Chatham main line
| Chatham main line | |
|---|---|
| Overview | |
| Type | Commuter rail |
| System | National Rail |
| Status | Operational |
| Locale |
Greater London South East England |
| Termini |
London Victoria Ramsgate Dover Priory |
| Operation | |
| Owner | Network Rail |
| Operator(s) |
Southeastern Thameslink |
| Rolling stock |
Class 375 "Electrostar" Class 395 "Javelin" Class 465 "Networker" Class 466 "Networker" Class 700 "Desiro City" |
| Technical | |
| Track gauge | 4 ft 8 1⁄2 in (1,435 mm) standard gauge |
| Electrification | 750 V DC third rail |
| Operating speed | 145 km/h (90 mph) |
The Chatham main line is a railway line in England that links London Victoria[1] and Dover Priory / Ramsgate, travelling via Medway (of which the town of Chatham is part, hence the name).
Services to Cannon Street follow the route as far as St Mary Cray Junction where they diverge onto the South Eastern main line near Chislehurst.
Thameslink services to Luton run in parallel from Rainham to Rochester, diverging once across the River Medway at Rochester Bridge Junction onto the North Kent Line via Gravesend and Dartford.
A shuttle service operates on the Sheerness Line which starts at Sittingbourne.
Heading away from Victoria, between Farningham Road and Longfield Stations, the line which was used by Eurostar trains running from Waterloo International towards Fawkham Junction to pick up High Speed 1 still exists but is no longer used. At one time this line was reserved for emergency use only by Class 395 Javelins travelling to/from Ashford International, but as the route knowledge has not been kept up to date, nothing uses this line any more. The Eurostar trains can no longer use this line as the Class 373's had their 750V shoes removed and most have been replaced by Class 374 trains which have not been fitted with 750V shoes in the first place.
Services
Most services on the Line are run by Southeastern, part of Govia Group, which also operate the Southern, Thameslink and the Great Northern franchises. Govia Thameslink Railway run a Thameslink service, starting from London Blackfriars and travelling via Denmark Hill on the Catford Loop, joining at Shortlands Junction. It then travels to Swanley before heading to Sevenoaks. This service was previously mainly run by Southeastern, with a few Thameslink services beyond St Pancras.
While travelling between Bromley South and London Victoria, the trains can either travel on the main line, through Beckenham Junction, Herne Hill and Brixton, or can be divert via the Catford Loop Line, coming away from the main line at Shortlands Junction, travelling through Catford and Peckham Rye, and then just past Brixton it either picks up the Southeastern line all the way, or can follow the Southern (Atlantic) Line through Clapham High Street before crossing back over to the Southeastern Line to London Victoria. The train scheduled to run via Catford now stop additionally at Denmark Hill.
The off-peak timetable consists of two trains per hour from Victoria, calling at Bromley South, Longfield, Meopham, Rochester, Chatham, and Rainham. One service will call at Newington, Sittingbourne, Teynham and Faversham, then all stations to Dover Priory via Canterbury East. The other service will only call at Sittingbourne and Faversham then all stations to Margate and Ramsgate. These trains no longer split or join up at Faversham. There is an hourly service from Victoria calling at Denmark Hill via the Catford Loop, Bromley South, St Mary Cray then all stations to Gillingham. It then becomes a semi-fast service, calling at Rainham, Sittingbourne, Faversham, Canterbury East, terminating at Dover Priory. A High Speed Service sees two trains per hour from St Pancras International to Faversham via Gravesend and Chatham. One service terminates at Faversham before travelling back to St Pancras International via Chatham and Gravesend. The other service continues coastbound as a semi-fast service calling at Whitstable, Herne Bay, Birchington, Margate, Broadstairs and Ramsgate. It then carries on, stopping at Sandwich, Deal, Walmer, Martin Mill, Dover Priory, Folkestone Central, Folkestone West and Ashford International, before picking up the High Speed Line to Ebbsfleet International, Stratford International and arriving back at St Pancras International. A service operates in the opposite direction. There is one other High Speed Service that runs on a small part of the line, starting from Margate and calling at Broadstairs and Ramsgate before heading to Canterbury West, and Ashford International, then picking up the High Speed Line and calling at the remaining stations to St Pancras International. A Thameslink service now starts from Rainham and calls at nearly all stations via Strood, Gravesend, Dartford, Abbey Wood (for future Crossrail), Woolwich Arsenal and Greenwich (both for the Docklands Light Railway), London Bridge and Blackfriars. Passengers for Charing Cross and Cannon Street now have to change at London Bridge.
Rolling stock
The following trains are operated on the line : Class 465 "Networker" since 1992, Class 466 "Networker" since 1993, Class 375 "Electrostar" since 2001, Class 395 "Javelin" since 2009, and British Rail Class 700 since 2018.
History
The line was built by the London, Chatham and Dover Railway, who were in competition with the South Eastern Railway (hence the duplication of stations in Kent). They subsequently built lines to Sevenoaks and Ashford (via Maidstone) from the Chatham main line.
