California High-Speed Rail
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Overview | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Owner | California High-Speed Rail Authority | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Area served |
San Francisco Bay Area San Joaquin Valley Southern California | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Locale | California, United States | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Transit type | High-speed rail | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Number of stations | 24 (total proposed) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chief executive | Brian P. Kelly | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Website | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operation | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operator(s) | DB International USA | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Technical | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| System length |
c. 520 mi (840 km) (Phase 1) c. 800 mi (1,300 km) (proposed including Phase 2)[1] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| No. of tracks | 2 (4 in stations) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Track gauge | 4 ft 8 1⁄2 in (1,435 mm) standard gauge | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electrification | 25 kV 60 Hz AC overhead line[2][3] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Top speed |
220 mph (350 km/h) maximum 125 mph (201 km/h) San Francisco–San Jose[4] 90 mph (140 km/h) Los Angeles–Anaheim[5] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
California High-Speed Rail (abbreviated CAHSR or CHSR) is a high-speed rail system under construction in California in the United States. It is projected to connect the Anaheim Regional Transportation Intermodal Center in Anaheim and Union Station in Downtown Los Angeles with the Transbay Transit Center in San Francisco via the Central Valley, providing a one-seat ride between Union Station and San Francisco in 2 hours and 40 minutes. Future extensions are planned to connect to stations to San Diego County via the Inland Empire, and to Sacramento.
CAHSR plans to operate on dedicated, grade-separated tracks for the entirety of its route between San Jose and Burbank with speeds of up to 220 miles per hour (350 km/h), with early ridership projections for the San Francisco to Los Angeles leg at 28.4 million per year. The San Francisco–San Jose and Los Angeles–Anaheim sections will be shared with local trains in a "blended system". The project is owned and managed by the state of California through the California High-Speed Rail Authority (CHSRA).
The CAHSRA was established by an act of the California State Legislature and tasked with presenting a high-speed rail plan to the voters. This plan, Proposition 1A, was presented to and approved by voters in 2008 and included a $9-billion bond to begin construction on the initial leg of the network. Construction began in 2015 after a groundbreaking ceremony in Fresno. Completion of the initial operating segment between San Jose Diridon Station and Bakersfield is expected in 2027,[6] and the complete first phase between San Francisco and Anaheim is expected in 2033.[7] Phase 2 extensions to Sacramento and San Diego are still in the planning stages.
Route and stations
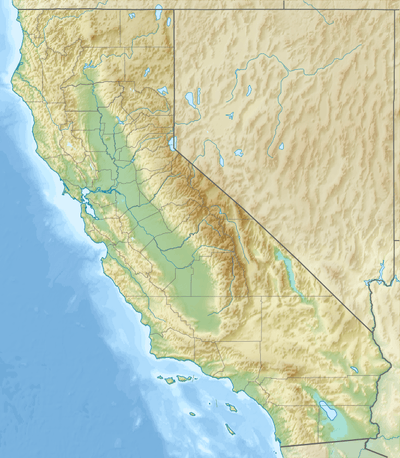
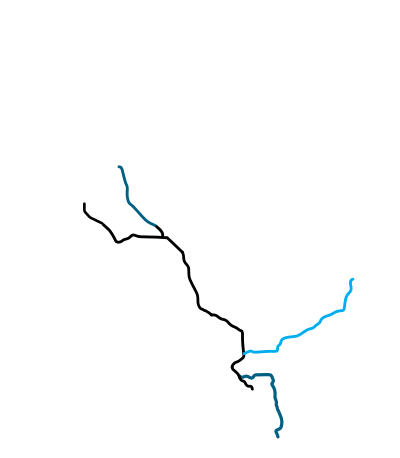
On August 13, 2008, California Assembly Bill 3034 (AB 3034) was approved by the state legislature and signed by Governor Arnold Schwarzenegger on August 26, 2008.[8] The bill was submitted to California voters in the November 2008 election as Proposition 1A and approved.[9] With the voter's mandate, AB 3034 specified certain route and travel time requirements. Among these were that the route must link downtown San Francisco with Los Angeles and Anaheim, and link the state's major population centers together "including Sacramento, the San Francisco Bay Area, the Central Valley, Los Angeles Basin, the Inland Empire, Orange County, and San Diego." The first phase of the project must link San Francisco with Los Angeles and Anaheim. Up to 24 stations were authorized for the completed system.[10]
This system is scheduled be built in two phases. Phase 1 will be approximately 520 miles (840 km) long, with completion expected in 2029. Phase 1 will connect the downtowns of San Francisco, Los Angeles, and Anaheim using high-speed rail through the Central Valley.[11] In Phase 2, the route will be extended north from the Central Valley to Sacramento, and east from Los Angeles through the Inland Empire and then south to San Diego. Upon completion the total system length will be approximately 800 miles (1,300 km).
On February 18, 2016, the Authority released its 2016 Draft Business Plan,[12] which significantly altered its near-term plans for the system implementation. While construction was always intended to begin in the Central Valley, the Initial Operating Section (IOS) has always had two options: extend from the Central Valley northward toward the Bay Area (the IOS-North, San Jose to Bakersfield), or southward to Southern California (IOS-South, Merced to San Fernando Valley). In the 2012 and 2014 Business Plans the goal was to implement the IOS-South, but a more recent analysis of the funding available and time necessary to bring an IOS online the rail authority proposes the IOS-North be implemented instead. The proposal, named the Silicon Valley to Central Valley Line, is expected that sufficient funding will be available to bring this segment online by 2025.[13] The rail authority state its commitment to pursue additional funding to complete the Phase 1 system by 2029.[13]
The new business plan also reduces the cost of the system from US$67.6 billion to US$64.2 billion for Phase 1; this includes a savings of US$5.5 billion based on actual experience, improved plans, and other feedback, but also an additional US$2.1 billion cost for improvements to the Los Angeles to Anaheim corridor.[14] The 2016 Business Plan estimates the cost to completion of the Silicon Valley to Central Valley line is US$20.6 billion.[15] The public had 60 days, from February 19, 2016, to submit comments on the Draft 2016 Business Plan to the rail authority. The plan was adopted by the rail authority in April 2016, and submitted by legal requirement to the California State Legislature on May 1, 2016.[13]
The Initial Construction Segment (ICS) of high-speed tracks runs from Merced to Bakersfield in the Central Valley. Simultaneously with the ICS construction, there are "bookend" and connectivity investments[16] including electrification of the San Francisco Peninsula Corridor used by Caltrain, improvements to tracks and signaling for both Metrolink in the LA area and Caltrain, and better passenger interconnections for Caltrain, Amtrak, and other Northern California rail lines.
