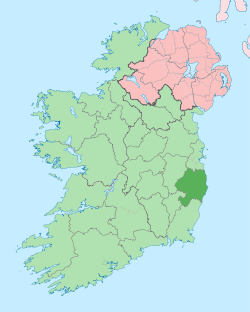
County Wicklow
| County Wicklow Contae Chill Mhantáin | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
|
Motto(s): Meanma Saor (Irish) "Free Spirits" | ||
 | ||
| Country | Ireland | |
| Province | Leinster | |
| Dáil Éireann | Wicklow | |
| EU Parliament | South | |
| County town | Wicklow | |
| Government | ||
| • Type | County Council | |
| Area | ||
| • Total | 2,027 km2 (783 sq mi) | |
| Area rank | 17th | |
| Population (2016)[1] | 142,332 | |
| • Rank | 16th | |
| Vehicle index mark code | WW | |
| Website |
www | |
County Wicklow (Irish: Contae Chill Mhantáin, [ˈkɔnˠt̪ˠeː ˈçɪl̪ʲ ˈwanˠt̪ˠaːnʲ]) is a county in Ireland. The last of the traditional 32 counties to be formed, as late as 1606, it is part of the Mid-East Region and is also located in the province of Leinster. It is named after the town of Wicklow, which derives from the Old Norse name Víkingaló, which means "Vikings' Meadow". Wicklow County Council is the local authority for the county. The population of the county is 142,332 according to the 2016 census.[1]
| Historical population | ||
|---|---|---|
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
| 1659 | 6,066 | — |
| 1821 | 110,767 | +1726.0% |
| 1831 | 121,557 | +9.7% |
| 1841 | 126,143 | +3.8% |
| 1851 | 98,979 | −21.5% |
| 1861 | 86,479 | −12.6% |
| 1871 | 78,697 | −9.0% |
| 1881 | 70,386 | −10.6% |
| 1891 | 62,136 | −11.7% |
| 1901 | 60,824 | −2.1% |
| 1911 | 60,711 | −0.2% |
| 1926 | 57,591 | −5.1% |
| 1936 | 58,569 | +1.7% |
| 1946 | 60,451 | +3.2% |
| 1951 | 62,590 | +3.5% |
| 1956 | 59,906 | −4.3% |
| 1961 | 58,473 | −2.4% |
| 1966 | 60,428 | +3.3% |
| 1971 | 66,295 | +9.7% |
| 1979 | 83,950 | +26.6% |
| 1981 | 87,449 | +4.2% |
| 1986 | 94,542 | +8.1% |
| 1991 | 97,265 | +2.9% |
| 1996 | 102,683 | +5.6% |
| 2002 | 114,676 | +11.7% |
| 2006 | 126,194 | +10.0% |
| 2011 | 136,640 | +8.3% |
| 2016 | 142,332 | +4.2% |
| [2][3][4][5][6][7][1] | ||
Wicklow is colloquially known as the Garden of Ireland.[8] It is the 17th-largest of Ireland's 32 counties by area, being thirty-three miles in length by twenty miles in breadth,[9] and 16th-largest by population.[10] It is the fourth-largest of Leinster's twelve counties by size and the fifth-largest in terms of population. Between 2011 and 2016 the population of the county grew by 4.2%.[1] The adjoining counties are Wexford to the south, Carlow to the southwest, Kildare to the west and Dublin to the north.
Demographics
| Main immigrant groups, 2016[11] | |
| Nationality | Population |
|---|---|
| 8,388 | |
| 2,759 | |
| 849 | |
| 767 | |
| 644 | |
| 624 | |
| 498 | |
| 458 | |
| 362 | |
| 336 | |
Towns and villages
| Rank | Municipal District | Settlement Population | Municipal District Population | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Bray | Bray Mun. District | 32,600 | 35,531 |
| 2. | Greystones | Greystones Mun. District | 18,140 | 26,323 |
| 3. | Arklow | Arklow Mun. District | 14,353 | 26,185 |
| 4. | Wicklow Town | Wicklow Mun. District | 10,584 | 28,219 |
| 5. | Blessington | Baltinglass Mun. District | 5,520 | 26,167 |
Total list of Settlements:
- Aghavannagh
- Annacurra
- Annamoe
- Arklow
- Ashford
- Aughrim
- Avoca
- Ballinaclash
- Ballinakil
- Ballycoogue
- Baltinglass
- Blessington
- Bray
- Brittas Bay
- Carnew
- Coolafancy
- Coolboy
- Coolkenno
- Delgany
- Donard
- Dunlavin
- Enniskerry
- Glencree
- Glendalough
- Glenealy
- Grangecon
- Greenan
- Greystones
- Hollywood
- Kilbride
- Kilcoole
- Killincarrig
- Kilmacanogue
- Kilpedder
- Kiltegan
- Knockananna
- Lacken
- Laragh
- Manor Kilbride
- Meeting of the Waters
- Newcastle
- Newtownmountkennedy
- Poulaphouca
- Rathnew
- Rathdrum
- Redcross
- Roundwood
- Shillelagh
- Stratford-on-Slaney
- Tinahely
- Valleymount
- Wicklow
- Woodenbridge
Physical geography
Geology
The Wicklow Mountains form the largest continuous upland region in Ireland. The highest mountain in the range, Lugnaquilla, rises to 925 metres (3,035 ft), giving Wicklow the second-highest county peak after Kerry.
