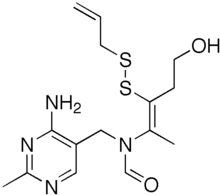
Allithiamine
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C15H22N4O2S2 |
| Molar mass | 354.49 g/mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Allithiamine (thiamine allyl disulfide or TAD) is a lipid-soluble form of vitamin B1 which was discovered in garlic (Allium sativum) in the 1950s along with its homolog prosultiamine.[1] They were both investigated for their ability to treat Wernicke–Korsakoff syndrome and beriberi better than thiamine.[2]
See also
References
- ↑ Fujiwara, Motonori; Watanabe, Hiroshi; Matsui, Kiyoo (1954). ""Allithiamine" A Newly Found Derivative of Vitamin B1". The Journal of Biochemistry. 41: 29. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a126421.
- ↑ Rogers, Edward F (1962). "Thiamine Antagonists". Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 98 (2): 412. Bibcode:1962NYASA..98..412R. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.1962.tb30563.x.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.