Regional Municipality of York
The Regional Municipality of York, also called York Region, is a regional municipality in Southern Ontario, Canada, between Lake Simcoe and Toronto. It replaced the former York County in 1971, and is part of the Greater Toronto Area and the inner ring of the Golden Horseshoe. The regional government is headquartered in Newmarket.
York Region | |
|---|---|
Regional municipality (upper-tier) | |
| Regional Municipality of York | |
Clockwise from top left: Historic Aurora Cultural Centre, Sibbald Point Provincial Park, Vaughan Metro Centre, rural Nobleton, Markham Civic Centre, Canada's Wonderland | |
Seal | |
| Motto(s): Ontario's Rising Star | |
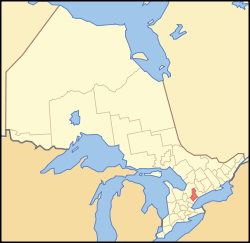 Map showing York Region's location in Ontario | |
| Coordinates: 44°3′5″N 79°28′49″W | |
| Country | Canada |
| Province | Ontario |
| Established | 1792 (County) |
| Established | 1971 (Regional Municipality) |
| Seat | Newmarket |
| Government | |
| • Chair | Wayne Emmerson[1] |
| • Governing Body | York Regional Council |
| Area | |
| • Total | 1,762.13 km2 (680.36 sq mi) |
| Population (2016)[2] | |
| • Total | 1,109,909 |
| • Density | 629.9/km2 (1,631/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC-5 (Eastern (EST)) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC-4 (Eastern (EDT)) |
| Website | www.york.ca |
The 2016 census population was 1,109,909, with a growth rate of 7.5% from 2011 to 2016.[3] The Government of Ontario expects its population to surpass 1.5 million residents by 2031.[4]
History
At a meeting in Richmond Hill on May 6, 1970, officials representing the municipalities of York County approved plans for the creation of a regional government entity to replace York County.[5] The plan had been presented in 1969 by Darcy McKeough, the Ontario Minister of Municipal Affairs, taking about a year to determine municipal boundaries within the new regional government.[5]
The Regional Municipality of York was created by Act of the Legislative Assembly of Ontario in 1970, which took effect on January 1, 1971.[6] The creation of the regional municipality resulted in the consolidation of the fourteen former municipalities of York County into nine new municipalities:[7]
| Area municipality | Created from | Police villages dissolved |
|---|---|---|
| Town of Aurora | Town of Aurora, annexing portions of the Townships of King and Whitchurch | |
| Town of East Gwillimbury | Portion of the Township of East Gwillimbury |
|
| Town of Georgina | Townships of Georgina and North Gwillimbury, and the Village of Sutton | |
| Township of King | Portion of the Township of King | |
| City of Markham | Town of Markham, annexing portion of the Township of Markham |
|
| Town of Newmarket | Town of Newmarket, annexing portions of the Townships of East Gwillimbury, King and Whitchurch | |
| City of Richmond Hill | City of Richmond Hill, annexing portions of the Townships of King, Markham, Vaughan and Whitchurch | |
| City of Vaughan | Village of Woodbridge, annexing portions of the Townships of King and Vaughan |
|
| Town of Whitchurch–Stouffville | Village of Stouffville, annexing portions of the Townships of Markham (four lots south of Main Street) and Whitchurch |
The township of Whitchurch merged with the town of Stouffville to create the town of Whitchurch–Stouffville, ceding land to Aurora, Newmarket, and Richmond Hill to the west of the proposed Highway 404 and annexing a northern strip of land from the township of Markham.[9] The eastern boundary of the new town of Markham was defined to be at Yonge Street, where its northern boundary was formed with Richmond Hill (to which it ceded land[5]) and its western boundary with the new town Vaughan.[9] The new town of Vaughan would consist of all communities in the area bounded by Markham and Richmond Hill in the east, Metro Toronto in the south, the periphery of the regional municipality in the west, and the new township of King in the north.[9]
The townships of Georgina, North Gwillimbury, and Sutton were merged into the township of Georgina, and the East Gwillimbury neighbourhood of East Gwillimbury Heights was merged into Newmarket.[9] King formed the northwestern part of the new region, but the eastern lot from Bathurst Street to Yonge Street was ceded to Newmarket, Aurora, and Oak Ridges, the last of which became a part of Richmond Hill.[9] The boundary between Aurora and Newmarket was defined to be St. John's Sideroad, and Newmarket's northern boundary was defined to be Green Lane.[9]
The towns of Aurora, Newmarket, and Richmond Hill were defined to be the growth centres for the regional municipality, which was to become a greenbelt between the denser urban areas of Toronto to the south and Barrie to the north.[7] The growth centres were each restricted to grow to a maximum population of 25,000 by 2000,[7] and the regional municipality to 300,000.[9]
The municipal realignment merged 40% of East Gwillimbury's population into Newmarket.[10] The council of East Gwillimbury voted to amalgamate with Newmarket, but Newmarket council opposed the amalgamation.[10] In the plan presented by McKeough, the councils of the towns of Newmarket and Aurora were given ten years to decide whether or not to amalgamate.[7]
The internal municipal realignments resulted in some politicians residing in a new municipality from that which they represented at the time of realignment.[5] The reeve of Whitchurch Township resided in the western portion of the town that was annexed by Aurora, three East Gwillimbury councillors resided in land annexed by Newmarket, including its future mayor Ray Twinney, and King councillor Gordon Rowe was a resident of Oak Ridges, which became part of Richmond Hill.[5]
Hydro Commissions
Because of the mix of urban and rural areas in the Region, the provision of electricity was governed in a different manner from the rest of the regional services:[11]
- the hydro-electric commissions and public utilities commissions that existed at the end of 1970 continued to provide electricity within their respective areas;
- the councillors of the former Township of Vaughan and the trustees of the former Police Village of King City became members of new Hydro-Electric Commissions for their respective areas;
- Ontario Hydro continued to have responsibility for providing electricity to those portions of the Region that were not served by any of the above commissions.
