Brielle
| Brill Brielle | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Municipality | |||
 Historic city centre | |||
| |||
.svg.png) Location in South Holland | |||
| Coordinates: 51°54′N 4°10′E / 51.900°N 4.167°ECoordinates: 51°54′N 4°10′E / 51.900°N 4.167°E | |||
| Country | Netherlands | ||
| Province | South Holland | ||
| Government[1] | |||
| • Body | Municipal council | ||
| • Mayor | Gregor Rensen (PvdA) | ||
| Area[2] | |||
| • Total | 31.14 km2 (12.02 sq mi) | ||
| • Land | 27.56 km2 (10.64 sq mi) | ||
| • Water | 3.58 km2 (1.38 sq mi) | ||
| Elevation[3] | 2 m (7 ft) | ||
| Population (August 2017)[4] | |||
| • Total | 16,976 | ||
| • Density | 616/km2 (1,600/sq mi) | ||
| Demonym(s) | Briellenaar | ||
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) | ||
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+2 (CEST) | ||
| Postcode | 3230–3232 | ||
| Area code | 0181 | ||
| Website |
www | ||
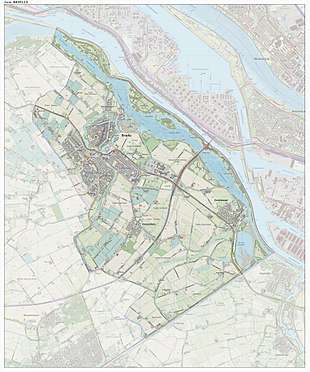
Brielle (pronounced [ˈbrilə] (![]()
The municipality of Brielle also includes the communities Vierpolders and Zwartewaal.
History
Brielle is a very old, fortified town. Its name is derived from the Celtic word brogilo (meaning "closed area" or "hunting grounds"). The oldest writings about Brielle indicate that the current location is the "new" Brielle. Den ouden Briel (Old Brill) must have been situated somewhere else on the Voorne-Putten Island. It received city rights in 1306. The city was for a long time the seat of the Count of Voorne, until this fiefdom was added to Holland in 1371. It had its own harbour and traded with the countries around the Baltic Sea. Brielle even had its own trading colony in Sweden.
During the Eighty Years' War between the Netherlands and Spain, the Capture of Brielle on April 1, 1572, by Protestant rebels, the Watergeuzen, marked a turning point in the conflict, as many towns in Holland then began to support William of Orange against the Spanish Duke Fernando Álvarez de Toledo, 3rd Duke of Alba who was sent to pacify The Netherlands. This event is still celebrated each year on April 1 and the night before (known as Chalk Night (kalknacht) when the city is defaced with chalk - and now also white paint). Dutch students are taught a short rhyme to remember this fact, which rhyme refers to April Fools' Day:
|
|
In Dutch, "bril" is the word for "glasses," and it closely rhymes with Briel; as does "Fles" which stands for the town of Vlissingen, and was the next town to be captured by the Dutch rebels.
After the capture of Brielle the Protestant rebels tortured and murdered the Catholic Martyrs of Gorkum and Brielle has become a pilgrimage location since then.
In August 1585, Brielle was one of the four Dutch towns that became an English possession by the Treaty of Nonsuch when Queen Elizabeth I received it as security of payment for 5000 soldiers (led by the Earl of Leicester) and used by the Dutch in their struggle against the Spanish. The first English governor of Brielle was Thomas Cecil, 1st Earl of Exeter, succeed by Edward Conway, 1st Viscount Conway who named his daughter Brilliana in honour of the city. English garrisons were stationed here and at Flushing.[5] In 1617, these cities returned to the Netherlands.
Twin cities
Brielle is twinned with:

Gallery
- Brielle, church: de Sint Catharijnekerk
- Brielle, view to a street: het Wellerondom
- Brielle, former orphanage
- Brielle, monumental houses Vischstraat
See also
References
- ↑ "College van B & W" [Board of mayor and aldermen]. Bestuur, organisatie en beleid (in Dutch). Gemeente Brielle. Archived from the original on 17 May 2013. Retrieved 16 July 2013.
- ↑ "Kerncijfers wijken en buurten" [Key figures for neighbourhoods]. CBS Statline (in Dutch). CBS. 2 July 2013. Retrieved 12 March 2014.
- ↑ "Postcodetool for 3231AP". Actueel Hoogtebestand Nederland (in Dutch). Het Waterschapshuis. Retrieved 16 July 2013.
- ↑ "Bevolkingsontwikkeling; regio per maand" [Population growth; regions per month]. CBS Statline (in Dutch). CBS. 27 October 2017. Retrieved 27 October 2017.
- ↑ Garrett Mattingly (1959), The Armada, Boston: Houghton Mifflin, Ch. V, "Plans of Operations", p. 44.
External links
| Wikisource has the text of the 1911 Encyclopædia Britannica article Brielle. |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Brielle. |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Brielle. |
- Official website (some pages in English)
- http://www.catharijnekerk.nl Website of St Catharijnekerk