Phorbol esters
Phorbol esters are a class of chemical compounds found in a variety of plants, particularly in the families Euphorbiaceae and Thymelaeaceae.[1] Chemically, they are ester derivatives of the tetracyclic diterpenoid phorbol.
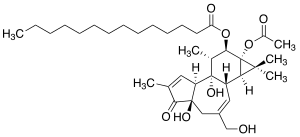
Chemical structure of 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate, a phorbol ester
Biological activity
Phorbol esters are known for their ability to promote tumors. In particular, 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA) is used as a biomedical research tool in models of carcinogenesis.[2][3]
Plants that contain phorbol esters are often poisonous.[3]
References
- Goel, G; Makkar, H. P.; Francis, G; Becker, K (2007). "Phorbol esters: Structure, biological activity, and toxicity in animals". International Journal of Toxicology. 26 (4): 279–88. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.320.6537. doi:10.1080/10915810701464641. PMID 17661218.
- Emerit, Ingrid; Cerutti, Peter A. (1981). "Tumour promoter phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate induces chromosomal damage via indirect action". Nature. 293 (5828): 144–6. Bibcode:1981Natur.293..144E. doi:10.1038/293144a0. PMID 7266668.
- Abdel-Fatta Rizk (1990). Poisonous Plant Contamination of Edible Plants. CRC Press. pp. 43–44. ISBN 9780849363696.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.