Phase 1
All stations in this table represent proposed service. Station names in italics are optional stations that may not be constructed. In most cases existing stations will be re-purposed for high-speed rail service, with the exception of completely new stations at Merced, Fresno, Kings–Tulare, and Bakersfield.
Note: The California High-Speed Rail Authority considered a mid-peninsula station in Redwood City, Mountain View, or Palo Alto, but it was removed from the business plan in May 2016 due to low ridership projections, although the possibility was raised of adding one in the future.[20]
Phase 2
In 2015, the following stations and options were proposed. Existing train stations, if any, are linked. There is often a choice of alignments, some of which may involve the construction of a new station at a different location.
- Sacramento extension
The 110-mile (180 km) segment from Merced to Sacramento will be built on dedicated high-speed rail tracks and go to:
Proposals for San Jose–Oakland and Stockton–Union City lines have been studied, but are not in the Phase 2 plan which was adopted by voters statewide.
- San Diego extension
The 167-mile (269 km) segment from Los Angeles to San Diego will be built on dedicated high-speed rail tracks and may run to:[21]
- East San Gabriel Valley (El Monte, Covina, or Pomona)
- Montclair
- Rancho Cucamonga or Fontana
- San Bernardino (San Bernardino Transit Center, or the San Bernardino Santa Fe Depot)
- Riverside
- Corona
- Murrieta/Temecula
- Escondido Transit Center
- San Diego
History
Legislative
In 1996 the California High-Speed Rail Authority (CHSRA) was established to begin formal planning in preparation for a ballot measure in 1998 or 2000.[22][23] The CHSRA, a state agency run by a board of governors, is required by law to operate without a subsidy, and to connect the state's major cities in the Bay Area, Central Valley, and Los Angeles Basin. Phase 2 (which has no timetable yet) would extend the system northward through the Central Valley to the Sacramento Valley Station in Sacramento, and southward (through the Inland Empire) to the San Diego International Airport in San Diego.
In 2008, California voters approved the issuance of $9 billion in bonds for high speed rail in Proposition 1A,[24] a measure to construct the initial segment of the network.
On January 28, 2010, the White House announced that California would receive $2.25 billion for California High Speed Rail.[25] Over the course of 2010 and 2011, the federal government awarded the Authority a further $4 billion in high-speed rail funding.[26][27][28]
In June 2014 state legislators and Governor Jerry Brown agreed to apportion the state's annual cap-and-trade funds so that 25% goes to high speed rail.[29] The state's Legislative Analyst's Office estimated that cap-and-trade income in 2015 and 2016 could total $3.7 billion, of which $925 million would be allocated to HSR.[30] The LAO's predictions were proven incorrect in its own revised report dated May 26, 2016, "State auction revenue will be about $1.8 billion in 2015-16" due to a weak May 2016 auction.[31]
On September 30, 2015, the Authority posted the names of 30 large firms who were interested in financing, constructing, and operating the California HSR system. .[32]
Proposition 1A and other legislation set certain performance standards for the project:[33]
- Minimum 200 miles per hour (320 km/h) where conditions permit
- Maximum travel time between SF and LA not to exceed 2 hr 40 min
- Financially self-sustaining (operation and maintenance costs fully covered by revenue)
Legal
In 2014, the CHSRA was challenged on its compliance with its statutory obligations under Proposition 1A (John Tos, Aaron Fukuda, and the Kings County Board of Supervisors v. California High-Speed Rail Authority). The case was split into two parts. The ruling in the first was that the requirements for the financing plan, environmental clearances, and construction plans did not need to be secured for the entire project before construction began, but only for each construction segment. The second part considered three Proposition 1A legal requirements: (1) Can the train travel from Los Angeles (Union Station) to San Francisco (Transbay Terminal) in two hours and 40 minutes? (2) Will the train require an operational subsidy? (3) Does the new "blended system" approach meet the definition of high-speed rail in Proposition 1A? Judge Kenny ruled on March 8, 2016, that although serious issues were raised, they are not "ripe for review" and that (because this is "an ongoing, dynamic, changing project") he noted "the authority may be able to accomplish these objectives at some point in the future." This did not preclude the possibility of future legal action against the Authority on these issues.[34]
On December 15, 2014, the federal Surface Transportation Board determined (using well-understood preemption rules) that its approval of the HSR project in August "categorically preexempts" lawsuits filed under the California Environmental Quality Act (CEQA). This determination is still being tested in the California courts in a similar case, Friends of Eel River v. North Coast Railroad Authority.[35]
Construction
On December 2, 2010, the Authority Board of Directors voted to begin construction on the first section of the system from Madera to Fresno. Fresno hosted a groundbreaking ceremony on January 6, 2015, to mark the commencement of sustained construction activities.[36]
In July 2012, the California legislature and Gov. Jerry Brown approved construction of the high-speed system.[37][38]
Speed requirements
According to Proposition 1A, the train must be electric and capable of a sustained operating speed of no less than 200 miles per hour (320 km/h).[39] There are also a number of travel time benchmarks. The important benchmarks applicable to Phase 1 of the project are: (1) a maximum nonstop travel time between San Francisco and San Jose of 30 minutes, and (2) a maximum nonstop travel time between San Jose and Los Angeles of 2 hours and 10 minutes. (Thus, a nonstop time from San Francisco to Los Angeles in 2 hours and 40 minutes.) In addition, the time between successive trains must be less than 5 minutes.[39]
Maximum nonstop travel times for each corridor must not exceed the following times, according to Proposition 1A:[39]
- San Francisco - Los Angeles Union Station: 2 hours, 40 minutes
- Oakland - Los Angeles Union Station: 2 hours, 40 minutes
- San Francisco - San Jose: 30 minutes
- San Jose - Los Angeles: 2 hours, 10 minutes
- San Diego - Los Angeles: 1 hour, 20 minutes
- Inland Empire - Los Angeles: 30 minutes
- Sacramento - Los Angeles: 2 hours, 20 minutes
There have been some comments by critics (such as the Due Diligence Report (2008)) that the proposed system will not meet the Proposition 1A requirement of downtown San Francisco to Los Angeles travel time of 2 hours and 40 minutes.
