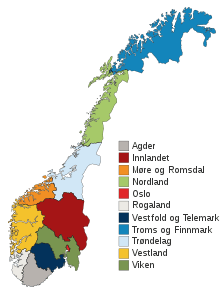
Counties of Norway
Norway is divided into 11 administrative regions, called counties (singular Norwegian: fylke, plural Norwegian: fylker (Bokmål) / fylke (Nynorsk) from Old Norse: fylki from the word "folk", Northern Sami: fylka, Southern Sami: fylhke, Lule Sami: fylkka, Kven: fylkki) until 1918, they were known as amter. The counties form the first-level subdivisions of Norway and are further divided into 356 municipalities (kommune, pl. kommuner / kommunar). The island territories of Svalbard and Jan Mayen are outside the county division and ruled directly at the national level. The capital Oslo is considered both a county and a municipality.
| Counties of Norway Norges fylker (Bokmål) Noregs fylke (Nynorsk) | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Category | Unitary unit |
| Location | |
| Number | 11 counties |
| Populations | Minimum: Nordland, 241,235 Maximum: Viken, 1,241,165 |
| Areas | Minimum (including water): Oslo, 454.12 km2 (175.34 sq mi) Maximum (including water): Troms og Finnmark, 74,829.68 km2 (28,891.90 sq mi) |
| Government | County municipality |
| Subdivisions | Municipalities |
Kingdom of Norway
|
|---|
 |
| This article is part of a series on the politics and government of Norway |
| Constitution |
|
Government |
|
Parliament
|
|
Local government
|
|
|
|
In 2017 the government decided to abolish some of the counties and to merge them with other counties to form larger ones, reducing the number of counties from 19 to 11, which was implemented on January 1, 2020.[1]
List of counties
Below is a list of the Norwegian counties, with their current administrative centres. Note that the counties are administered both by appointees of the national government and to a lesser extent by their own elected bodies. The county numbers are from the official numbering system ISO 3166-2:NO, which originally was set up to follow the coastline from the Swedish border in the southeast to the Russian border in the northeast, but with the numbering has changed with county mergers.
| ISO-code | County | Administrative centre(s) | Most populous municipality | Governor | Mayor | Area (km2) | Population | Official language form |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 03 | ||||||||
| 11 | ||||||||
| 15 | ||||||||
| 18 | ||||||||
| 30 | ||||||||
| 34 | ||||||||
| 38 | ||||||||
| 42 | ||||||||
| 46 | ||||||||
| 50 | ||||||||
| 54 | ||||||||
Responsibilities and significance
Every county has two main organisations, both with underlying organisations.
- The county municipality (no: Fylkeskommune) has a county council (Norwegian: Fylkesting), whose members are elected by the inhabitants. The county municipality is responsible mainly for some medium level schools, public transport organisation, regional road planning, culture and some more areas.
- The county governor (no: Fylkesmannen) is an authority directly overseen by the Norwegian government. It surveills the municipalities and receives complaints from people over their actions. It also controls areas where the government needs local direct ruling outside the municipalities.
History
Fylke (1st period)
From the consolidation to a single kingdom, Norway was divided into a number of geographic regions that had its own legislative assembly or Thing, such as Gulating (Western Norway) and Frostating (Trøndelag). The second-order subdivision of these regions was into fylker, such as Egdafylke and Hordafylke. In 1914, the historical term fylke was brought into use again to replace the term amt introduced during the union with Denmark. Current day counties (fylker) often, but not necessarily, correspond to the historical areas.
Fylke in the 10th-13th centuries
Counties (folkland) under the Borgarting, located in Viken with the seat at Sarpsborg:[2]
Counties (first three fylke, last two bilandskap) under the Eidsivating, located in Oplandene with the seat at Eidsvoll:[2]
- Raumafylke (Glåmdalen, Romerike, Solør)
- Heinafylke (Gjøvik, Hedmark)
- Hadafylke (Hadeland, Land, Toten)
- Gudbrandsdal
- Østerdal
Counties under the Gulating, located in Vestlandet with the seat at Gulen:[3]
- Sunnmærafylke
- Firdafylke (Nordfjord, Sunnfjord)
- Sygnafylke
- Valdres and Hallingdal
- Hordafylke
- Rygjafylke
- Setesdal
- Egdafylke
Counties under the Frostating, located in Trøndelag with the seat at Frosta:
- Eynafylke
- Sparbyggjafylke
- Verdælafylke
- Skeynafylke
- Orkdælafylke
- Gauldælafylke
- Stjordælafylke
- Strindafylke
- Naumdælafylke
- Nordmærafylke
- Romsdælafylke
Counties not attached to a thing:
- Jamtaland
- Herjedalen
- Håløygjafylke
Finnmark (including northern Troms), the Faroe Islands, the Orkney Islands, Shetland, the Hebrides, Isle of Man, Iceland and Greenland were Norwegian skattland ("taxed countries"), and did not belong to any known counties or assembly areas.
