ICAM2
Intercellular adhesion molecule 2 (ICAM2), also known as CD102 (Cluster of Differentiation 102), is a human gene, and the protein resulting from it.
Protein structure
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM) family. All ICAM proteins are type I transmembrane glycoproteins, contain 2–9 immunoglobulin-like C2-type domains, and bind to the leukocyte adhesion LFA-1 protein.
Protein functions
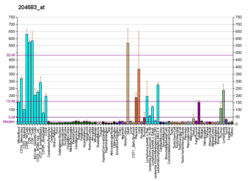
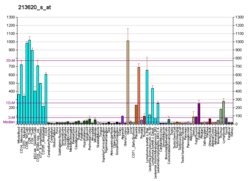
ICAM-2 molecules regulate spermatid adhesion on Sertoli cell on the apical side of the blood-testis barrier (towards the lumen), thus playing a major role in spermatogenesis.[5]
This protein may also play a role in lymphocyte recirculation by blocking LFA-1-dependent cell adhesion. It mediates adhesive interactions important for antigen-specific immune response, NK-cell mediated clearance, lymphocyte recirculation, and other cellular interactions important for immune response and surveillance.[6]
See also
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000108622 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000001029 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Xiao X, Mruk DD, Cheng CY (2013). "Intercellular adhesion molecules (ICAMs) and spermatogenesis". Human Reproduction Update. 19 (2): 167–86. doi:10.1093/humupd/dms049. PMC 3576004. PMID 23287428.
- "Entrez Gene: ICAM2 intercellular adhesion molecule 2".
- Heiska L, Alfthan K, Grönholm M, Vilja P, Vaheri A, Carpén O (August 1998). "Association of ezrin with intercellular adhesion molecule-1 and -2 (ICAM-1 and ICAM-2). Regulation by phosphatidylinositol 4, 5-bisphosphate". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 273 (34): 21893–900. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.34.21893. PMID 9705328.
Further reading
- Simmons DL (1995). "The role of ICAM expression in immunity and disease". Cancer Surveys. 24: 141–55. PMID 7553659.
- Hayflick JS, Kilgannon P, Gallatin WM (1998). "The intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM) family of proteins. New members and novel functions". Immunologic Research. 17 (3): 313–27. doi:10.1007/BF02786454. PMID 9638475.
- Lalor PF, Shields P, Grant A, Adams DH (February 2002). "Recruitment of lymphocytes to the human liver". Immunology and Cell Biology. 80 (1): 52–64. doi:10.1046/j.1440-1711.2002.01062.x. PMID 11869363.
- Yonekawa K, Harlan JM (February 2005). "Targeting leukocyte integrins in human diseases". Journal of Leukocyte Biology. 77 (2): 129–40. doi:10.1189/jlb.0804460. PMID 15548573.
- de Fougerolles AR, Stacker SA, Schwarting R, Springer TA (July 1991). "Characterization of ICAM-2 and evidence for a third counter-receptor for LFA-1". The Journal of Experimental Medicine. 174 (1): 253–67. doi:10.1084/jem.174.1.253. PMC 2118873. PMID 1676048.
- Sansom D, Borrow J, Solomon E, Trowsdale J (October 1991). "The human ICAM2 gene maps to 17q23-25". Genomics. 11 (2): 462–4. doi:10.1016/0888-7543(91)90157-A. PMID 1769660.
- Staunton DE, Dustin ML, Springer TA (May 1989). "Functional cloning of ICAM-2, a cell adhesion ligand for LFA-1 homologous to ICAM-1". Nature. 339 (6219): 61–4. doi:10.1038/339061a0. PMID 2497351.
- Bujía J, Holly A, Kim C, Scanady N, Kastenbauer E (1994). "Expression of human intercellular adhesion molecules in middle ear cholesteatoma". American Journal of Otolaryngology. 15 (4): 271–5. doi:10.1016/0196-0709(94)90094-9. PMID 7526720.