Electric distribution was partially rationalized in 1978,[12] when:
- hydro-electric commissions were established for all area municipalities except East Gwillimbury[13] (but it could establish a commission later on, subject to Ontario Hydro's consent);[14]
- effective January 1, 1979, all assets of the former commissions in the Region were transferred to the new commissions;[15]
- Ontario Hydro withdrew its provision of services from all areas except those in East Gwillimbury, Georgina, King and Whitchurch-Stouffville;[15]
- Georgina, King and Whitchurch-Stouffville could take over responsibility for such areas at a later date, subject to Ontario Hydro's consent[15]
Police
The York Regional Police was also created at this time, amalgamating the fourteen town, township, and village police forces.[5]
Geography
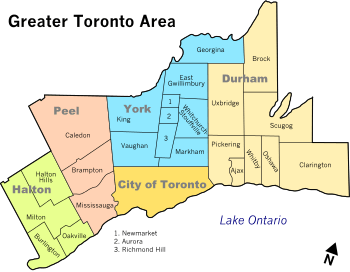
York Region covers 1,762 square kilometres from Lake Simcoe in the north to the city of Toronto in the south. Its eastern border is shared with Durham Region, to the west is Peel Region, and Simcoe County is to the northwest. A detailed map of the region[16] showing its major roads, communities and points of interest is available.
Towns and cities in York Region include:
- Town of Aurora
- Town of East Gwillimbury
- Town of Georgina
- Township of King
- City of Markham
- Town of Newmarket
- City of Richmond Hill
- City of Vaughan
- Town of Whitchurch–Stouffville
There is also one First Nation with an Indian reserve, where the Chippewas of Georgina Island First Nation reside on Georgina Island, Fox Island and Snake Island.
York Region's landscape includes farmlands, wetlands and kettle lakes, the Oak Ridges Moraine and over 2,070 hectares of regional forest, in addition to the built-up areas of its municipalities. The highest point in the region is within the rolling hills of the moraine near Dufferin St. & Aurora Side Road at 360m ASL (1,243 feet) [17]
Climate
York Region is situated in the humid continental climate (Köppen Dfb) zone with warm summers and cold winters, ample snowfall, more in the northern part of York region much of it derived from the wind driven snowbelt streamer activity.
| Climate data for Markham 1981–2010 (Toronto/Buttonville Municipal Airport) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high humidex | 16.0 | 14.4 | 29.2 | 35.7 | 41.0 | 44.6 | 50.9 | 47.4 | 43.6 | 37.8 | 24.9 | 20.6 | 50.9 |
| Record high °C (°F) | 14.9 (58.8) |
14.9 (58.8) |
26.0 (78.8) |
31.7 (89.1) |
34.6 (94.3) |
36.6 (97.9) |
37.2 (99.0) |
37.8 (100.0) |
34.4 (93.9) |
31.0 (87.8) |
22.1 (71.8) |
18.0 (64.4) |
37.8 (100.0) |
| Average high °C (°F) | −1.5 (29.3) |
−0.9 (30.4) |
4.5 (40.1) |
12.1 (53.8) |
19.1 (66.4) |
24.6 (76.3) |
27.1 (80.8) |
26.0 (78.8) |
21.5 (70.7) |
14.1 (57.4) |
7.2 (45.0) |
0.9 (33.6) |
12.9 (55.2) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −5.8 (21.6) |
−5.6 (21.9) |
−0.4 (31.3) |
6.7 (44.1) |
13.0 (55.4) |
18.6 (65.5) |
21.2 (70.2) |
20.2 (68.4) |
15.7 (60.3) |
8.9 (48.0) |
3.1 (37.6) |
−2.9 (26.8) |
7.7 (45.9) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −10.1 (13.8) |
−10.2 (13.6) |
−5.3 (22.5) |
1.2 (34.2) |
6.8 (44.2) |
12.6 (54.7) |
15.2 (59.4) |
14.3 (57.7) |
9.9 (49.8) |
3.6 (38.5) |
−1.1 (30.0) |
−6.8 (19.8) |
2.5 (36.5) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −35.2 (−31.4) |
−25.7 (−14.3) |
−25.6 (−14.1) |
−10.1 (13.8) |
−2.1 (28.2) |
1.9 (35.4) |
6.9 (44.4) |
4.2 (39.6) |
−2.0 (28.4) |
−7.4 (18.7) |
−15.0 (5.0) |
−26.0 (−14.8) |
−35.2 (−31.4) |
| Record low wind chill | −42.6 | −37.4 | −35.6 | −18.6 | −4.4 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | −4.2 | −8.8 | −23.9 | −36.6 | −42.6 |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 62.1 (2.44) |
50.5 (1.99) |
53.2 (2.09) |
74.1 (2.92) |
79.6 (3.13) |
82.8 (3.26) |
79.0 (3.11) |
76.2 (3.00) |
81.8 (3.22) |
68.0 (2.68) |
80.0 (3.15) |
65.7 (2.59) |
852.9 (33.58) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 26.0 (1.02) |
22.9 (0.90) |
33.6 (1.32) |
66.7 (2.63) |
79.5 (3.13) |
82.8 (3.26) |
78.8 (3.10) |
76.2 (3.00) |
81.8 (3.22) |
