Solar power in Chile
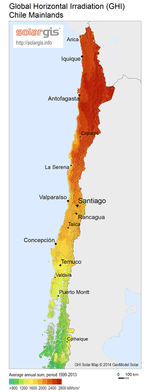
Northern Chile has the highest solar incidence in the world.[1] In October 2015 Chile's Ministry of Energy announced its "Roadmap to 2050: A Sustainable and Inclusive Strategy", which plans for 19% of the country's electricity to be from solar energy, 23% wind power and 29% hydroelectric power.[2]
Timeline of key developments
2016
In 2016, SolarPack won an electricity auction by bidding $29.1/MWh;[3] a record low price.[4]
2014-2015
The Atacama 1 solar complex was proposed as a 110 MW solar thermal electric plant (the first in Latin America) and a 100 MW photovoltaic plant. The solar thermal plant will include 17.5 hours of thermal storage. These technologies complement each other to supply clean and stable energy 24 hours a day. The complex is located in the commune of María Elena, Segunda Región. Construction of the solar thermal electric plant commenced in 2014 and the plant is scheduled to begin operating in the second quarter of 2017. Construction of the photovoltaic plant commenced in January 2015 and the plant began operating in June 2016 with 160 MW of panels, the largest solar plant in Chile at the time.[5][6]
Irradiance and installed capacity
|
| Chile Photovoltaics Capacity (MWp)[8] | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| End of the year | Installed capacity operating | Under construction | Presented for environmental assessment |
| 2011 | 0 | 1 | <769 |
| 2012 | 2 | 2.5 | 4,109 |
| 2013 | 6.7 | 128 | 8,184 |
| 2014 | 362 | 983 | 12,559 |
| 2015 | 750 | 2380 | 15,769[9] |
Projects

In June 2014, the 100-megawatt (MW) Amanecer Solar CAP, a photovoltaic power plant located near Copiapó in the Atacama Desert was inaugurated. It was developed by the company with the same name, Amanecer Solar CAP, and was the largest in Latin America at the time. It is capable of generating 270 gigawatt-hours (GWh) of electricity per year.[10][11]
The 70 MW photovoltaic Salvador Solar Park went online in November 2014, followed by an official inauguration ceremony on January 23, 2015.[12] It was expected to produce 200 GWh of electricity per year. The plant is located approximately 5 kilometres south of El Salvador, in the Atacama region. It is one of the first in the world to supply competitively priced solar energy to the open market without government subsidy.[13]
The 60 MW photovoltaic Lalackama I plant went online in 2014 and is expected to produce 160 GWh of electricity per year. The nearby 18 MW Lalackama II plant went online in May 2015 and is capable of generating approximately 50 GWh per year.[14][15][16] Both plants feature photovoltaic inverters designed and manufactured by Elettronica Santerno,[17] an Italian company.
The 141 MW photovoltaic Luz Del Norte (Light of the North) plant, located 58 kilometres northeast of the city of Copiapó in the Atacama region, began construction in October 2014 and is scheduled for completion in December 2015.[18] It uses more than 1.7 million cadmium telluride modules.[19] The first two blocks of this project (approximately half of the project’s total capacity) was connected to Chile’s central power grid in October 2015.[20]
The 79 MW Pampa Norte PV solar plant began operating in April 2016 at a site 32 kilometres southwest of Taltal in Chile's Antofagasta Region. It uses approximately 258,000 polycrystalline silicon photovoltaic modules and is capable of generating more than 200 GWh per year.[21] The plant was developed by Enel Green Power and features photovoltaic inverters designed and manufactured by Elettronica Santerno.[17][22]
The 97 MW Carrera Pinto photovoltaic plant began is located 60 kilometres from the city of Copiapó in the Atacama Region. The first 20 MW of the plant was connected to the grid in early January 2016, with the remaining 77 MW connected in August 2016. The plant is capable of generating over 260 GWh per year.[23][24]
The 246 MW El Romero single-axis tracking solar photovoltaic plant began operating in November 2016 at Vallenar in the Atacama region, with a 493 GWh annual average output.[25][26] It was the largest solar farm in Latin America when it opened. It uses 776,000 polycrystalline silicon photovoltaic modules. The solar irradiance has been measured at 853 W/m2.[27]
See also
References
- ↑ Inter-American Development Bank (Dec 15, 2011). "Renewable energy to power irrigation in the Atacama desert". Retrieved 22 July 2014.
- ↑ Chile sets 70 pct. non-conventional renewable energy target for 2050, Fox News Latino from EFE, September 30, 2015
- ↑ "Licitaciones: piso ofertas es de US$ 29 y Colbún entre las más afectadas".
- ↑ "Wind Energy Scores Big In Chile's Electricity Auction". CleanTechies. 18 August 2016. Retrieved 10 September 2016.
- ↑ "Abengoa :: Press Room :: News :: News Archive :: 2015 :: January".
- ↑ Saurabh Mahapatra (2016-06-01). "Enel Commissions Its Largest Solar PV Project In Chile". CleanTechnica.
- ↑ "PV Watts". NREL. Retrieved 9 April 2013.
- ↑ Centro de Energías Renovables, CORFO (July 2014). "Reporte CER". Archived from the original on 6 July 2014. Retrieved 22 July 2014.
- ↑ "Reporte CIFES (Diciembre 2015)". Centro Nacional para la Innovación y Fomento de las Energías Sustentables - Comité CORFO. Retrieved 18 January 2016.
- ↑ "President Bachelet of Chile Inaugurates Latin America's Largest Solar Photovoltaic Power Plant". Newswire.ca. 6 June 2014.
- ↑ "Chile Solar Power Plant Is Now Latin America's Largest". 9 June 2014.
- ↑ Etrion Announces Completion of 70 MW Solar Park in Chile, Etrion (press release), 04 November 2014
- ↑ Total and SunPower Celebrate Completion of 70-megawatt PV Salvador solar power plant in Chile, SunPower Corp., January 23, 2015
- ↑ "EGP's largest solar plant is in Chile".
- ↑ "ENEL GREEN POWER BRINGS NEW PHOTOVOLTAIC PLANT ONLINE IN CHILE".
- ↑ "Enel Green hooks to grid 18-MW PV plant in Chile". SeeNews. Retrieved 6 December 2016.
- 1 2 "Elettronica Santerno website". santerno.com.
- ↑ "First solar panel for the 141 Megawatt (MW)ac Luz del Norte Solar Power plant in Chile - REVE".
- ↑ "Luz del Norte Solar Project". First Solar. Retrieved 6 December 2016.
- ↑ "First Solar Connects Luz del Norte to Chilean Central Grid". Business Wire. Retrieved 6 December 2016.
- ↑ "Enel Starts Production at Pampa Norte PV Plant in Chile". Enel Green Power. Retrieved 6 December 2016.
- ↑ "Estudio de Coordinación de Protecciones" (PDF). coordinadorelectrico.cl.
- ↑ "Enel Green Power's Carrera Pinto PV Plant in Chile Starts Producing Energy". Enel Green Power. Retrieved 6 December 2016.
- ↑ "Enel Starts Production at 97 MW Carrera Pinto PV Plant in Chile". Enel Green Power. Retrieved 6 December 2016.
- ↑ Chile connects Latin America's largest solar plant to the national grid, MercoPress, November 14th 2016
- ↑ "El Romero Solar PV Plant". Acciona Energy. Retrieved 6 December 2016.
- ↑ "Acciona and Spanish university claim world record solar generation measurement in Chile". Retrieved 6 September 2017.