The Authority's plan is close to the requirement, but does push the limits of conventional HSR speed.
- San Francisco to San Jose nonstop over the blended-system trackage at 102 miles per hour (164 km/h) for (51 miles (82 km)) = 30 min. (note 30 min. is the maximum allowed).
- San Jose to Los Angeles nonstop at 220 miles per hour (350 km/h) for (417 miles (671 km) or 437 miles (703 km)) = 1 hr. 54 min. or 1 hr. 59 min. (note 2 hr. 10 min. is the maximum allowed). Even at a slower 200 miles per hour (320 km/h) the times would be 2 hrs. 5 min. or 2 hrs. 11 min. (Note: since the final SF-LA route has not been adopted, the route length will be between the two numbers given.)
Both the Due Diligence Report (2008) and Updated Due Diligence Report (2013) state that no existing high-speed system currently meets the proposed operation speed and safety goals. It notes that the highest cruising HSR speed in the world on production runs is about 200 miles per hour (320 km/h) in France, and this is significantly less than the sustained speed of 220 miles per hour (350 km/h) the CHSRA plan requires. They also note safety concerns in running at top speed through highly populated urban areas such as Fresno.[40] For three years Chinese HSR trains ran at 217 miles per hour (349 km/h), but the speeds were reduced due to safety concerns and – mostly – costs.[41] In fact a Siemens Velaro trainset without any modifications has posted a speed record well in excess of 400 kilometres per hour (250 mph), though economic considerations keep them limited to 320 kilometres per hour (200 mph) in revenue service.
The current trainset specification requires the capability of sustained speeds of 220 miles per hour (350 km/h).[39] So, ultimately it is up to the trainset manufacturers to meet the Authority's speed requirement, since the proposed route and speed do meet the Proposition 1A requirements.
Rolling stock

Acquisition
In January 2015 the California High Speed Rail Authority issued an RFP (request for proposal) for rolling stock for complete trains (known as "trainsets"). The proposals received will be reviewed so that acceptable bidders can be selected, and then requests for bids will be sent out. The winning bidder will likely not be selected until 2016.
It is estimated that for the entire Phase 1 system up to 95 trainsets might be required.[42] Initially only 16 trainsets are anticipated to be purchased.[43] Trainset expenses, according to the 2014 Business Plan, are planned at $889 million for the IOS (Initial Operating Segment) in 2022, $984 million for the Bay to Basin in 2027, and $1.4 billion for the completed Phase 1 in 2029, for a total of $3.276 billion.[44]
The new rolling stock bidding has been changed.
In February 2015 nine companies formally expressed interest in producing trainsets for the system: Alstom, AnsaldoBreda (now Hitachi Rail Italy), Bombardier Transportation, CSR, Hyundai Rotem, Kawasaki Rail Car, Siemens, Sun Group U.S.A. partnered with CNR Tangshan, and Talgo.[45]
Specifications
In addition to many other requirements:[46]
- each trainset will have a sustained continuous speed of 220 miles per hour (350 km/h);
- a maximum testing speed of 242 miles per hour (389 km/h);
- a lifespan of at least 30 years;
- a length no longer than about 680 feet (210 m);
- the ability to operate two trainsets as a single "consist" (a long train);
- have control cabs at both ends of each trainset and the ability to go equally well in either direction;
- pass-by noise levels (82 feet (25 m) from track) not to exceed 88 dB at 155 miles per hour (249 km/h) and 96 dB at 220 miles per hour (350 km/h)
- have at least 450 seats and carry 8 bicycles;
- have seating for first class and business class passengers as well as have space for wheelchairs;
- have food service similar to airplane-style serving;
- allow for use of cellphones, broadband wireless internet access, and onboard entertainment services;
- have a train communications network to notify passengers of travel/train/station/time information;
- and also have earthquake safety systems for safe stopping and exiting.
One specification that is causing some difficulty is the HSR train requirement for a floor height of 50 in. (127 cm) above the rails. This is the international standard for high-speed rail trains, but Caltrain trains have a floor height of only 25 in. (63.5 cm). (Metrolink trains have a similar issue.) In October 2014 Caltrain and the Authority agreed to work together to try to implement "level-boarding" on the shared station platforms.[47] The Authority resisted lowering their trainset floor height,[48] but a solution was found with Caltrain's new EMUs which will feature doors at two heights, with the higher doors compatible with the CHSR platforms.[3]
An additional factor for the selection of a model is the Buy America regulation. The FRA has granted a waiver for just two prototypes to be manufactured off-shore before the remaining trainsets (initially 15 to 20 trains) would need to be built according to the rules.[49] These were mentioned as a significant reason that Chinese manufacturers dropped out of the XpressWest project with similar technical trainset specifications.[50]
Operations
In April 2017, the CHSRA announced it had received five responses to its request for qualifications for the contract to assist with the development and management of the initial phase of the high speed line and be the initial operator.[51][52]
- China HSR ETO Consortium: China Railway International, Beijing Railway Administration, China Railway Eryuan Engineering Group, China Railway Corporation
- DB International US: DB International USA, Deutsche Bahn, Alternate Concepts, HDR
- FS First Rail Group: Ferrovie dello Stato Italiane, FirstGroup, Trenitalia, Rete Ferroviaria Italiana, Centostazioni, Italferr, McKinsey & Company
- Renfe: Renfe Operadora, Globalvia Inversiones, Administrador de Infraestructuras Ferroviarias
- Stagecoach Group: Stagecoach Group, Coach USA
In October 2017 the DB International US consortium was announced as the winner.[53]
Economic projections
In addition to the direct reduction in travel times the HSR project will produce, there are other anticipated benefits, both general to the state, to the regions the train will pass through, and to the areas immediately around the train stations.
Statewide economic growth and job creation
In 2009, the Authority projected that construction of the system will create 450,000 permanent jobs through the new commuters that will use the system,[54] and that the Los Angeles-San Francisco route will generate a net operating revenue of $2.23 billion by 2023,[54] consistent with the experience of other high-speed intercity operations around the world.[55][56]The 2012 Economic Impact Analysis Report by Parson Brinkerhoff (project managers for the Authority) also indicated substantial economic benefits from high-speed rail.