66.7 (2.63) |
68.3 (2.69) |
34.2 (1.35) |
717.4 (28.24) |
| Average snowfall cm (inches) | 38.9 (15.3) |
29.9 (11.8) |
19.3 (7.6) |
7.5 (3.0) |
0.1 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.6 (0.2) |
12.1 (4.8) |
34.2 (13.5) |
142.6 (56.1) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.2 mm) | 16.7 | 12.9 | 12.0 | 12.3 | 12.0 | 11.8 | 11.2 | 9.9 | 10.8 | 13.2 | 14.5 | 15.3 | 152.7 |
| Average rainy days (≥ 0.2 mm) | 5.8 | 3.8 | 6.7 | 10.8 | 12.0 | 11.8 | 11.2 | 9.9 | 10.8 | 13.0 | 11.3 | 6.6 | 113.7 |
| Average snowy days (≥ 0.2 cm) | 13.4 | 10.8 | 7.0 | 2.9 | 0.13 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.48 | 4.7 | 10.8 | 50.2 |
| Average relative humidity (%) (at 1500 LST) | 69.6 | 64.0 | 57.8 | 52.9 | 52.3 | 53.9 | 53.4 | 55.9 | 59.2 | 62.4 | 68.9 | 71.1 | 60.1 |
| Source: Environment Canada[18] | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Richmond Hill (1981−2010) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 14.5 (58.1) |
14.5 (58.1) |
25.5 (77.9) |
31.0 (87.8) |
34.5 (94.1) |
35.0 (95.0) |
37.0 (98.6) |
37.0 (98.6) |
34.4 (93.9) |
29.4 (84.9) |
23.3 (73.9) |
20.0 (68.0) |
37.0 (98.6) |
| Average high °C (°F) | −2.2 (28.0) |
−0.6 (30.9) |
4.4 (39.9) |
12.1 (53.8) |
19.0 (66.2) |
24.2 (75.6) |
26.8 (80.2) |
25.6 (78.1) |
20.9 (69.6) |
13.7 (56.7) |
6.7 (44.1) |
0.8 (33.4) |
12.6 (54.7) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −6.2 (20.8) |
−4.9 (23.2) |
−0.3 (31.5) |
6.9 (44.4) |
13.3 (55.9) |
18.7 (65.7) |
21.4 (70.5) |
20.3 (68.5) |
15.9 (60.6) |
9.1 (48.4) |
3.1 (37.6) |
−2.7 (27.1) |
7.9 (46.2) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −10.2 (13.6) |
−9.1 (15.6) |
−5 (23) |
1.7 (35.1) |
7.7 (45.9) |
13.1 (55.6) |
15.9 (60.6) |
15.1 (59.2) |
10.8 (51.4) |
4.5 (40.1) |
−0.5 (31.1) |
−6.1 (21.0) |
3.2 (37.8) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −32.5 (−26.5) |
−29 (−20) |
−27 (−17) |
−15 (5) |
−5.6 (21.9) |
0.6 (33.1) |
4.4 (39.9) |
3.0 (37.4) |
−3.3 (26.1) |
−7.8 (18.0) |
−15.5 (4.1) |
−30 (−22) |
−32.5 (−26.5) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 62.3 (2.45) |
58.0 (2.28) |
58.8 (2.31) |
70.1 (2.76) |
81.6 (3.21) |
80.2 (3.16) |
83.5 (3.29) |
89.2 (3.51) |
88.4 (3.48) |
69.1 (2.72) |
87.2 (3.43) |
66.8 (2.63) |
895.2 (35.24) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 25.2 (0.99) |
26.3 (1.04) |
33.6 (1.32) |
62.5 (2.46) |
81.5 (3.21) |
80.2 (3.16) |
83.5 (3.29) |
89.2 (3.51) |
88.4 (3.48) |
67.6 (2.66) |
73.5 (2.89) |
33.1 (1.30) |
744.6 (29.31) |
| Average snowfall cm (inches) | 37.1 (14.6) |
31.7 (12.5) |
25.2 (9.9) |
7.6 (3.0) |
0.1 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
1.5 (0.6) |
13.7 (5.4) |
33.7 (13.3) |
150.6 (59.3) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.2 mm) | 18.3 | 13.9 | 14.4 | 13.6 | 13.6 | 11.9 | 11.3 | 11.2 | 12.4 | 13.4 | 15.2 | 16.2 | 165.2 |
| Average rainy days (≥ 0.2 mm) | 4.9 | 4.3 | 7.4 | 11.7 | 13.6 | 11.9 | 11.3 | 11.2 | 12.4 | 13.3 | 11.4 | 7.0 | 120.2 |
| Average snowy days (≥ 0.2 cm) | 15.3 | 11.3 | 9.0 | 3.2 | 0.12 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.62 | 5.3 | 11.6 | 56.5 |
| Source: Environment Canada[19] | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Stouffville 1971–2000 | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 11.0 (51.8) |
13.5 (56.3) |
23.0 (73.4) |
30.5 (86.9) |
32.0 (89.6) |
34.0 (93.2) |
35.5 (95.9) |
36.5 (97.7) |
32.8 (91.0) |
25.5 (77.9) |
22.8 (73.0) |
18.0 (64.4) |
36.5 (97.7) |
| Average high °C (°F) | −3.2 (26.2) |
−2.4 (27.7) |
3.1 (37.6) |
11.1 (52.0) |
18.5 (65.3) |
23.1 (73.6) |
26.2 (79.2) |
24.7 (76.5) |
19.9 (67.8) |
12.8 (55.0) |
6.0 (42.8) |
−0.6 (30.9) |
11.6 (52.9) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −11.6 (11.1) |
−10.9 (12.4) |
−5.7 (21.7) |
1.2 (34.2) |
7.4 (45.3) |
11.8 (53.2) |
14.8 (58.6) |
14 (57) |
9.6 (49.3) |
3.5 (38.3) |
−1.0 (30.2) |
−7.7 (18.1) |
2.1 (35.8) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −35.5 (−31.9) |
−28.3 (−18.9) |
−28.0 (−18.4) |
−17.0 (1.4) |
−3.3 (26.1) |
0.0 (32.0) |
7.0 (44.6) |
2.5 (36.5) |
−2.0 (28.4) |
−7.2 (19.0) |
