Rubitecan
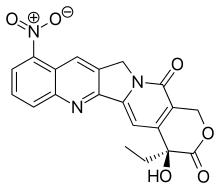 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Orathecin |
| Synonyms |
9-Nitrocamptothecin 9-NC 9-nitro-20(S)-camptothecin Camptogen (19S)-19-Ethyl-19-hydroxy-10-nitro-17-oxa-3,13-diazapentacyclo[11.8.0.02,11.04,9.015,20]henicosa-1(21),2,4,6,8,10,15(20)-heptaene-14,18-dione |
| Routes of administration | Oral (capsules) |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 25–30% (rubitecan and 9-AC; in dogs) |
| Protein binding | 97% (rubitecan), 65% (9-AC) |
| Metabolism | Probably CYP-dependent |
| Metabolites | 9-Aminocamptothecin (9-AC) |
| Elimination half-life | 15–18 hours (rubitecan), 18–22 hours (9-AC) |
| Excretion | Bile and feces (major proportion), urine (the minor one)[1] |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C20H15N3O6 |
| Molar mass | 393.349 g/mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Rubitecan (INN, marketing name Orathecin) is an oral topoisomerase inhibitor, developed by Supergen (now Astex Pharmaceuticals, Inc.; a member of the Otsuka Group).
History
On January 27, 2004, Supergen announced that it has completed the submission of an NDA for rubitecan to the US FDA,[2] and was accepted for filing on March 2004.[3]
On January 2005, Supergen withdrew the NDA for rubitecan, based on feedback indicating that the current data package would not be sufficient to gain US approval,[4] and on January 2006, the Marketing Authorization Application (MAA) filed with the European Medicines Agency (EMA) was also withdrawn.[5]
Synthesis
Large scale production of Rubitecan has encountered problems. The direct nitration of camptothecin results in regioselectivity problems. One way that has been used to synthesize Rubitecan is to nitrate 10-hydroxycamptothecin than remove the hydroxyl functional group.[6]
Use as Anti-Cancer Drug
Rubitecan is a compound used extensively in cancer research. Rubitecan is an effective drug against pancreatic cancer and other solid tumors. One major problem is the lack of oral bioavailability due to low permeability and poor water solubility. One study shows 9-NC-SD through Soluplus1-based solid dispersion system is a much more effective delivery method than free 9-NC.[7]
References
- ↑ "Withdrawal Assessment Report for Orathecin (rubitecan). Applicant: EuroGen Pharmaceuticals, Ltd" (PDF). European Medicines Agency. 30 November 2007. pp. 4–8. Retrieved 15 July 2016.
- ↑ "Drugs.com, SuperGen completes submission of New Drug Application (NDA) for Orathecin as an oral treatment for pancreatic cancer". Retrieved 2008-03-25.
- ↑ "Drugs.com, SuperGen's New Drug Application for Orathecin (rubitecan) capsules accepted by FDA for filing". Retrieved 2008-03-25.
- ↑ "Drugs.com, SuperGen Announces Withdrawal of Orathecin NDA". Retrieved 2008-03-25.
- ↑ "Press release from the EMEA website regarding withdrawal of Orathecin MAA" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2007-06-11. Retrieved 2008-03-25.
- ↑ "A Practical Regiospecific Synthesis of 9-Nitrocamptothecin" (PDF). Retrieved 2017-10-10.
- ↑ "Soluplus® based 9-nitrocamptothecin solid dispersion for peroral administration" (PDF). Retrieved 2017-10-10.