Even Amtrak's high-speed Acela Express service generates an operating surplus that is used to cover operating expenses of other lines, Amtrak says.[57] Amtrak calculates this in a way which is not equivalent to the way that it determines the costs of other train services, and most of the Acela's costs for using track and fuel are paid for by Silver Service long distance trains, according to TRAINS Magazine's Fred Frailey.
The 2012 Business Plan also estimates that the Initial Construction Segment (ICS) construction will "generate 20,000 jobs over five years," with the Phase 1 system requiring 990,000 job-years over 15 years, averaging 66,000 annually.[58]
Environmental benefits
According to a fact sheet on the Authority website[59] the environmental benefits of the system include:
- In 2022, when the Initial Operating Section (Merced to the San Fernando Valley) is up and running, the resulting greenhouse gas reductions will be between 100,000 and 300,000 metric tons of carbon dioxide (CO2) in the first year. That’s the equivalent of from between 17,700 and 53,000 personal vehicles taken off the road.
- Between 2022 and 2040, the cumulative reduction of CO2 is estimated to be between 5 and 10 million metric tons. By 2040, the system is estimated to reduce vehicles miles of travel in the state by almost 10 million miles of travel every day (16,000,000 km).
- Over a 58-year period (from the start of operations in 2022 through 2080), the system is estimated to reduce auto travel on the state’s highways and roads by over 400 billion miles of travel (6.4×1011 km).
Regional benefits
In its 67-page ruling in May 2015, the federal Surface Transportation Board noted: "The current transportation system in the San Joaquin Valley region has not kept pace with the increase in population, economic activity, and tourism. ... The interstate highway system, commercial airports, and conventional passenger rail systems serving the intercity market are operating at or near capacity and would require large public investments for maintenance and expansion to meet existing demand and future growth over the next 25 years or beyond."[60] Thus, the Board sees the HSR system as providing valuable benefits to the region's transportation needs.
The San Joaquin Valley is also one of the poorest areas of the state. For example, the unemployment rate near the end of 2014 in Fresno County was 2.2% higher than the statewide average.[61] And, of the five poorest metro areas in the country, three are in the Central Valley.[62] The HSR system has the potential to significantly improve this region and its economy. A large January 2015 report to the CHSRA examined this issue.[63]
In addition to jobs and income levels in general, the presence of HSR is expected to benefit the growth in the cities around the HSR stations. It is anticipated that this will help increase population density in those cities and reduce "development sprawl" out into surrounding farmlands.[64]
Ridership and revenue concerns
In May 2015, the Los Angeles Times published an article by critics on the estimated operational revenue of the system in "Doing the math on California's bullet train fares".[65] The article raised a number of doubts that the system could be self-supporting, as required by Prop 1A, and ended by quoting Louis Thompson (chairman of an unnamed state-created review panel) who said "We will not know until late in the game how everything will turn out."[66]
The Due Diligence Report (2008) projected fewer riders by 2030 than officially estimated: 23.4 to 31.1 million intercity riders a year instead of the 65.5 to 96.5 million forecast by the Authority and later confirmed by an independent peer review.[67]
The Authority's ridership estimates initially were unrealistically high, and have been revised several times using progressively better estimating models, including risk analysis and confidence levels. The 2014 study (at a 50% confidence level) estimated the following ridership/revenue figures:
2022 (IOS): 11.3 million riders / $625 million
2027 (Bay to Basin): 19.1 million riders / $1055.6 million
2029 (Phase 1 initial): 28.4 million riders / $1350.4 million
2040 (Phase 1 mature): 33.1 million riders / $1559.4 million[68]
Project budget concerns
The project's cost and scope have long been a source of controversy. The Authority has estimated the project's year-of-expenditure cost at $68.4 billion (2012 estimate).[69]. In March 2018, the Authority revised its estimate to $77.3 billion and up to $98.1 billion, and pushed initial service to 2029, with L.A. to S.F. service in 2033.[70][71]
The Reason Foundation's Due Diligence Report (2008) projected that the final cost for the complete system (including both Phases I, II and an additional East Bay phase) would be $65.2 to $81.4 billion (2008). Current estimates from the Authority estimate a total cost for Phase 1 of $64.2 billion.[72] The Authority is using Design-Build construction contracts to counter the tendency toward cost over-runs. All of the construction is to be done via "design-build" proposals wherein each builder is given leeway in the design and management of construction, but not the ability to run back with contract change orders except for extraordinary problems. The builder is given specifications but also given the freedom to meet them in their own way, plus the ability to modify the construction plans in an expeditious and cost-effective manner.[73]
The California Legislative Analyst's Office published recommendations on May 10, 2011, which they said will help the high-speed rail project be developed successfully. They recommended that the California legislature seek flexibility on use of federal funds and then reconsider where construction of the high-speed rail line should start. They also recommended that the California legislature shift responsibility away from the Authority and fund only the administrative tasks of the Authority in the 2011–12 budget.[74]
In January 2012, an independent peer review panel published a report recommending the Legislature not approve issuing $2.7 billion in bonds to fund the project.[75] The panel of experts was created by state law to help safeguard the public's interest. The report said that moving ahead on the high-speed rail project without credible sources of adequate funding represents a financial risk to California.
Prior to the July 2012 vote, State Senator Joe Simitian, (D-Palo Alto), expressed concerns about financing needed to complete the project, asking: "Is there additional commitment of federal funds? There is not. Is there additional commitment of private funding? There is not. Is there a dedicated funding source that we can look to in the coming years? There is not."[76] The lobbying and advocacy group Train Riders Association of California also considers that Bill SB 1029 "provides no high-speed service for the next decade".[77]
In July 2014 The World Bank reported that the per kilometer cost of California's high-speed rail system was $56 million, more than double the average cost of $17–21 million per km of high speed rail in China and more than the $25–39 million per km average for similar projects in Europe.[78] It should be noted, though, that high real estate prices in California and three mountain ranges to cross contribute to the difference. For example, Construction Package 2-3 in the farmland of the flat Central Valley works out to $11.4 million per km, although this figure does not include electrification or property values, so it's roughly comparable internationally. Furthermore, the proposed High Speed 2 in Great Britain is estimated to be more expensive on a per mile basis than the Californian system.
