2018 Florida elections
A general election was held in the U.S. state of Florida on November 6, 2018. All of Florida's executive officers were up for election as well as Florida's Class I Senate seat and all 27 seats in the United States House of Representatives. Primary elections were on August 28, 2018. The Republicans took control of the U.S. Senate seat held by three-term Democrat Bill Nelson while the Democrats picked up two House seats as well as the office of the Commissioner of Agriculture.
| Elections in Florida | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | ||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
North Miami
|
||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
|
| ||||||||||||||
United States Senate
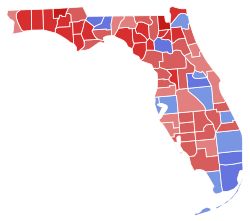
Senator Bill Nelson (D) ran for a fourth term against Governor Rick Scott (R). The race ended up being the most expensive Senate race in U.S. History.[1] Nelson was narrowly defeated by then-Governor Rick Scott.
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | ± | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Rick Scott | 4,099,505 | 50.06% | +7.82% | |
| Democratic | Bill Nelson (incumbent) | 4,089,472 | 49.93% | −5.30% | |
| Write-in | 607 | <0.01% | N/A | ||
| Total votes | '8,190,005' | '100%' | N/A | ||
| Republican gain from Democratic | |||||
United States House of Representatives
Florida elects 27 U.S. Representatives from its congressional districts. Democrat Donna Shalala defeated Maria Elvira Salazar to succeed retiring Republican congresswoman Ileana Ros-Lehtinen in the Miami-based 27th District, and Debbie Mucarsel-Powell defeated incumbent Republican congressman Carlos Curbelo in the 26th District in Miami-Dade and Monroe Counties. This changed Florida's congressional delegation from a 16–11 Republican majority to a narrow 14–13 majority.
Governor
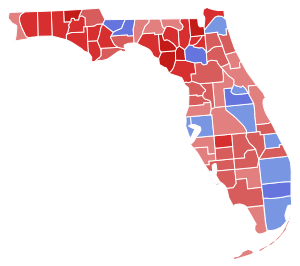
Then-incumbent Republican Governor Rick Scott (since 2011) was term-limited and prohibited from seeking a third consecutive term. Democratic Mayor of Tallahassee Andrew Gillum ran against Republican former U.S. Representative Ron DeSantis. DeSantis narrowly defeated Gillum.
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | ± | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Ron DeSantis / Jeanette Nuñez | 4,076,186 | 49.59% | +1.45% | |
| Democratic | Andrew Gillum / Chris King | 4,043,723 | 49.19% | +2.12% | |
| Reform | Darcy G. Richardson / Nancy Argenziano | 47,140 | 0.57% | N/A | |
| Independent | Kyle "KC" Gibson / Ellen Wilds | 24,310 | 0.30% | N/A | |
| Independent | Ryan Christopher Foley / John Tutton Jr. | 14,630 | 0.18% | N/A | |
| Independent | Bruce Stanley / Ryan Howard McJury | 14,505 | 0.18% | N/A | |
| n/a | Write-ins | 67 | 0.00% | N/A | |
| Total votes | '8,220,561' | '100.0%' | N/A | ||
| Republican hold | |||||
Attorney General
Incumbent Republican Florida Attorney General Pam Bondi (since 2011) was term-limited and prohibited from seeking a third consecutive term.
Chief Financial Officer
Incumbent Republican Chief Financial Officer of Florida Jimmy Patronis was appointed to the office in June 2017 and is seeking a full term in 2018.
Commission of Agriculture
Incumbent Republican Florida Commissioner of Agriculture Adam Putnam (since 2011) is term-limited and prohibited from seeking a third consecutive term.
