France accounted for 80% of the world's 10+ tonnes/year of production. 55% of sales is destined for animal feed, while the remaining 45% is for human consumption.[11]
Metabolism
The two bioactive forms of vitamin B
12r are methylcobalamin in cytosol and adenosylcobalamin in mitochondria. Multivitamins often contain cyanocobalamin, which is presumably converted to bioactive forms in the body. Both methylcobalamin and adenosylcobalamin are commercially available as supplement pills. The MMACHC gene product catalyzes the decyanation of cyanocobalamin as well as the dealkylation of alkylcobalamins including methylcobalamin and adenosylcobalamin.[12] This function has also been attributed to cobalamin reductases.[13] The MMACHC gene product and cobalamin reductases enable the interconversion of cyano- and alkylcobalamins.[14]
B12 cyanocobalamin is added to fortify[15] nutrition, including baby milk powder, breakfast cereals and energy drinks for humans, also animal feed for poultry, swine and fish. Vitamin B
12 becomes inactive due to Hydrogen cyanide and Nitric oxide in cigarette smoke. Vitamin B
12 also becomes inactive due to Nitrous oxide N
2O commonly known as laughing gas, used for anaesthesia and abused as a recreational drug.[16] Vitamin B
12 becomes inactive due to microwaving or other forms of heating.[17]
In the cytosol
Vitamin B
12 methylcobalamin and 5-methyltetrahydrofolate are needed by Methionine synthase in the Methionine cycle to transfer a methyl group from 5-methyltetrahydrofolate to homocysteine, thereby generating tetrahydrofolate (THF) and methionine, which is used to make SAMe. SAMe is the universal methyl donor and is used for DNA methylation and to make phospholipid membranes, choline, sphingomyelin and acetylcholine and other neurotransmitters.
In mitochondria
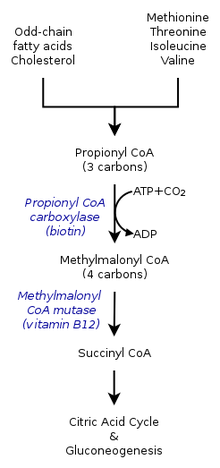
The enzymes that use B
12 as a built-in cofactor are methylmalonyl-CoA mutase (PDB 4REQ[18]) and methionine synthase (PDB 1Q8J).[19]
The metabolism of propionyl-CoA occurs in the mitochondria and requires Vitamin B
12 (as adenosylcobalamin) to make succinyl-CoA. When the conversion of propionyl-CoA to succinyl-CoA in the mitochondria fails due to Vitamin B
12 deficiency, elevated blood levels of methylmalonic acid (MMA) occur. Thus, elevated blood levels of homocysteine and MMA may both be indicators of Vitamin B
12 deficiency.
Vitamin B
12 adenosylcobalamin is needed as cofactor in methylmalonyl-CoA mutase—MUT enzyme. Processing of cholesterol and protein gives propionyl-CoA that is converted to methylmalonyl-CoA, which is used by MUT enzyme to make succinyl-CoA. Vitamin B
12 is needed to prevent anemia, since making porphyrin and heme in mitochondria for producing hemoglobin in red blood cells depends on succinyl-CoA made by vitamin B
12.
Absorption and transport
Poor absorption of vitamin B
12 may be related to coeliac disease. Intestinal absorption of vitamin B
12 requires successively three different protein molecules: haptocorrin, Intrinsic Factor and Transcobalamin II.
References
- ↑ Quadros, EV. "Advances in the Understanding of Cobalamin Assimilation and Metabolism". Br J Haematol. 2010 Jan; 148(2): 195–204.
- ↑ Cyanocobalamin. University of Maryland Medical Center
- ↑ "Cyanocobalamin Injection". MedlinePlus. Archived from the original on 19 April 2015. Retrieved 4 July 2015.
- ↑ "Clinical Vitamin B12 Deficiency. Managing Patients". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Archived from the original on 26 April 2015. Retrieved 4 July 2015.
- ↑ "Vitamin B12". MedlinePlus. Archived from the original on 5 April 2015. Retrieved 4 July 2015.
- 1 2 3 4 5 David Dophin. Preparation of the Reduced Forms of Vitamin B
12 and of Some Analogs of the Vitamin B
12 Coenzyme Containing a Cobalt-Carbon Bond. D.B. McCormick and L.D. Wright, Eds. 1971;Vol. XVIII:34-54. - ↑ Brodie, J. D. (1969). "On the mechanism of catalysis by vitamin B12". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 62 (2): 461–7. Bibcode:1969PNAS...62..461B. doi:10.1073/pnas.62.2.461. PMC 277821. PMID 5256224.
- ↑ Shimakoshi, Hisashi; Yoshio Hisaeda. "Environmental-friendly catalysts learned from Vitamin B
12-dependent enzymes" (PDF). TCIMAIL. 128: 2. - ↑ Riaz, Muhammad; Fouzia Iqbal; Muhammad Akram (2007). "Microbial production of vitamin B12 by methanol utilizing strain of Pseudomonas specie". Pak J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1. 40: 5–10.
- ↑ Herbert, V (1988). "Vitamin B-12: Plant sources, requirements, and assay". The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 48 (3 Suppl): 852–8. PMID 3046314.
- ↑ Eggersdorfer, Manfred; Adam, Geo; John, Michael; Hähnlein, Wolfgang; Labler, Ludvik; Baldenius, Kai-U.; et al. (2000). "Vitamins". doi:10.1002/14356007.a27_443.
- ↑ Hannibal, Luciana; Kim, Jihoe; Brasch, Nicola E.; Wang, Sihe; Rosenblatt, David S.; Banerjee, Ruma; Jacobsen, Donald W. (Aug 2009). "Processing of alkylcobalamins in mammalian cells: a role for the MMACHC (cblC) gene product". Mol Genet Metab. 97 (4): 260–266. doi:10.1016/j.ymgme.2009.04.005. PMC 2709701. PMID 19447654.
- ↑ Watanabe, F; Nakano, Y (1997). "Purification and characterization of aquacobalamin reductases from mammals". Methods Enzymol. 281: 295–305.
- ↑ Quadros EV, Jackson B, Hoffbrand AV, Linnell JC. "Interconversion of cobalamins in human lymphocytes in vitro and the influence of nitrous oxide on the synthesis of cobalamin coenzymes". Vitamin B12, Proceedings of the Third European Symposium on Vitamin B12 and Intrinsic Factor. 1979;1045-1054.
- ↑ "DSM in Food, Beverages & Dietary Supplements". DSM. Retrieved 2 March 2015.
- ↑ Thompson AG, Leite MI, Lunn MP, Bennett DL (2015). "Whippits, nitrous oxide and the dangers of legal highs". Pract Neurol. 15 (3): 207–9. doi:10.1136/practneurol-2014-001071. PMC 4453489. PMID 25977272.
- ↑ Watanabe F, Abe K, Fujita T, Goto M, Hiemori M, Nakano Y (1998). "Effects of Microwave Heating on the Loss of Vitamin B(12) in Foods". J. Agric. Food Chem. 46 (1): 206–210. doi:10.1021/jf970670x. PMID 10554220.
- ↑ F, Mancia,; P.R., Evans, (1 January 1998). "Conformational changes on substrate binding to methylmalonyl CoA mutase and new insights into the free radical mechanism". 6.
- ↑ J.C, Evans,; D.P, Huddler,; M.T, Hilgers,; G, Romanchuk,; R.G, Matthews,; M.L., Ludwig, (1 January 2004). "Structures of the N-terminal modules imply large domain motions during catalysis by methionine synthase". 101.