As of May 2015, both construction packages awarded have come in significantly under staff estimates. For example, Construction Package 1 came in 20% under staff estimates ($985 million versus $1.2 billion),[79] and Construction Package 2-3 came in under by 17% to 28% ($1.234567 billion versus $1.5–2 billion).
In December 2016, an internal-use-only draft risk assessment produced by the Federal Railroad Administration was delivered to the California Rail Authority which warned that the ICS (Merced-Bakersfield) segment could cost as much as $9.5 billion instead of the $6.4 billion originally budgeted, if certain challenges weren't addressed, including delays in environmental planning, lags in processing invoices and failures to acquire needed property. Federal Railroad Administration spokesman Matthew Lehner said that the draft risk assessment "is a standard oversight tool used on major capital projects — not just California", and he is confident the state can meet its deadline with continued focus and hard work.[80] Concern over the article prompted the Authority to send a letter on January 13, 2017 to the Legislature that said that the characterization of cost overruns, delays, and potential lapses of funds are not borne out by the facts, and that other key federal findings were ignored.[81] After downplaying risks of cost overruns, in January 2018 the Authority acknowledged that cost estimates for the initial segment had increased to $10.6 billion. [82][83]
In 2018, it is estimated that the line will cost $77 billion.[84]
Public opinion and peer review
There are two types of criticism: the legally established "peer review" process that the legislature established for an independent check on the Authority's planning efforts,[85] and public criticisms by groups, individuals, public agencies, and elected officials.
As of the February 2015 conference Bold Bets: California on the Move?, which is hosted by The Atlantic magazine and Siemens, Dan Richard, the chair of the Authority, warned that not all issues to get the HSR system in place had yet been resolved.[86]
Peer Review Group
The California Legislature established the California High-Speed Rail Peer Review Group to provide independent analysis of the Authority's business plans and modeling efforts. Their documents are submitted to the Legislature as needed.
The most recent critiques are "Statement of Louis S. Thompson, Chairman, Peer Review Group, to California Assembly Transportation Committee Oversight Hearing", March 28, 2016, and "Comment on Revised 2016 Business Plan, April 25, 2016.
Key points in the 2016 business plan review include:
- The Group still believes the Southern IOS is superior, but recognizes that the Northern IOS is more financially feasible at this time with limited resources.
- Future funding sources are still uncertain for meeting projected needs, so there is a critical need for the Legislature to provide future guidance re financing sources and amounts.
- The lack of connection to downtown San Francisco and downtown Bakersfield will adversely affect ridership and income, especially in the initial startup period.
- To close these gaps, significant additional funding in the amount of $2.9 billion would be needed. The Authority is suggesting that Federal monies could be obtained for this, although this is very uncertain now.
- The blended system approach raises some significant issues that need resolution before it is feasible.
- There are some critical assumptions concerning construction costs, the ability to spend American Recovery and Reinvestment Act funding while it is still available, and the ability to securitize Cap and Trade funding for future use.
Professional studies
Two peer studies have been made of station siting and design in Europe.
Eric Eidlin, an employee of the Federal Transit Administration (Region 9, San Francisco), in 2015 wrote a study funded by the German Marshall Fund of the United States comparing the structural differences of the three relative to HSR and their historical development.[87] He also focused on the issue of station siting, design, use, and impact on the surrounding community. From this, he developed ten recommendations for CASHRA. Among these are:
- Develop bold, long-term visions for the HSR corridors and stations.
- Where possible site HSR stations in central city locations.
- In rural areas emphasize train speed, in urban areas emphasize transit connectivity.
- Plan for and encourage the non-transit roles of the HSR stations.
Eidlin's study also notes that in California there has been debate on the disadvantages of the proposed blended service in the urban areas of San Francisco and Los Angeles, including reduced speeds, more operating restraints, and complicated track-sharing agreements. There are some inherent advantages in blended systems that have not received much attention: shorter transfer distances for passengers, and reduced impacts on the neighborhoods. Blended systems are in use in Europe.[88]
A July 2015 study by A. Loukaitou-Sideris, D. Peters, and W. Wei of the Mineta Transportation Institute at San Jose State University compared the rail systems of Spain and Germany, and how blended high-speed rail lines have succeeded there.[89] Emphasis was also given to station siting, design, and use. Similarly to Eidlin's study, they found that the best stations not only provided high connectivity, but they also had a broader role by providing shops and services to community members as well as travelers.
Think tank studies
Reason Foundation, the Howard Jarvis Taxpayers Association, and the Citizens Against Government Waste published a study which they named the "Due Diligence Report" (2008) critiquing the project.[90] In 2013 Reason Foundation published an "Updated Due Diligence Report" (2013).[40] Key elements of the updated critique include:
- operating train speed higher than any existing HSR system
- unrealistic ridership projections
- increasing costs
- no clear funding plan
- incorrect assumptions regarding HSR alternatives
- increasing fare projections
This 2013 critique is based on the 2012 Business Plan. Although the 2012 Business Plan has been superseded by the 2016 Business Plan, the critique does include the Blended System approach using commuter tracks in SF and LA.
James Fallows in The Atlantic magazine summarized all the public criticisms thus, "It will cost too much, take too long, use up too much land, go to the wrong places, and in the end won't be fast or convenient enough to do that much good anyway."[66]
Public opinion surveys
The Public Policy Institute of California (PPIC) March 2016 Statewide Survey[91] indicated that 63% of Californians think the project is either very important or somewhat important, but costs are an issue. Currently over 50% favor building the system, but this increases to 66% if costs could be reduced. Note that the levels of support have generally been similar since the 2012 survey.
Support also varies by location (with the San Francisco Bay Area the highest at 72%, and lowest in Central Valley at 56%), by race (Asians 66%, Latinos 58%, whites 44%, and blacks 42%), and age (declining sharply with increasing age). Support also notably varies by political orientation. The percentage of supporters and opponents by party is: Democrat (supporters 59% v. opponents 38%), Independent (supporters 47% v. opponents 50%), and Republican (supporters 29% v. opponents 69%).