−15.0 (5.0) |
−31.5 (−24.7) |
−35.5 (−31.9) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 52.8 (2.08) |
53.5 (2.11) |
62.8 (2.47) |
65.5 (2.58) |
81.2 (3.20) |
73.3 (2.89) |
75.8 (2.98) |
99.3 (3.91) |
79.2 (3.12) |
81.2 (3.20) |
78.5 (3.09) |
65.6 (2.58) |
868.6 (34.20) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 17.9 (0.70) |
23.3 (0.92) |
43.5 (1.71) |
60.5 (2.38) |
81.1 (3.19) |
73.3 (2.89) |
75.8 (2.98) |
99.3 (3.91) |
79.2 (3.12) |
80.6 (3.17) |
70.3 (2.77) |
33.0 (1.30) |
737.7 (29.04) |
| Average snowfall cm (inches) | 34.9 (13.7) |
30.2 (11.9) |
19.3 (7.6) |
5.0 (2.0) |
0.1 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.6 (0.2) |
8.2 (3.2) |
32.7 (12.9) |
131.0 (51.6) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.2 mm) | 11.0 | 10.3 | 10.1 | 10.8 | 11.0 | 10.7 | 9.2 | 10.8 | 10.4 | 13.0 | 12.6 | 12.3 | 131.9 |
| Average rainy days (≥ 0.2 mm) | 2.9 | 3.1 | 6.2 | 9.8 | 11.0 | 10.7 | 9.2 | 10.8 | 10.4 | 13.0 | 10.7 | 5.1 | 102.6 |
| Average snowy days (≥ 0.2 cm) | 8.4 | 7.7 | 4.7 | 1.2 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 2.6 | 8.3 | 33.1 |
| Source: Environment Canada[20] | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Vaughan 1981–2010 (Woodbridge) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 17.0 (62.6) |
15.5 (59.9) |
26.5 (79.7) |
31.5 (88.7) |
33.0 (91.4) |
36.0 (96.8) |
39.0 (102.2) |
37.2 (99.0) |
36.1 (97.0) |
30.6 (87.1) |
25.0 (77.0) |
19.5 (67.1) |
39.0 (102.2) |
| Average high °C (°F) | −2.5 (27.5) |
−0.5 (31.1) |
4.3 (39.7) |
12.0 (53.6) |
18.8 (65.8) |
24.1 (75.4) |
26.9 (80.4) |
25.4 (77.7) |
20.9 (69.6) |
13.9 (57.0) |
6.9 (44.4) |
0.8 (33.4) |
12.6 (54.7) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −6.6 (20.1) |
−4.8 (23.4) |
−0.4 (31.3) |
6.6 (43.9) |
12.9 (55.2) |
18.1 (64.6) |
20.8 (69.4) |
19.6 (67.3) |
15.4 (59.7) |
9.0 (48.2) |
3.1 (37.6) |
−2.8 (27.0) |
7.6 (45.7) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −10.7 (12.7) |
−9.2 (15.4) |
−5.2 (22.6) |
1.2 (34.2) |
6.8 (44.2) |
12.0 (53.6) |
14.7 (58.5) |
13.8 (56.8) |
9.8 (49.6) |
4.0 (39.2) |
−0.8 (30.6) |
−6.4 (20.5) |
2.5 (36.5) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −34.5 (−30.1) |
−30.0 (−22.0) |
−29.4 (−20.9) |
−17.2 (1.0) |
−6.7 (19.9) |
−1.7 (28.9) |
2.8 (37.0) |
−0.6 (30.9) |
−5.0 (23.0) |
−11.7 (10.9) |
−18.3 (−0.9) |
−30.0 (−22.0) |
−34.5 (−30.1) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 50.3 (1.98) |
44.2 (1.74) |
49.2 (1.94) |
63.3 (2.49) |
79.1 (3.11) |
76.3 (3.00) |
70.4 (2.77) |
80.4 (3.17) |
84.6 (3.33) |
66.5 (2.62) |
78.3 (3.08) |
57.4 (2.26) |
799.8 (31.49) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 20.4 (0.80) |
23.2 (0.91) |
31.4 (1.24) |
59.6 (2.35) |
79.1 (3.11) |
76.3 (3.00) |
70.4 (2.77) |
80.4 (3.17) |
84.6 (3.33) |
66.0 (2.60) |
71.1 (2.80) |
34.6 (1.36) |
697.0 (27.44) |
| Average snowfall cm (inches) | 29.9 (11.8) |
21.1 (8.3) |
17.8 (7.0) |
3.7 (1.5) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.45 (0.18) |
7.2 (2.8) |
22.8 (9.0) |
102.8 (40.5) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.2 mm) | 13.5 | 10.3 | 10.7 | 11.8 | 12.0 | 10.8 | 9.5 | 9.6 | 10.6 | 12.7 | 13.1 | 12.8 | 137.4 |
| Average rainy days (≥ 0.2 mm) | 4.2 | 4.4 | 6.4 | 10.7 | 12.0 | 10.8 | 9.5 | 9.6 | 10.6 | 12.6 | 11.1 | 6.5 | 108.3 |
| Average snowy days (≥ 0.2 cm) | 10.2 | 6.8 | 5.1 | 1.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.23 | 3.0 | 7.5 | 34.3 |
| Source: Environment Canada[21] | |||||||||||||
Government


The region is governed by York Regional Council, which consists of 20 elected representatives from each of the constituent towns and cities in the region. These include each of the nine mayors, and 11 regional councillors who are elected from the constituent municipalities as follows:[22]
- 1 from Georgina
- 1 from Newmarket
- 2 from Richmond Hill
- 3 from Vaughan
- 4 from Markham
The leader of Council is referred to as "Regional Chair and CEO". Wayne Emmerson, a former mayor of Whitchurch-Stouffville, was elected to this office in December 2014.[1]