- de Fougerolles AR, Qin X, Springer TA (February 1994). "Characterization of the function of intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM)-3 and comparison with ICAM-1 and ICAM-2 in immune responses". The Journal of Experimental Medicine. 179 (2): 619–29. doi:10.1084/jem.179.2.619. PMC 2191386. PMID 7905020.
- Butini L, De Fougerolles AR, Vaccarezza M, Graziosi C, Cohen DI, Montroni M, Springer TA, Pantaleo G, Fauci AS (September 1994). "Intercellular adhesion molecules (ICAM)-1 ICAM-2 and ICAM-3 function as counter-receptors for lymphocyte function-associated molecule 1 in human immunodeficiency virus-mediated syncytia formation". European Journal of Immunology. 24 (9): 2191–5. doi:10.1002/eji.1830240939. PMID 7916296.
- Maruyama K, Sugano S (January 1994). "Oligo-capping: a simple method to replace the cap structure of eukaryotic mRNAs with oligoribonucleotides". Gene. 138 (1–2): 171–4. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(94)90802-8. PMID 8125298.
- Hirao M, Sato N, Kondo T, Yonemura S, Monden M, Sasaki T, Takai Y, Tsukita S, Tsukita S (October 1996). "Regulation mechanism of ERM (ezrin/radixin/moesin) protein/plasma membrane association: possible involvement of phosphatidylinositol turnover and Rho-dependent signaling pathway". The Journal of Cell Biology. 135 (1): 37–51. doi:10.1083/jcb.135.1.37. PMC 2121020. PMID 8858161.
- Bernstein CN, Sargent M, Gallatin WM, Wilkins J (October 1996). "Beta 2-integrin/intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM) expression in the normal human intestine". Clinical and Experimental Immunology. 106 (1): 160–9. PMID 8870715.
- Bonaldo MF, Lennon G, Soares MB (September 1996). "Normalization and subtraction: two approaches to facilitate gene discovery". Genome Research. 6 (9): 791–806. doi:10.1101/gr.6.9.791. PMID 8889548.
- Casasnovas JM, Springer TA, Liu JH, Harrison SC, Wang JH (May 1997). "Crystal structure of ICAM-2 reveals a distinctive integrin recognition surface". Nature. 387 (6630): 312–5. doi:10.1038/387312a0. PMID 9153399.
- Suzuki Y, Yoshitomo-Nakagawa K, Maruyama K, Suyama A, Sugano S (October 1997). "Construction and characterization of a full length-enriched and a 5'-end-enriched cDNA library". Gene. 200 (1–2): 149–56. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(97)00411-3. PMID 9373149.
- Sainio M, Zhao F, Heiska L, Turunen O, den Bakker M, Zwarthoff E, Lutchman M, Rouleau GA, Jääskeläinen J, Vaheri A, Carpén O (September 1997). "Neurofibromatosis 2 tumor suppressor protein colocalizes with ezrin and CD44 and associates with actin-containing cytoskeleton". Journal of Cell Science. 110. 110 (18): 2249–60. PMID 9378774.
- Yonemura S, Hirao M, Doi Y, Takahashi N, Kondo T, Tsukita S, Tsukita S (February 1998). "Ezrin/radixin/moesin (ERM) proteins bind to a positively charged amino acid cluster in the juxta-membrane cytoplasmic domain of CD44, CD43, and ICAM-2". The Journal of Cell Biology. 140 (4): 885–95. doi:10.1083/jcb.140.4.885. PMC 2141743. PMID 9472040.
- Bernstein CN, Sargent M, Gallatin WM (February 1998). "Beta2 integrin/ICAM expression in Crohn's disease". Clinical Immunology and Immunopathology. 86 (2): 147–60. doi:10.1006/clin.1997.4462. PMID 9473377.
External links
- ICAM2+protein,+human at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- PDBe-KB provides an overview of all the structure information available in the PDB for Human Intercellular adhesion molecule 2 (ICAM2)
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.