Dan Richard, chair of the Authority, says in an interview with James Fallows that he believes approval levels will increase when people can start seeing progress, and trains start running on the tracks.[86]
Related projects
XpressWest connection to Las Vegas
XpressWest is a company that since 2007 has been trying to build a high-speed rail line between Southern California and Las Vegas, Nevada, part of the "Southwest Rail Network" they hope to create. The rail line would begin in Las Vegas and cross the Mojave Desert stopping in Victorville, California and terminating in Palmdale, California (where it would connect with the CAHSR line and Metrolink). This route would total about 230 miles (370 km). Lisa Marie Alley, speaking for CAHSRA, said that there have been ongoing discussions concerning allowing the trains to use CAHSRA lines to go further into the Los Angeles area, although no commitments have been made as yet. While many approvals have been obtained for the rail line from Victorville to Las Vegas, the section from Palmdale to Victorville has none as yet.[92] In September 2018 Florida based railway company Brightline earlier known as "All Aboard Florida" purchased the rights and assets to the connection and plan to start construction subsequently.[93]
Alternative infrastructure proposals
Some have offered the idea that instead of risking the large expenditures of high-speed rail, existing transportation methods should be increased to meet transportation needs. In a report commissioned by the Authority, a comparison was made to the needed infrastructure improvements if high-speed rail were not constructed. According to the report, the cost of building equivalent capacity to the $68.4 billion (YOE) Phase 1 Blended plan, in airports and freeways, is estimated to be $119.0 billion (YOE) for 4,295 new lane-miles (6,912 km) of highway, plus $38.6 billion (YOE) for 115 new airport gates and 4 new runways, for a total estimated cost of $158 billion.[94]
"Hyperloop" is an alternative system that Elon Musk has championed. He has criticized the high-speed rail project as too expensive and not technologically advanced enough (trains that are—according to Musk—too slow). On August 12, 2013 he released a high-level alpha design for a Hyperloop transit system concept which he claimed would travel over three times as fast and cost less than a tenth of the rail proposal.[95][96] The following day he announced a plan to construct a demonstration of the concept.[97] Musk's claims have been subject to significant debate and criticism, in particular that the costs are still unknown and likely understated, the technology is not proven enough for statewide implementation, the route proposed doesn't meet the needs of providing statewide transportation, and it does not meet the legal requirements of Proposition 1A and so would require a whole new legal underpinning.[98] A flaw of the hyperloop is that it can carry far fewer passengers per trip compared to HSR.
Further reading
- CHSRA's 2018 Business Plan describes the latest project goals, financing, and development plans. (SB 1029 (enacted in 2012) requires the Authority to produce a revised business plan every two years.[38])
- CHSRA's March 2017 Project Update details the current status of the project. (SB 1029 also requires that twice a year, on March 1 and November 15, the Authority provide a project status report.)
- James Fallows in The Atlantic magazine wrote a series of 17 articles (from July 2014 to January 2015) about the HSR system which covers many aspects of the system, criticisms of it, and responses to those criticisms.
- The "Bold Bets: California on the Move?" conference was hosted February 2015 by The Atlantic magazine and Siemens. There were some significant discussions, presentations, and interviews. Dan Richard, chair of the Authority, was interviewed by James Fallows.[86]
Footnotes
- ↑ California High-Speed Rail Authority. "Implementation Plan" (PDF). pp. 23, 25. Archived from the original (PDF) on September 10, 2008. Retrieved July 17, 2008.
- ↑ "TECHNICAL MEMORANDUM: Traction Power 2x25kV Autotransformer Feed Type Electrification System & System Voltages" (PDF). HSR.CA.gov. CHSRA. Retrieved 3 November 2016.
- 1 2 "KISS Double-Decker Electric Multiple Unit EMU for Peninsula Corridor Joint Powers Board (CALTRAIN), California, USA" (PDF). Retrieved 16 October 2016.
- ↑ "Project Vision and Scope". California High-Speed Rail Authority. 2008. Archived from the original on November 26, 2011. Retrieved November 26, 2011.
- ↑ "ES.0 Executive Summary: ES.1 Supplemental Alternatives Analysis Report Results" (PDF). Hsr.ca.gov. Retrieved January 14, 2016.
- ↑ "Draft 2018 Business Plan" (PDF). California High-Speed Rail Authority. Retrieved 21 April 2018.
- ↑ Adam Nagourney (30 July 2018). "A $100 Billion Train: The Future of California or a Boondoggle?". The New York Times. Retrieved 30 July 2018.
The 800-mile line from Los Angeles to San Francisco is scheduled for completion by 2033.
- ↑ "AB-3034 Safe, Reliable High-Speed Passenger Train Bond Act for the 21st Century. (2007-2008) - History". California State Assembly. 2008. Retrieved 16 September 2018.
- ↑ "Statement of Vote - November 4, 2008 General Election" (PDF). California Secretary of State. 2008. p. 9. Archived from the original (PDF) on 15 November 2012. Retrieved 16 September 2018.
- ↑ "AB-3034 Safe, Reliable High-Speed Passenger Train Bond Act for the 21st Century. (2007-2008) - Text". California State Assembly. 2008. Retrieved 16 September 2018.
- ↑ "2012 Business Plan | Business Plans | California High-Speed Rail Authority". Hsr.ca.gov. Retrieved January 14, 2016.
- ↑ "2016 Draft Business Plan" (PDF). California High Speed Rail Authority.
- 1 2 3 "CHSRA Draft Business Plan 2016" (PDF). CHRSA. Retrieved 2 August 2017.
- ↑ Draft 2016 Business Plan, pp. 28, 55.
- ↑ Draft 2016 Business Plan, p. 57.
- ↑ "Statewide Rail Modernization | Programs | California High-Speed Rail Authority". Hsr.ca.gov. Retrieved January 14, 2016.
- ↑ "Caltrain/California HSR Blended Operations Analysis" (PDF). Caltrain.com. LTK Engineering Services. Retrieved 13 November 2016.
- ↑ Cruickshank, Robert (April 21, 2016). "CHSRA Proposes Revisions to 2016 Business Plan". California High Speed Rail Blog. Retrieved April 24, 2016.
- ↑ "Dodger Stadium Express". www.metro.net. Retrieved October 4, 2018.
- ↑ Noack, Mark (May 6, 2016). "High-speed rail team makes whistle stop in MV". Mountain View Voice. Retrieved May 10, 2016.
- ↑ "Los Angeles to San Diego Section" (PDF). California High Speed Rail. Retrieved 31 July 2017.
- ↑ "SB 1420 Senate Bill – Chaptered". ca.gov. Retrieved January 14, 2016.
- ↑ "California High Speed Rail Authority". Hsr.ca.gov. Retrieved January 14, 2016.