In October 2008, York Regional Municipality was named one of Greater Toronto's Top Employers by Mediacorp Canada Inc.[23]
Federal and provincial representation
Starting with the 2015 federal election, York Region encompasses all or part of the federal electoral districts of Aurora—Oak Ridges—Richmond Hill, King—Vaughan, Markham—Stouffville, Markham—Thornhill, Markham—Unionville, Newmarket—Aurora, Richmond Hill, Thornhill, Vaughan—Woodbridge, and York—Simcoe.
Provincially, York Region is represented in the Legislative Assembly of Ontario by Members of Provincial Parliament for the electoral districts of Aurora—Oak Ridges—Richmond Hill, Markham—Unionville, Newmarket—Aurora, Markham—Thornhill, Markham—Stouffville, Richmond Hill, Thornhill, King—Vaughan, Vaughan—Woodbridge, and York—Simcoe.
Economy

The economy of York Region is diverse. In general, the economy includes a full range of businesses from industrial to high-tech to rural/agricultural. New developments continually consume space year after year, and tend to be focused along the Yonge Street corridor from Vaughan/Richmond Hill in the south to Newmarket/Aurora in the north. There are ongoing conflicts between conservationists and developers over land use. Most contentious is the conflict use of the Oak Ridges Moraine.
Shopping
Major shopping centres in York Region include:
- Aurora North Smart Centre (Aurora)
- Hillcrest Mall (Richmond Hill)
- Green Lane Centre (East Gwillimbury)
- King Square Shopping Mall (Markham)
- Markville Shopping Centre (Markham)
- Pacific Mall (Markham)
- The Promenade Shopping Centre (Vaughan)
- Times Square (Richmond Hill)
- Langham Square (Markham)
- Upper Canada Mall (Newmarket)
- Woodside Mall (Markham)
- Vaughan Mills (Vaughan)
- First Markham Place (Markham)
Demographics
The 2016 census population estimate by Statistics Canada was 1,109,909 residents.[2] It is the third-largest census division in Ontario, next to that of Toronto and Peel Region,[24] and seventh-largest in Canada.[25] Its population density of 585.9 residents per square km is 11th highest in Canada.[25]
Population by municipalities:
| Municipality | Status | Population (1996) | Population (2001) | Population (2006) | Population (2011) | Population (2016)[26] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aurora | Town | 34,857 | 40,167 | 47,629 | 53,203 | 55,445 |
| East Gwillimbury | Town | 19,770 | 20,555 | 21,069 | 22,473 | 23,991 |
| Georgina | Town | 34,777 | 39,263 | 42,346 | 43,517 | 45,418 |
| King | Township | 18,223 | 18,533 | 19,487 | 19,899 | 24,512 |
| Markham | City | 173,383 | 208,615 | 261,573 | 301,709 | 328,966 |
| Newmarket | Town | 57,125 | 65,788 | 74,295 | 79,978 | 84,224 |
| Richmond Hill | City | 101,725 | 132,030 | 162,704 | 185,541 | 195,022 |
| Vaughan | City | 132,549 | 182,022 | 238,866 | 288,301 | 306,233 |
| Whitchurch–Stouffville | Town | 19,835 | 22,008 | 24,390 | 37,628 | 45,837 |
| York (total) | Regional Municipality | 592,445 | 729,254 | 892,712 | 1,032,524 | 1,109,909 |
| Ontario | Province | 10,753,573 | 11,410,046 | 12,160,282 | 12,851,821 | 13,448,494 |
In the 2016 Canadian census, English is the mother tongue of 47.6% of the residents of York Region. Cantonese is the mother tongue for 9.9% of the population, followed by Mandarin (7.2%), Italian (5.0%), Russian and Persian (3.4% each).[27] The most common ethnic and pan-ethnic origins in the Regional Municipality of York were as follows:
| Ethnic origin | Population[28] | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Chinese | 255,965 | 23.3 |
| Italian | 159,465 | 14.5 |
| Canadian | 125,575 | 11.4 |
| English | 116,760 | 10.6 |
| Scottish | 81,155 | 7.4 |
| Irish | 78,645 | 7.1 |
| East Indian | 72,855 | 6.6 |
| Russian | 47,550 | 4.3 |
| German | 42,540 | 3.9 |
| Iranian | 41,005 | 3.7 |
| Polish | 39,255 | 3.6 |
| French | 34,620 | 3.1 |
| Filipino | 28,835 | 2.6 |
| Ukrainian | 26,070 | 2.4 |
| Sri Lankan | 22,040 | 2.0 |
| Canada 2016 Census | Population | % of Total Population | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Panethnicity group Source:[29] |
European | 523,255 | 47.5% |