Hydrodrology
The River Liffey, chief river of Dublin, rises in the county, and is a major source of water for Greater Dublin. The Liffey's leading tributary, the River Dodder, rises just across the border in southern County Dublin, and receives some minor flows from extreme northern Wicklow. The River Dargle runs to the Irish Sea at Bray. The River Avoca forms from the confluence of the Avonmore and Avonbeg at the Meeting of the Waters, before discharging into the Irish Sea at Arklow. The River Aughrim is a tributary of the Avoca. The River Slaney is in the western part of the county, bordering County Carlow. One of the smaller rivers of the county, the River Vartry is important to Dublin's water supply.
Lakes are small but numerous, located mainly in mountain valleys or glacial corries. They include Lough Dan, Lough Tay, Lough Brae, the lakes of Glendalough, and the Poulaphouca reservoir (the largest by volume).
Built environment
Wicklow is home to several major water supply and hydroelectric facilities. The Turlough Hill pumped-storage scheme, a significant civil engineering project, was carried out in the mountains in the 1960s and 1970s.
Leisure and tourism
Wicklow, often called "The Garden of Ireland" has been a popular tourist destination for many years, due to its scenery, beaches, walking, hiking and climbing options, and attractions including the ruins of the monastic city of Glendalough, Wicklow Gaol and water-based activities on reservoirs and the coast.
The Wicklow Way is the oldest waymarked long-distance walking trail in Ireland.
The popular annual mass participation bike ride Wicklow 200 has taken place in the county ever year since 1982.[12]
History

County Wicklow was the last of the traditional counties of Ireland to be shired in 1606 from land previously part of counties Dublin and Carlow. Established as a distinct county, it was aimed at controlling local groups such as the O'Byrnes. The Military Road, stretching from Rathfarnham to Aghavannagh crosses the mountains, north to south, was built by the British Army to assist them in defeating the rebels still active in the Wicklow Mountains following the failed 1798 rebellion.[13] It provided them with access to an area that had been a hotbed of Irish rebellion for centuries. Several barracks to house the soldiers were built along the route and the Glencree Centre for Peace and Reconciliation was built alongside the remains of barracks there. Battalions of the Irish Army use firing ranges in County Wicklow for tactical exercises, especially the largest one in the Glen of Imaal which was previously used by the British Army prior to independence.
The ancient monastery of Glendalough is located in County Wicklow. During the Cromwellian invasion of Ireland, local authorities immediately surrendered without a fight. During the 1798 rebellion, some of the insurgents took refuge in the Wicklow Mountains, resulting in clashes between British troops and the troops commanded by General Joseph Holt (1756–1826) near Aughrim and later at Arklow.
The boundaries of the county were extended in 1957 by the Local Government Act[14] which "detached lands from the County of Dublin and from the jurisdiction and powers of the Council of the County of Dublin" near Bray and added them to the County of Wicklow.
Local government and politics
The local government authority is Wicklow County Council which returns 32 councillors from five municipal districts (Arklow, Baltinglass, Bray, Greystones, Wicklow). All of the previous Town Councils (Arklow, Bray, Greystones, Wicklow) were abolished under a new Local Government Act at the 2014 Local Elections. For elections to Dáil Éireann, the entire county in included in the Wicklow constituency along with some eastern parts of County Carlow. The constituency returns five TDs to the Dáil.