- ↑ "California Proposition 1A, High-Speed Rail Act (2008)". ballotpedia.org. Retrieved January 14, 2016.
- ↑ "Fact Sheet: High Speed Intercity Passenger Rail Program: California" (Press release). The White House. January 27, 2010. Archived from the original on February 28, 2011. Retrieved March 1, 2011.
- ↑ "California High-Speed Rail Awarded $715 Million" (Press release). California High-Speed Rail Authority. October 28, 2010. Archived from the original on November 3, 2010. Retrieved November 17, 2010.
- ↑ "U.S. Department of Transportation Redirects $1.195 Billion in High-Speed Rail Funds" (Press release). U.S. Department of Transportation. December 9, 2010. Archived from the original on December 11, 2010. Retrieved December 10, 2010.
- ↑ "U.S. Transportation Secretary LaHood Announces $2 Billion for High-Speed Intercity Rail Projects to Grow Jobs, Boost U.S. Manufacturing and Transform Travel in America" (Press release). U.S. Department of Transportation. May 9, 2011. Archived from the original on October 17, 2011. Retrieved November 26, 2011.
- ↑ "Cap-and-Trade Revenue: Likely Much Higher Than Governor's Budget Assumes". ca.gov. Retrieved January 14, 2016.
- ↑ "Capitol Alert". The Sacramento Bee. Archived from the original on March 4, 2016. Retrieved January 14, 2016.
- ↑ "May 2016 Cap-and-Trade Auction Update". www.lao.ca.gov. Retrieved 2018-01-09.
- ↑ "HSR 15-02 Request for Expressions of Interest for Delivery of an Initial Operating Segment" (PDF). Hsr.ca.gov. Retrieved January 14, 2016.
- ↑ "AB 3034". State of California. Retrieved 2 August 2017.
- ↑ "California High-Speed Rail Project Chugs Ahead". Courthousenews.com. Retrieved April 29, 2016.
- ↑ Sheehan, Tim (June 2, 2015). "Farm Bureaus jump into Supreme Court high-speed rail case". The Fresno Bee.
- ↑ "High-Speed Rail Authority Hosts Official Groundbreaking Ceremony" (PDF). California High-Speed Rail Authority. January 6, 2015.
- ↑ Michael Martinez (July 19, 2012). "Governor signs law to make California home to nation's first truly high-speed rail". CNN. Retrieved September 3, 2012.
- 1 2 "Office of Governor Edmund G. Brown Jr". ca.gov. Retrieved January 14, 2016.
- 1 2 3 4 "Official Voter Information Guide - Proposition 1A" (PDF). California State Legislature. 2008. Retrieved 2018-03-22.
- 1 2 "An Updated Due Diligence Report" (PDF). Hsr.ca.gov. Retrieved January 14, 2016.
- ↑ "World's longest high-speed train to decelerate a bit". People's Daily Online. April 15, 2011.
- ↑ "California High Speed Rail Blog » HSR Trainset Bids Could Create New Domestic Industry". Cahsrblog.com. February 23, 2015. Retrieved January 14, 2016.
- ↑ Respaut, Robin (May 21, 2015). "China may have edge in race to build California's bullet train". News.yahoo.com. Retrieved January 14, 2016.
- ↑ "Connecting California : 2014 Business Plan" (PDF). Hsr.ca.gov. Retrieved January 14, 2016.
- ↑ "Expressions of Interest Received : HSR 14-30: Request for Expressions of Interest for Tier III Trainsets" (PDF). Hsr.ca.gov. Retrieved 4 October 2018.
- ↑ "Aft schedule 1part a: authority tier iii trainsets performance specification" (PDF). Hsr.ca.gov. Retrieved January 14, 2016.
- ↑ Cruickshank, Robert (October 7, 2014). "Caltrain and CHSRA To Work Together for Level Boarding". California High Speed Rail Blog.
- ↑ Boone, Andrew (May 19, 2015). "Design of High-Speed Trains Threatens to Diminish Caltrain Capacity". Streetsblog San Francisco.
- ↑ "In California's high-speed train efforts, worldwide manufacturers jockey for position". The Fresno Bee. December 27, 2014. Retrieved February 18, 2015.
- ↑ "XpressWest, seeking to build U.S. high-speed rail, ends deal with China group". Reuters.com. June 9, 2016.
- ↑ Operators from five countries interested in California high speed rail contract Railway Gazette International April 6, 2017
- ↑ International consortia bid to become California high speed rail early operator Global Rail News April 6, 2017
- ↑ DB consortium selected for California high speed rail consultancy contract Railway Gazette International October 9, 2017
- 1 2 California High-Speed Rail Authority (December 14, 2009). "December 2009 Business Plan Report to the Legislature" (PDF). pp. 109–10. Archived from the original (PDF) on November 8, 2011. Retrieved June 24, 2011
- ↑ Druce, Paul (June 6, 2011). "High speed rail operational surplus". Reason & Rail. Retrieved November 26, 2011.
- ↑ Murakami, Jin; Cervero, Robert (2017). "High-speed rail and economic development: business agglomerations and policy implications". High-Speed Rail and Sustainability: Decision-making and the Political Economy of Investment. New York: Routledge, B. Henriguez and E. Deakin, eds.
- ↑ Yarow, Jay. "Amtrak Loses $32 Per Passenger". Business Insider.
- ↑ "California High Speed Rail Authority" (PDF). ca.gov. Archived from the original (PDF) on December 3, 2012. Retrieved January 14, 2016.
- ↑ "Environmental Report : October 2013" (PDF). Hsr.ca.gov. Retrieved January 14, 2016.
- ↑ Juliet Williams (June 14, 2013). "Key green light for California high-speed rail". Bakersfield.com. Associated Press. Retrieved January 14, 2016.
- ↑ "California High Speed Rail Blog » HSR: A Pathway Out of Poverty". Cahsrblog.com. December 17, 2014. Retrieved January 14, 2016.
- ↑ "California High Speed Rail Blog » The End of the Beginning". Cahsrblog.com. January 6, 2015. Retrieved January 14, 2016.
- ↑ "California High-Speed Rail and the Central Valley Economy : January 2015" (PDF). Hsr.ca.gov. Retrieved January 14, 2016.
- ↑ "High-speed rail and infill: A great marriage for California". sacbee. Retrieved January 14, 2016.