| East Asian | 264,030 | 24% | |
| South Asian | 116,695 | 10.6% | |
| Middle Eastern | 54,840 | 5% | |
| Southeast Asian | 39,920 | 3.6% | |
| Black | 27,775 | 2.5% | |
| Latin American | 13,650 | 1.2% | |
| Aboriginal | 9,930 | 0.9% | |
| Other | 24,295 | 2.2% | |
| Total population | 1,100,950 | 100% | |
Health Care
There are currently three hospitals within the Municipality of York including:
All three hospitals are part of the Local Health Integration Network (LHIN) Hospital Partnerships.
In 2011 the construction of Mackenzie Vaughan Hospital was approved by the Minister of Health and Long-Term Care, Deb Matthews. The hospital site is proposed within the City of Vaughan at Major Mackenzie Drive on the east side of Highway 400. Current plans include a new $80 million building.
Boomerang Health, in Vaughan, is a centre that provides multidisciplinary rehabilitation and medical services geared specifically for children and adolescents, in collaboration with The Hospital for Sick Children.[30]
Transportation

The arterial road network in York Region is a grid, with most roads running north–south or east–west. This was done under the orders of British surveyor Augustus Jones during the 1790s. York Region assigned approximately 50 roads as York Regional Routes, meaning that the cost of maintaining of these roads is paid for by York Region.
The major highways in the Region are:
- Highway 7 (east-west)
- Highway 9 (east-west)
- Highway 48 (north-south)
- Highway 400 (north-south)
- Highway 404 (north-south)
- Highway 407 (east-west)
- Highway 427 (north-south)
Former highways include:
- Highway 11 (north-south)
- Highway 27 (north-south)
- Highway 47 (east-west)
- Highway 49 (east-west)
- Highway 50 (north-south)
- Note: Highway 27 and Highway 50 are still referred to as such on municipal road signs, but are no longer provincial highways.
Air transportation

Most air travel is served by Toronto Pearson International Airport, which is outside of York Region and is Canada's largest airport. Buttonville Municipal Airport is a regional airport in Markham, used for general aviation and business aircraft. There are also a few unpaved airports serving the region: Hare Field in Holland Landing (East Gwillimbury), Belhaven Airport in Georgina, and Stouffville Aerodrome north of Stouffville.
Public transportation
York Region is served by:
- York Region Transit (YRT), which includes the Viva bus rapid transit network
- GO Transit, which offers bus and train service
- Toronto Transit Commission (TTC), which has several bus routes which cross York's southern border, and which provide service along many north-south arterial streets in Vaughan, Richmond Hill and Markham. Since December 17, 2017, Vaughan has been served by the University portion of the Line 1 Yonge-University of Toronto's subway system, and a future extension of the Yonge Street portion of the line will eventually serve Richmond Hill and Markham.
Until 2001, the towns of York Region operated separate public transit services, which did not connect very well with each other. YRT was created by the Regional Government to combine five of these services:
- Vaughan Transit
- Markham Transit
- Richmond Hill Transit
- Aurora Transit - merged in 1999 with Newmarket Transit
- Newmarket Transit
Since 2001, bus routes have been extensively enhanced in the five communities which had pre-existing services, but YRT's services to East Gwillimbury is limited to two routes, and service to King, Georgina and Whitchurch-Stouffville are even more limited due to the relatively small populations in each of those towns.
Water
Water in southern York is provided by Toronto Water and Peel Region by way of 3 pumping stations and reservoirs (Bayview, Dufferin and Milliken (tank and underground reservoir)) using water from Lake Ontario.[31] Keswick and Sutton obtain water from Lake Simcoe by way of water treatment plants. The remainder of York obtains water from a combination of water from Lake Ontario and underground wells. Some wells are maintained by the Region and the rest privately.
