Fluorine nitrate
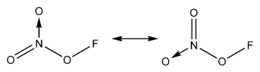
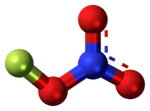
Fluorine nitrate is an unstable derivative of nitric acid with the formula FNO
3. It is shock-sensitive.[1] Due to its instability, it is often produced from chlorine nitrate as needed.
 | |
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| FNO3 | |
| Molar mass | 81.002 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 2.217 g/L[1] |
| Melting point | −175 °C (−283.0 °F; 98.1 K) |
| Boiling point | −46 °C (−51 °F; 227 K) |
| Thermochemistry | |
Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
+10.46 kJ/mol |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Explosive gas |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Synthesis and properties
Fluorine nitrate is formed when fluorine gas is bubbled through nitric acid or reacted with solid potassium nitrate:[2]
F
2 + HNO
3 → FNO
3 + HF
F
2 + KNO
3 → FNO
3 + KF
It decomposes in water to form oxygen gas, oxygen difluoride, hydrofluoric acid, and nitric acid.[1]
References
- Ruff, Otto; Kwasnik, Walter (1935). "The fluorination of nitric acid. The nitroxyfluoride, NO3F". Angewandte Chemie. 48: 238–240. doi:10.1002/ange.19350481604.
- Yost, Don M.; Beerbower, Alan. "The Reaction of Fluorine with Nitric acid and with Solid Potassium Nitrate to Form NO3F". Communication. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help)
- Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
Salts and covalent derivatives of the nitrate ion
| HNO3 | He | ||||||||||||||||
| LiNO3 | Be(NO3)2 | B(NO 3)− 4 |
RONO2 | NO− 3, NH4NO3 |
O | FNO3 | Ne | ||||||||||
| NaNO3 | Mg(NO3)2 | Al(NO3)3 | Si | P | S | ClONO2 | Ar | ||||||||||
| KNO3 | Ca(NO3)2 | Sc(NO3)3 | Ti(NO3)4 | VO(NO3)3 | Cr(NO3)3 | Mn(NO3)2 | Fe(NO3)2, Fe(NO3)3 |
Co(NO3)2, Co(NO3)3 |
Ni(NO3)2 | CuNO3, Cu(NO3)2 |
Zn(NO3)2 | Ga(NO3)3 | Ge | As | Se | Br | Kr |
| RbNO3 | Sr(NO3)2 | Y(NO3)3 | Zr(NO3)4 | Nb | Mo | Tc | Ru(NO3)3 | Rh(NO3)3 | Pd(NO3)2, Pd(NO3)4 |
AgNO3, Ag(NO3)2 |
Cd(NO3)2 | In | Sn | Sb(NO3)3 | Te | I | Xe(NO3)2 |
| CsNO3 | Ba(NO3)2 | Hf | Ta | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt(NO3)2, Pt(NO3)4 |
Au(NO3)3 | Hg2(NO3)2, Hg(NO3)2 |
TlNO3, Tl(NO3)3 |
Pb(NO3)2 | Bi(NO3)3 BiO(NO3) |
Po(NO3)4 | At | Rn | |
| FrNO3 | Ra(NO3)2 | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Nh | Fl | Mc | Lv | Ts | Og | |
| ↓ | |||||||||||||||||
| La(NO3)3 | Ce(NO3)3, Ce(NO3)4 |
Pr(NO3)3 | Nd(NO3)3 | Pm(NO3)3 | Sm(NO3)3 | Eu(NO3)3 | Gd(NO3)3 | Tb(NO3)3 | Dy(NO3)3 | Ho(NO3)3 | Er(NO3)3 | Tm(NO3)3 | Yb(NO3)3 | Lu(NO3)3 | |||
| Ac(NO3)3 | Th(NO3)4 | PaO2(NO3)3 | UO2(NO3)2 | Np(NO3)4 | Pu(NO3)4 | Am(NO3)3 | Cm(NO3)3 | Bk | Cf | Es | Fm | Md | No | Lr | |||
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.