- ↑ Vartabedian, Ralph; Weikel, Dan (May 10, 2015). "Doing the math on California's bullet train fares". Los Angeles Times.
- 1 2 Fallows, James (July 11, 2014). "California High-Speed Rail—the Critics' Case". The Atlantic.
- ↑ "Final Report: Independent Peer Review of the California High-Speed Rail Ridership and Revenue Forecasting Process" (PDF). August 1, 2011. Archived from the original (PDF) on November 9, 2011.
We are satisfied with the documentation presented in Cambridge Systematics, and conclude that it demonstrates that the model produces results that are reasonable and within expected ranges for the current environmental planning and Business Plan applications of the model. We were very pleased with the content, quality and quantity of the information.
- ↑ "California High-Speed Rail 2014 Business Plan" (PDF). Hsr.ca.gov. Retrieved January 14, 2016.
- ↑ "Revised 2012 Business Plan" (PDF). Hsr.ca.gov. Retrieved January 14, 2016.
- ↑ RALPH VARTABEDIAN (9 March 2018). "Cost for California bullet train system rises to $77.3 billion". Los Angeles Times. Retrieved 10 March 2018.
- ↑ CNBC. "Transportation". CNBC. Retrieved October 4, 2018.
- ↑ "2016 Draft Business Plan" (PDF). California High Speed Rail Authority.
- ↑ Fallows, James (December 13, 2014). "That Winning Bid for California's High-Speed Rail: Is It Suspiciously Low?". The Atlantic.
- ↑ "High-Speed Rail Is at a Critical Juncture". California Legislative Analyst's Office.
- ↑ Buchanan, Wyatt (January 4, 2012). "High-speed rail shouldn't be funded, report says". The San Francisco Chronicle. Retrieved January 4, 2012
- ↑ Judy Lin (July 6, 2012). "California High Speed Rail Funding Approved". The Huffington Post. Retrieved September 3, 2012.
- ↑ Tolmach, Richard F. (August 2012). "High Speed Bait and Switch: $8 billion bill to produce zero miles of HSR". California Rail News. 24 (2). Sacramento, CA: TRAC. p. 1.
- ↑ Press release (July 10, 2014). "Cost of High Speed Rail in China One Third Lower than in Other Countries". The World Bank.
- ↑ Cruickshank, Robert (April 13, 2015). "CHSRA Selects Tutor Perini-Zachry-Parsons Bid for Central Valley Section". California High Speed Rail Blog.
- ↑ California's bullet train is hurtling toward a multibillion-dollar overrun, a confidential federal report warns; Los Angeles Times; Ralph Vartabedian; January 13, 2017
- ↑ "Letter to Legislature" (PDF). Hsr.ca.gov. Retrieved 4 October 2018.
- ↑ Vartabedian, Ralph. "California bullet train cost surges by $2.8 billion: 'Worst-case scenario has happened'". Los Angeles Times. Retrieved 22 January 2018.
- ↑ TIM SHEEHAN. "Cost of high-speed rail project in the Valley leaps by $2.8 billion". Fresno Bee. Retrieved 22 January 2018.
- ↑ Vartabedian, Ralph (29 July 2018). "California bullet train might not attain state's mandated speed". Marin Independent Journal. Los Angeles Times. Retrieved 15 August 2018 – via Los Angeles Times.
- ↑ Official website: California High Speed Rail Peer Review Group
- 1 2 3 "Bold Bets: California on the Move?". The Atlantic. February 25, 2015.
Video of event
- ↑ "Making the Most of High-Speed Rail in California: Lessons from France and Germany". gmfus.org. Retrieved January 14, 2016.
- ↑ "Blended Service". Midwesthsr.org. June 7, 2013. Retrieved October 4, 2018.
- ↑ "Promoting Intermodal Connectivity at California's High-Speed Rail Stations" (PDF). Hsr.ca.gov. Retrieved January 14, 2016.
- ↑ "The California High Speed Rail Proposal: A Due Diligence Report" (PDF). Hsr.ca.gov. Retrieved January 14, 2016.
- ↑ "Californians & Their Government" (PDF). Ppic.org. p. 20. Retrieved 4 October 2018.
- ↑ Makien, Julie (September 17, 2015). "A high-speed rail from L.A. to Las Vegas? China says it's partnering with U.S. to build". Los Angeles Times. Retrieved September 19, 2015.
- ↑ "Brightline to Build Express Intercity Passenger Rail Connecting Southern California and Las Vegas". Press.gobrightline.com. Retrieved October 4, 2018.
- ↑ "Comparison of Providing the Equivalent Capacity to High-Speed Rail through Other Modes" (PDF). April 2012. Retrieved October 31, 2013.
After adjusting the analysis to be more comparable to the costs described in the Business Plan, the total costs of equivalent investment in airports and highways would be $123-138 billion (in 2011 dollars) to build 4,295-4652 lane-miles of highways, 115 gates, and four runways for Phase 1 Blended and Phase 1 Full Build, respectively... In year-of-expenditure (YOE) dollars, the highway and airport costs would be $158–186 billion.
- ↑ Vance, Ashlee (August 12, 2013). "Revealed: Elon Musk Explains the Hyperloop, the Solar-Powered High-Speed Future of Inter-City Transportation". Bloomberg Businessweek. Bloomberg L.P. Retrieved August 13, 2013.
- ↑ Musk, Elon (August 12, 2013). "Hyperloop Alpha" (PDF). SpaceX. Retrieved August 13, 2013.
- ↑ "Musk announces plans to build Hyperloop demonstrator". Gizmag.com. August 13, 2013. Retrieved August 14, 2013.
[Musk] will develop and construct a Hyperloop demonstrator.
- ↑ "Experts Raise Doubts Over Elon Musk's Hyperloop Dream". MIT Technology Review. August 12, 2013. Retrieved December 30, 2014.
References
- CHSRA (May 1, 2016). ""Business Plan 2016. Connecting and Transforming California."" (PDF). California High-Speed Rail Authority.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to California High-Speed Rail. |
- California High-Speed Rail Authority – official website
- California State Rail Plan (2013) – official document
- AB 3034 – official document (the authorizing legislation for Proposition 1A)
- San Jose Mercury News coverage
- Huffington Post coverage
- Progressive Railroading coverage
- The Fresno Bee coverage
