Nonivamide
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
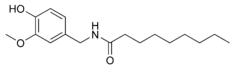
| IUPAC name
N-[(4-Hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)methyl]nonanamide | |
| Other names
Pseudocapsaicin; Vanillyl-N-nonylamide; Vanillylamide of n-nonanoic acid; VNA; Nonylic acid vanillyl amide; Pelargonic acid vanillylamide (PAVA); Pelargonyl vanillyl amide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.017.713 |
| EC Number | 219-46-4 |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C17H27NO3 | |
| Molar mass | 293.41 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White to off-white powder |
| Odor | Pungent |
| Density | 1.10 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 54 °C (129 °F; 327 K) |
| Insoluble | |
| Solubility | Soluble in methanol |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | 190 °C (374 °F; 463 K) (closed cup) |
| 330 °C (626 °F; 603 K) | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose) |
511 mg/kg (rat, oral) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
| Nonivamide | |
|---|---|
|
| |
| Heat | Above peak |
| Scoville scale | 9,200,000[1] SHU |
Nonivamide, also called pelargonic acid vanillylamide or PAVA, is an organic compound and a capsaicinoid. It is an amide of pelargonic acid (n-nonanoic acid) and vanillyl amine. It is present in chili peppers,[2] but is commonly manufactured synthetically. It is more heat-stable than capsaicin.
Nonivamide is used as a food additive to add pungency to seasonings, flavorings, and spice blends. It is also used in the confectionery industry to create a hot sensation, and in the pharmaceutical industry in some formulations as a cheaper alternative to capsaicin.
Like capsaicin, it can deter mammals (but not birds or insects) from consuming plants or seeds (e.g. squirrels and bird feeder seeds).[3] This is consistent with nonivamide's role as a TRPV1 ion channel agonist. Mammalian TRPV1 is activated by heat and capsaicin, but the avian form is insensitive to capsaicin.[4]
Nonivamide is used (under the name PAVA) as the payload in "less-lethal munitions" such as the Fabrique Nationale Herstal FN 303[5] or as the active ingredient in most pepper sprays[3] – in both applications, the idea is to temporarily incapacitate people so that they can either be detained prior to arrest or deterred from acts of violence toward law-enforcement personnel or third parties (such as rioting or other group violence).
See also
References
- ↑ Govindarajan, Sathyanarayana (1991). "Capsicum — Production, Technology, Chemistry, and Quality. Part V. Impact on Physiology, Pharmacology, Nutrition, and Metabolism; Structure, Pungency, Pain, and Desensitization Sequences". Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition. 29 (6): 435–474.
- ↑ Howard L. Constant, Geoffrey A. Cordell and Dennis P. West (1996). "Nonivamide, a Constituent of Capsicum oleoresin". J. Nat. Prod. 59 (4): 425–426. doi:10.1021/np9600816.
- 1 2 http://www.aversiontech.com/hot-and-spicy/nonivamide-pava/ Retrieved 16 July 2010
- ↑ Rohm, Barbara; Riedel, Annett; Ley, Jakob P; Widder, Sabine; Krammer, Gerhard E; Somoza, Veronika (2015). "Capsaicin, nonivamide and trans-pellitorine decrease free fatty acid uptake without TRPV1 activation and increase acetyl-coenzyme a synthetase activity in Caco-2 cells". Food & Function. 6: 172. doi:10.1039/C4FO00435C.
- ↑ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2013-05-04. Retrieved 2013-04-14.