The line was electrified (750 V DC third rail) in a series of stages. Initially the new Southern Railway electrified the urban (within London) workings of the SECR in the 1920s. In July 1925 "South Eastern Electrification (Stage 1)" saw the line from Victoria to junction with the South Eastern main line at Bickley, including the Catford Loop Line electrified.[2] This was extended to outer suburban workings to Sevenoaks via Swanley (Bickley junction to Swanley) in two stages, reaching St Mary Cray in May 1934[2] and Swanley in January 1935.[2] Full outer suburban electrification was achieved with the "Maidstone & Gillingham Electrification" scheme in July 1939, extending electrification from Swanley to Gillingham.[2] Post war, under the BR's 1955 Modernisation plan, electrification was completed (Gillingham to Ramsgate and Dover) under "Kent Coast Electrification" stage 1 in 1959.[2] At the same time the four track section between Shortlands and St Mary Cray junction was extended to Swanley Junction with a complete rebuilding of the St Mary Cray Junction. Two passing loops were added (to create a four-track section) between Rainham and Newington.
A short branch was built during World War One to service the construction of RAF Manston with a junction off the up line at Birchington on Sea.
East Kent re-signalling project
The idea of this project is for control of East Kent from Longfield to Ramsgate and just short of Dover Priory to be under the control of the East Kent Signalling Centre (EKSC) based at Gillingham.
Phase 1 of the project was carried out over the Christmas and New Year period of 2011, which involved the complete re-signalling from just East of Sittingbourne to Faversham, then on to Minster Junction and Buckland Junction, just short of Dover Priory. The old signal boxes were then abolished at Faversham, Margate, Ramsgate, Canterbury East and Shepherdswell. Phase 2 involved the re-signalling of the line between Sittingbourne to Longfield and Strood, including the Sheerness Branch Line and the Medway Valley Line to operate from the East Kent Signalling Centre at Gillingham, which is now operational. This means that the Signal Boxes at Rainham and Rochester have now closed, although Sittingbourne remains open as a relay signal box for the Sheerness Branch Line, controlled from Gillingham.
On 13 December 2015, a new £26M Rochester station on Corporation Street opened 500 m west of the original station which it replaced. This station has three platforms and can accommodate 12-car trains instead of the 10-cars maximum length at the original station. Some 12-car peak-time trains are additionally stopping here. At the time, only platforms 1 and 2 were operational. From Easter 2016, Platform 3 was only a Bay Platform with a maximum length of eight cars, but since 10 October 2016, Platform 3 became a through platform with services either able to head towards the Kent Coast or terminating here before head back up towards London. At the East End of the platform, a third line now runs all the way up to the old Rochester Station passing through what was Platform 4 before rejoining the Down Main towards Chatham. This can also enable long freight trains to be held here, allowing passenger services to pass, therefore removing a potential bottleneck.
Rainham has a new bay platform off the up-line, which can accommodate a 12-car train, labelled Platform 0. It is now being used as a Terminus for a couple of evening rush hour trains. The draft Thameslink Metro timetable for 2018 shows that they intend to use this bay platform for two trains per hour for services to Luton via Gravesend, Dartford, Woolwich Arsenal and Greenwich, stopping at all but a few stations to London Bridge.
Strood has also been lengthened to accommodate 12-car trains.
Accidents and incidents
- On 10 September 1963, a freight train became divided and was derailed between Farningham Road and Longfield due to defects in a wagon. The line was closed until 13 September.[3]
Gallery
 A Class 375, near Farningham Road
A Class 375, near Farningham Road- Car parking at Chatham railway station, the Maidstone Road bridge and the portal to the Chatham Tunnel
- A Class 375 in Gillingham Depot
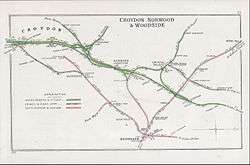 A 1908 Railway Clearing House map of Chatham main line and surrounding lines between Beckenham Jct and Herne Hill
A 1908 Railway Clearing House map of Chatham main line and surrounding lines between Beckenham Jct and Herne Hill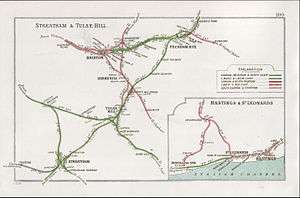 A 1908 Railway Clearing House map showing the two different routes of the Chatham main line in South London
A 1908 Railway Clearing House map showing the two different routes of the Chatham main line in South London A 1908 Railway Clearing House map of the end of the Dover branch of the Chatham main line
A 1908 Railway Clearing House map of the end of the Dover branch of the Chatham main line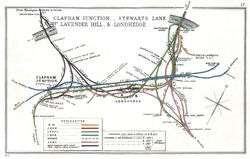 A 1912 Railway Clearing House map of the line's final approaches to Victoria
A 1912 Railway Clearing House map of the line's final approaches to Victoria
See also
References
- ↑ Quail Map 5 – England South [pages 2–13] Sept 2002 (Retrieved 14 December 2011)
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Electric Railways". 'Stendec Systems'. 2007. Archived from the original on 28 September 2007. Retrieved 29 March 2007.
- ↑ Glover, John (2001). Southern Electric. Hersham: Ian Allan. p. 141. ISBN 0 7110 2807 9.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Chatham Main Line. |