Dáil Éireann deputies
| TD | Party | |
|---|---|---|
| Andrew Doyle | Fine Gael | |
| Simon Harris | Fine Gael | |
| John Brady | Sinn Féin | |
| Stephen Donnelly | Fianna Fáil | |
| Pat Casey | Fianna Fáil | |
County Council councillors
| Political Party | Members | |
|---|---|---|
| Fine Gael | 8 | |
| Fianna Fáil | 7 | |
| Sinn Féin | 6 | |
| Green Party | 1 | |
| Others | 10 | |
Culture
Mermaid, County Wicklow Arts Centre is based in Bray. Mermaid is the county's hub of artistic activity and creation, offering a programme in many art forms: visual arts, theatre productions, opera, dance performances, arthouse cinema, comedy and a music programme.[15] Two of the county's festivals take place in Arklow, the Arklow music Festival and the Arklow Seabreeze Festival.
The county is a popular film-making location in Ireland. Bray is home to Ardmore Studios, where many of Ireland's best known feature films, including Rawhead Rex John Boorman's Excalibur and Zardoz, Jim Sheridan's Oscar-winning In the Name of the Father, and several Neil Jordan films, have been shot. The BBC series Ballykissangel was also filmed in County Wicklow. Scenes from the movie P.S. I Love You were shot in the Wicklow Mountains National Park while several scenes from other movies, from Barry Lyndon to Haywire, have been filmed in the county.[16]
Media
- WicklowNews.net is a popular news website in the county and was established in 2010.
- The local radio station in Wicklow is East Coast FM.In 2010, Radio Nova became the second local radio service to be licensed for North Wicklow. The station broadcasts to Bray, Greystones, Kilmacanogue, Enniskerry and Blessington, in addition to Dublin, North Kildare and South Meath. It broadcasts to North Wicklow on 95.7 from Bray Head and 100.3 FM. Beat 102–103 also broadcasts in parts of South and West Wicklow towns and villages such as Arklow, Tinahely, Shiellagh, Baltinglass, Kiltegan and Carnew where the borders of Wexford and Carlow meet.
- Local newspapers include The Bray People, Wicklow Times and Wicklow People.
Twinning
County Wicklow is twinned with Würzburg, Germany and Seminole County, Florida, USA.[17]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 4 "Table B - Population of administrative counties, 2011 and 2016". 2016 Census Preliminary Results. Central Statistics Office. 2016. Retrieved 8 January 2017.
- ↑ For 1653 and 1659 figures from Civil Survey Census of those years, Paper of Mr Hardinge to Royal Irish Academy 14 March 1865.
- ↑ "Server Error 404 - CSO - Central Statistics Office". www.cso.ie. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
- ↑ http://www.histpop.org Archived 7 May 2016 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ Northern Ireland Census of Population | Census Home Page Archived 17 February 2012 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ Lee, JJ (1981). "Pre-famine". In Goldstrom, J. M.; Clarkson, L. A. Irish Population, Economy, and Society: Essays in Honour of the Late K. H. Connell. Oxford, England: Clarendon Press.
- ↑ Mokyr, Joel; O Grada, Cormac (November 1984). "New Developments in Irish Population History, 1700–1850". The Economic History Review. Volume. 37 (4): 473–488. doi:10.1111/j.1468-0289.1984.tb00344.x. hdl:10197/1406.
- ↑ "Index of /". www.gardenexhibition.ie. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
- ↑ Wright, G. N. (1822). A Guide to the County of Wicklow. London: Baldwin, Cradock, and Joy. p. v.
- ↑ Corry, Eoghan (2005). The GAA Book of Lists. Hodder Headline Ireland. pp. 186–191. ISBN 0-340-89695-7.
- ↑ "Population Usually Resident and Present in the State 2011 to 2016 by Sex, Aggregate Town or Rural Area, Birthplace, County of Usual Residence and CensusYear - StatBank - data and statistics". www.cso.ie. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
- ↑ Wicklow 200
- ↑ See Philip Smith (writer), An Introduction to the Architectural Heritage of County Wicklow. Dublin: Wordwell Press / Government of Ireland, Department of the Environment, Heritage, and Local Government, National Inventory of Architectural Heritage, 2004.
- ↑ (eISB), electronic Irish Statute Book. "electronic Irish Statute Book (eISB)". www.irishstatutebook.ie. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
- ↑ "Mermaid is a leading space for ideas, creativity, imagination and artistic expression". Mermaid Arts Centre. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
- ↑ "Film History". Wicklow Film Office - Wicklow Local Enterprise Office. 2018. Retrieved 24 July 2018.
- ↑ "Town Twinning". Wicklow County Council. 2017. Retrieved 22 January 2018.
External links
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for County Wicklow. |