State Legislature
20 out of 40 seats in the Florida Senate and all 120 seats of the Florida House of Representatives were up for election. The balance of political power before the election for each chamber was:
Senate
|
House of Representatives
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The balance of political power after the election was:
Senate
|
House of Representatives
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Constitutional Amendments
Florida voters voted on 12 constitutional amendments. An amendment requires sixty percent to pass. Amendment 8 was removed from the ballot before the elections.[4]
| Amendment | Name | Summary | Sponsor | Notes | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Increased Homestead Property Tax Exemption | Proposing an amendment to the State Constitution to increase the homestead exemption by exempting the assessed valuation of homestead property greater than $100,000 and up to $125,000 for all levies other than school district levies. The amendment shall take effect January 1, 2019. | The Florida Legislature/House (HJR7105) | Failed to pass 58%–42% | |
| 2 | Limitations on Property Tax Assessments | Proposing an amendment to the State Constitution to permanently retain provisions currently in effect, which limit property tax assessment increases on specified nonhomestead real property, except for school district taxes, to 10 percent each year. If approved, the amendment removes the scheduled repeal of such provisions in 2019 and shall take effect January 1, 2019. | The Florida Legislature/House (CS/HJR 21) | Passed 66%–34% | |
| 3 | Voter Control of Gambling in Florida | This amendment ensures that Florida voters shall have the exclusive right to decide whether to authorize casino gambling by requiring that in order for casino gambling to be authorized under Florida law, it must be approved by Florida voters pursuant to Article XI, Section 3 of the Florida Constitution. Affects articles X and XI. Defines casino gambling and clarifies that this amendment does not conflict with federal law regarding state/tribal compacts. | Voters In Charge | Passed 71%–29% | |
| 4 | Voting Restoration Amendment | This amendment restores the voting rights of Floridians with felony convictions after they complete all terms of their sentence including parole or probation. The amendment would not apply to those convicted of murder or sexual offenses, who would continue to be permanently barred from voting unless the Governor and Cabinet vote to restore their voting rights on a case by case basis. | Floridians for a Fair Democracy, Inc. | Passed 65%–35% | |
| 5 | Supermajority Vote Required to Impose, Authorize, or Raise State Taxes or Fees | Prohibits the legislature from imposing, authorizing, or raising a state tax or fee except through legislation approved by a two-thirds vote of each house of the legislature in a bill containing no other subject. This proposal does not authorize a state tax or fee otherwise prohibited by the Constitution and does not apply to fees or taxes imposed or authorized to be imposed by a county, municipality, school board, or special district. | The Florida Legislature/House (HJR7001) | Passed 66%–34% | |
| 6 | Rights of Crime Victims; Judges | Creates constitutional rights for victims of crime; requires courts to facilitate victims’ rights; authorizes victims to enforce their rights throughout criminal and juvenile justice processes. Requires judges and hearing officers to independently interpret statutes and rules rather than deferring to government agency's interpretation. Raises mandatory retirement age of state justices and judges from seventy to seventy-five years; deletes authorization to complete judicial term if one-half of term has been served by retirement age. | Constitution Revision Commission | Passed 62%–38% | |
| 7 | First Responder and Military Member Survivor Benefits; Public Colleges and Universities | Grants mandatory payment of death benefits and waiver of certain educational expenses to qualifying survivors of certain first responders and military members who die performing official duties. Requires supermajority votes by university trustees and state university system board of governors to raise or impose all legislatively authorized fees if law requires approval by those bodies. Establishes existing state college system as constitutional entity; provides governance structure. | Constitution Revision Commission | Amendment was subject to litigation and the Florida Supreme Court has yet to rule on their constitutionality. | Passed 66%–34% |
| 9 | Prohibits Offshore Oil and Gas Drilling; Prohibits Vaping in Enclosed Indoor Workplaces | Prohibits drilling for the exploration or extraction of oil and natural gas beneath all state-owned waters between the mean high water line and the state's outermost territorial boundaries. Adds use of vapor-generating electronic devices to current prohibition of tobacco smoking in enclosed indoor workplaces with exceptions; permits more restrictive local vapor ordinances. | Constitution Revision Commission | Amendment was subject to litigation and the Florida Supreme Court has yet to rule on their constitutionality. | Passed 69%–31% |
| 10 | State and Local Government Structure and Operation | Requires legislature to retain department of veterans’ affairs. Ensures election of sheriffs, property appraisers, supervisors of elections, tax collectors, and clerks of court in all counties; removes county charters’ ability to abolish, change term, transfer duties, or eliminate election of these offices. Changes annual legislative session commencement date in even-numbered years from March to January; removes legislature's authorization to fix another date. Creates office of domestic security and counterterrorism within department of law enforcement | Constitution Revision Commission | Passed 63%–37% | |
| 11 | Property Rights; Removal of Obsolete Provision; Criminal Statutes | Removes discriminatory language related to real property rights. Removes obsolete language repealed by voters. Deletes provision that amendment of a criminal statute will not affect prosecution or penalties for a crime committed before the amendment; retains current provision allowing prosecution of a crime committed before the repeal of a criminal statute. | Constitution Revision Commission | Amendment was subject to litigation and the Florida Supreme Court has yet to rule on their constitutionality. | Passed 62%–38% |
| 12 | Lobbying and Abuse of Office by Public Officers | Expands current restrictions on lobbying for compensation by former public officers; creates restrictions on lobbying for compensation by serving public officers and former justices and judges; provides exceptions; prohibits abuse of a public position by public officers and employees to obtain a personal benefit. | Constitution Revision Commission | Passed 79%–21% | |
| 13 | Ends Dog Racing | Phases out commercial dog racing in connection with wagering by 2020. Other gaming activities are not affected. | Constitution Revision Commission | Passed 69%–31% |
References
- "Florida Senate race the most expensive ever, surpassing $200 million". OpenSecrets News. December 7, 2018.
- "Florida Election Watch - US Senator". floridaelectionwatch.gov. Archived from the original on November 10, 2018. Retrieved August 4, 2019.
- "Florida Election Watch - Governor". floridaelectionwatch.gov. Archived from the original on November 9, 2018. Retrieved August 4, 2019.
- "2018 Constitutional Amendments – Florida Chamber of Commerce". www.flchamber.com.