屎
| ||||||||
Translingual
Han character
屎 (radical 44, 尸+6, 9 strokes, cangjie input 尸火木 (SFD), four-corner 77294, composition ⿸尸米)
References
- KangXi: page 301, character 25
- Dai Kanwa Jiten: character 7689
- Dae Jaweon: page 598, character 15
- Hanyu Da Zidian: volume 2, page 973, character 6
- Unihan data for U+5C4E
Chinese
| simp. and trad. |
屎 | |
|---|---|---|
Glyph origin
| Historical forms of the character 屎 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Shang | Western Zhou | Warring States | Shuowen Jiezi (compiled in Han) |
| Oracle bone script | Bronze inscriptions | Bronze inscriptions | Small seal script |
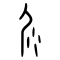 |
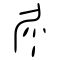 |
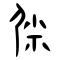 |
 |
| Characters in the same phonetic series (尸) (Zhengzhang, 2003) | |
|---|---|
| Old Chinese | |
| 杘 | *l̥ʰis |
| 尸 | *hli |
| 鳲 | *hli |
| 屍 | *hli, *hlis |
| 屎 | *hliʔ, *hri |
Ideogrammic compound (會意) : 尸 (“body”) + 米 (“rice”). The 米 component was originally three to five dots (four dots was the most common one; faeces coming out of the backside) in the oracle bone script, thus representing a man defecating.
Etymology 1
From Proto-Sino-Tibetan *kləj (“excrement”).
Pronunciation
Definitions
屎
Compounds
|
Etymology 2
Pronunciation
Definitions
屎
- † Only used in 殿屎 (“to groan”).
Japanese
Etymology 1
| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 屎 |
| くそ Hyōgaiji |
| kun’yomi |
From Proto-Japonic *kuso. Cognate with 臭い (kusai, “stinky, smelly”), 腐る (kusaru, “to rot, to become stinky”).[1]
Alternative forms
Derived terms
- 屎っ垂れ (kusottare): dingleberry (vulgar epithet)
- 目屎 (mekuso): rheum, eye mucus
Idioms
- 屎にする (kuso ni suru): “to turn something into shit; to treat something as shit” → to make something worthless; to treat something as worthless
- 屎の役にも立たぬ (kuso no yaku ni mo tatanu): “not even standing in the role of shit” → not even good for shit
- (See 役に立つ (yaku ni tatsu): “to be useful, to play a role”)
- 屎も味噌も一緒 (kuso mo miso mo issho): “both crap and miso together” → a situation where it is difficult to tell the good from the bad
Usage notes
This is not considered as profane as the English glosses. For instance, a child of five using the Japanese interjection kuso would be unremarkable, whereas it would be very socially inappropriate for a child of five to use the English interjection shit.
Suffix
屎 (hiragana くそ, rōmaji -kuso)
- A derogatory emphasizing suffix.
- 下手屎
- hetakuso
- crappy bad at something; to be shit at doing something
- 襤褸屎
- borokuso
- broken down for shit, raggedy-ass
- 下手屎
Etymology 2
| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 屎 |
| ばば Hyōgaiji |
| kun’yomi |
Appears to derive from baby talk.[1][2] Compare English poopoo.
Pronunciation
Alternative forms
Noun
Idioms
- 猫屎する (nekobabasuru): to sweep something under the rug → to hide a problem without actually dealing with it (from how a cat will bury its poop)
Korean
Hanja
屎 • (si) (hangeul 시, revised si, McCune–Reischauer si)
- This term needs a translation to English. Please help out and add a translation, then remove the text
{{rfdef}}.
Vietnamese
Han character
屎 (thỉ, xái)
- This term needs a translation to English. Please help out and add a translation, then remove the text
{{rfdef}}.