- Georgina -water from Lake Simcoe and private wells
- East Gwillimbury - region and private wells
- Newmarket - region wells and water from Lake Ontario [32]
- Whitchurch-Stouffville - Region wells, water from Lake Ontario, private wells
- Markham - water from Lake Ontario and private wells
- Richmond Hill - water from Lake Ontario and private wells
- Aurora - water from Lake Ontario and private wells
- Vaughan - water from Lake Ontario and private wells
- King - water from Lake Ontario, Region and private wells
Water is distributed from 14 water pumping stations and stored at 37 elevated tanks and reservoirs:
List of water tanks
- Reesor Park water tank - built 1971, now out of service and dismantled
- Newmarket - 211 Harry Walker Parkway South
- Richmond Hill - 81 Coons Road
- Schomberg - 186 Church Street, built 1997
- King - 60 Fisher Street, built 1982
- Stouffville - 12519 Tenth Line, built 1984
- Stouffville - Bethesda Rd, built 2005
- Aurora - 126 Allenvale Drive, 240 Orchard Heights Boulevard, built 1984
- Aurora - 180 Bloomington Road, built 2008
- Markham - 4355 14th Avenue
Treatment Plants
- Sutton Water Treatment Plant - closed
- Georgina Water Treatment Plant - replaces Sutton plant
- Keswick Water Treatment Plant
- Schomberg Water Treatment Plant
Education
Four public school boards operate primary and secondary institutions in York Region, Conseil scolaire catholique MonAvenir (CSCM), Conseil scolaire Viamonde (CSV), the York Catholic District School Board (YCDSB), and the York Region District School Board (YRDSB). CSV and YRDSB operate as secular public school boards, the former operating French first language institution, whereas the latter operated English first language institutions. The other two school boards, MonAvenir and YCDSB, operate as public separate school boards, the former operating French first language separate schools, the latter operating English first language separate schools.
YRDSB is the largest public school board in the region, operating 175 elementary schools, and 33 secondary schools. YCDSB operates 83 elementary schools, and 15 secondary schools, while MonAvenir operates five elementary schools, and two secondary schools. CSV is the smallest public school board in the York Region, operating three elementary schools, and one secondary school in the region.
Along with public schools, the region also holds a number of religious and private schools including:
- As-Sadiq Islamic School (Vaughan)
- Academy for Gifted Children (Richmond Hill)
- Country Day School (King)
- Holy Trinity School (Richmond Hill)
- Leo Baeck Day School (Vaughan)
- Ner Israel Yeshiva College (Vaughan)
- Netivot HaTorah Day School (Vaughan)
- Pickering College (Newmarket)
- St. Andrew's College (Aurora)
- St. Thomas of Villanova College (King)
- Town Centre Montessori Private School (Markham)
- Toronto Waldorf School (Vaughan)
In addition to primary and secondary levels of education, the region is also home to post-secondary institutions such as Seneca College. The college operates three campuses spread throughout York Region, in King, Markham and Newmarket, as well as additional campuses in Toronto. The region presently does not host a university.
News media
- York Region Media Group
- CKVR - CTV Two (based in Barrie)
- CFU758 - 90.7 RAV FM (Vaughan)
- CKDX 88.5FM - Foxy 88-5 (Newmarket)
- CFMS-FM - 105.9 The Region (Markham)
- CIWS-FM - WhiStle Community Radio Whitchurch–Stouffville
York's news media is also served by the outlets based in Toronto.
Attractions
York Region has an unusual assortment of points of interest, ranging from nature reserves to pioneer-era museums, to a modern amusement park.

Vaughan's major attractions include the McMichael Canadian Art Collection, in the community of Kleinburg, that features works by Canadian artists including Inuit and First Nations artists. Canada's Wonderland, which features roller coasters and other rides, concerts and fireworks shows, is also in Vaughan.
Heritage sites and historical museums in the Region include:
- Hillary House National Historic Site (Aurora)
- Historic Main Street Newmarket (Newmarket)
- Georgina Military Museum (Georgina)
- Georgina Village Museum (Georgina)
- King Township Museum (King)
- Markham Museum (Markham)[33]
- RHLS Narrow Gauge Railway (Whitchurch–Stouffville)[34]
- Sharon Temple National Historic Site (East Gwillimbury)
- Whitchurch-Stouffville Museum (Whitchurch–Stouffville)[35]
- York-Durham Heritage Railway (Whitchurch–Stouffville)[36]
Following is a sample of other attractions in the area:
- Applewood Farm Winery (Whitchurch–Stouffville)[37]
- Canadian Heritage Humber River
- Fred Varley Art Gallery (Markham)
- Canada's Wonderland (Vaughan)
- Oak Ridges Trail
- Puck's Farm (King)
- Richmond Hill Centre for the Performing Arts
- Sutton-Zephyr Trail
- Willow Springs Winery (Whitchurch–Stouffville)[38]
- Words Alive Literary Festival (East Gwillimbury)
- Bare Oaks Family Naturist Park (East Gwillimbury)
- York Demonstration Forest (Whitchurch–Stouffville)
- York9 FC - A professional soccer team (Vaughan)
Travel Region
York Region lies within the Central Counties of Ontario, a tourism related association.
Protected areas

- Baker Sugarbush Conservation Area
- Boyd Conservation Area
- Bruce's Mill Conservation Area
- Duclos Point Provincial Nature Reserve
- Gold Creek Conservation Area
- Holland Landing Prairie Provincial Nature Reserve
- Kortright Centre for Conservation
- Lake St. George Conservation Area
- Mabel Davis Conservation Area
- Milne Park
- Pickering Lands Preservation Site
- Rogers Reservoir Conservation Area
- Sheppards Bush Conservation Area
- Sibbald Point Provincial Park
- Thornton Bales King Conservation Area
- Wesley Brooks Memorial Conservation Area (known as "Fairy Lake" locally[39])
- Whitchurch Conservation Area
- Willow Beach Conservation Area
Sister city
The Region of York signed a "Twinning Agreement" with the city of Omsk, Russia, on August 28, 1997, after it signed a "Friendship Agreement" one year previous.
Adjacent census divisions
See also
- List of municipalities in Ontario
- Greater Toronto Area
- Province of Toronto
References
- "(Code 3519) Census Profile". 2011 census. Statistics Canada. 2012. Retrieved March 1, 2012.
Notes
- "Office of the Chairman and CEO". The Regional Municipality of York. Retrieved July 27, 2019.
- Statistics Canada: 2012
- "Census Profile, 2016 Census - York, Regional municipality [Census division], Ontario and Ontario [Province]". Statistics Canada. Retrieved July 27, 2017.
- "York Region Official Plan — December 2009". Regional Municipality of York. December 16, 2009. Archived from the original on July 6, 2011. Retrieved April 8, 2010.
- Lott, John (May 13, 1970). "Approval, relief first reactions of politicians". The Era. pp. 1, 2. Archived from the original on March 4, 2016. Retrieved April 30, 2015.
- The Regional Municipality of York Act, 1970, S.O. 1970, c. 50
- "Highlights". The Era. May 13, 1970. p. 1. Archived from the original on March 4, 2016. Retrieved April 30, 2015.
- 1970 Act, s. 2
- Carter, Terry (May 13, 1970). "Towns to win in regional land 'stakes". The Era. pp. 1, 17. Archived from the original on March 4, 2016. Retrieved April 30, 2015.
- "Amalgamation:E.G. yes, Newmarket no". The Era. May 13, 1970. p. 1, 2. Archived from the original on March 4, 2016. Retrieved April 30, 2015.
- 1970 Act, s. 178
- The York Municipal Hydro-Electric Service Act, 1978, S.O. 1978, c. 31
- 1978 Act, s.2
- 1978 Act, s.3
- 1978 Act, s.4
- "York Region Interactive Map". The Region of York Community Services. Archived from the original on August 2, 2013. Retrieved July 27, 2013.
- "Ontario County High Points". Retrieved March 31, 2020.
- "Toronto Buttonville Airport". Canadian Climate Normals 1981−2010. Environment Canada. Retrieved April 12, 2014.
- "Richmond Hill, Ontario". 1981–2010 Canadian Climate Normals. Environment Canada. Retrieved February 16, 2015.
- "Stouffville WPCP". Canadian Climate Normals 1971–2000. Environment Canada. Retrieved May 12, 2016.
- "Woodbridge, Ontario". Canadian Climate Normals 1981–2010. Environment Canada. Retrieved December 17, 2013.
- "Council". The Regional Municipality of York. Retrieved April 17, 2020.
- "Reasons for Selection, 2009 Greater Toronto's Top Employers Competition". Archived from the original on February 6, 2009. Retrieved January 28, 2009.
- "Ontario census divisions — Annual population estimates at July 1". Annual Demographic Estimates. Statistics Canada. Archived from the original on March 30, 2012. Retrieved April 4, 2010.
- "Population and dwelling counts, for Canada and census divisions, 2011 and 2006 censuses". Canada 2006 Census. Statistics Canada. Archived from the original on March 4, 2016. Retrieved April 25, 2015.
- "Immigration and Ethnocultural Diversity Highlight Tables". Statistics Canada. October 25, 2017. Archived from the original on October 28, 2017. Retrieved October 28, 2017.
- "Census Divisions". Statistics Canada.
- "Immigration and Ethnocultural Diversity Highlight Tables". Statistics Canada. October 25, 2017. Archived from the original on October 28, 2017. Retrieved October 28, 2017.
- "Census Profile, 2016 Census York, Regional municipality [Census division], Ontario and Ontario [Province]". Statistics Canada.
- "Our Connection to SickKids Hospital". Boomerang Health. Archived from the original on December 1, 2017. Retrieved November 27, 2017.
- "Water Supply". Archived from the original on April 7, 2012. Retrieved September 28, 2011.
- "2014 Newmarket Water Distribution System Annual Water Quality Summary Report" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on July 6, 2015. Retrieved July 6, 2015.
- "ABOUT MARKHAM MUSEUM". Markham. The Corporation of the City of Markham. Archived from the original on December 4, 2018. Retrieved December 3, 2018.
- Richmond Hill Live Steamers Archived July 17, 2011, at the Wayback Machine. Richmond-hill-live-steamers.tripod.com. Retrieved on July 26, 2013.
- Town of Whitchurch Stouffville Archived February 22, 2010, at the Wayback Machine. Townofws.com. Retrieved on July 26, 2013.
- "York-Durham Heritage Railway". Archived from the original on July 29, 2019. Retrieved July 28, 2019.
- Welcome To Applewood Farm Winery - Fruit Wines - Apple & Strawberry Picking Archived May 26, 2010, at the Wayback Machine. Applewoodfarmwinery.com (July 14, 2013). Retrieved on 2013-07-26.
- Willow Springs Winery Archived June 11, 2010, at the Wayback Machine. Willow Springs Winery. Retrieved on July 26, 2013.
- Wesley Brooks Memorial :: Lake Simcoe Region Conservation Authority Archived August 5, 2011, at the Wayback Machine. Lsrca.on.ca. Retrieved on July 26, 2013.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Regional Municipality of York. |
.jpg)
.jpg)