Syssel
Syssel in 1300
From the end of the 12th century, Norway was divided into several syssel. The head of the various syssel was the syslemann, who represented the king locally. The following shows a reconstruction of the different syssel in Norway c. 1300, including sub-syssel where these seem established.[4]
- Elvesysle
- Rånrike
- Borgarsysle (two parts)
- Romerike (two parts, "northern" and "southern")
- Hedmark (two parts, "northern" and "southern")
- Østerdalen
- "north of Åmot"
- "south of Åmot"
- Gudbrandsdalen
- "north of Ruste"
- "south of Ruste"
- Hadeland (later Ringerike, two parts, "northern" and "outer")
- Valdres and Hallingdal (two parts)
- Numedal and Telemark?
- Tverrdalane and Modum?
- Oslosysle (northern lut and western lut)
- Tønsbergsysle
- Skiensysle
- Eastern part (later Nedenes)
- Robyggjelag
- Agder Midtsysla
- Lista
- Rygjafylke
- "north of the fjord"
- "south of the fjord"
- Hordaland (Nordhordland? and Sunnhordland?)
- Hardanger
- Voss
- Sogn (two parts?)
- Sunnfjord
- Nordfjord
- Sunnmøre
- Romsdal
- Nordmøre?
- Nordmørafylke
- Orkdal
- Gauldal
- Strinda
- Herjedalen
- Jemtland
- Stjørdal
- Skogn
- Verdal
- Sparbu
- Eynafylke
- Northern part? (later Fosen)
- Namdalen
- "upper half" (Overhalla)
- "lower half (later Njardøy)
- Hålogaland (two parts)
- Troms?
- Finnmark?
Len
From 1308, the term len (plural len) in Norway signified an administrative region roughly equivalent to today's counties. The historic len was an important administrative entity during the period of Dano-Norwegian unification after their amalgamation as one state, which lasted for the period 1536[5]–1814.
At the beginning of the 16th century the political divisions were variable, but consistently included four main len and approximately 30 smaller sub-regions with varying connections to a main len. Up to 1660 the four principal len were headquartered at the major fortresses Bohus Fortress, Akershus Fortress, Bergenhus Fortress and the fortified city of Trondheim.[6] The sub-regions corresponded to the church districts for the Lutheran church in Norway.
Len in 1536
- Båhus len (later termed Bohuslän after Denmark-Norway ceded it to Sweden by the Treaty of Roskilde in 1658)
- Akershus len
- Trondheim len
- Bergenhus len (which included Northern Norway)
These four principal len were in the 1530s divided into approximately 30 smaller regions. From that point forward through the beginning of the 17th century the number of subsidiary len was reduced, while the composition of the principal len became more stable.
Len in 1660
From 1660 Norway had nine principal len comprising 17 subsidiary len:
- Akershus len
- Tunsberg len
- Bratsberg len
- Agdesiden len
- Stavanger len
- Bergenhus len
- Trondheim len
- Nordlandene len
- Vardøhus len
Len written as län continues to be used as the administrative equivalent of county in Sweden to this day. Each len was governed by a lenman.[7]
Amt
With the royal decree of February 19, 1662, each len was designated an amt (plural amt) and the lenmann was titled amtmann, from German Amt (office), reflecting the bias of the Danish court of that period.
Amt in 1671
After 1671 Norway was divided into four principal amt or stiftsamt and there were nine subordinate amt:
- Akershus amt
- Smålenene amt
- Brunla amt
- Agdesiden amt
- Bratsberg amt
- Stavanger amt
- Bergenhus amt
- Halsnøy klostergods
- Hardanger amt
- Nordlandene amt
- Trondheim amt
- Romsdalen amt
- Vardøhus amt
Amt in 1730
From 1730 Norway had the following amt:
- Vardøhus amt
- Tromsø amt
- Nordlands amt
- Nordre Trondhjems amt
- Søndre Trondhjems amt
- Romsdalen amt
- Nordre Bergenhus amt
- Søndre Bergenhus amt
- Stavanger amt
- Lister og Mandals amt
- Nedenes amt
- Bratsberg amt
- Buskerud amt
- Oplandenes amt
- Hedemarkens amt
- Akershus amt
- Smaalenenes amt
At this time there were also two counties (grevskap) controlled by actual counts, together forming what is now Vestfold county:
- Laurvigen county
- Jarlsberg county
Amt in 1760
In 1760 Norway had the following stiftamt and amt:[8]
- Akershus stiftamt
- Opplands amt
- Akershus amt
- Smålenenes amt
- Laurvigen county
- Jarlsberg county
- Bratsberg amt (eastern half)
- Agdesiden stiftamt
- Bratsberg amt (western half)
- Nedenes amt
- Lister and Mandal amt
- Stavanger amt
- Bergenhus stiftamt
- Romsdal amt (southern half)
- Trondheim stiftamt
- Romsdal amt (northern half)
- Nordlands amt
- Vardøhus amt
Fylke (2nd period)
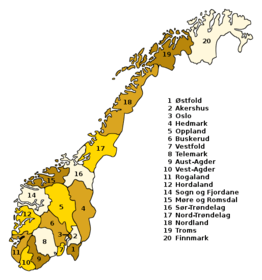
From 1919 each amt was renamed a fylke (plural fylke(r)) (county) and the amtmann was now titled fylkesmann (county governor).
- Østfold fylke
- Akershus fylke
- Oslo fylke
- Hedmark fylke
- Oppland fylke
- Buskerud fylke
- Vestfold fylke
- Telemark fylke
- Aust-Agder fylke
- Vest-Agder fylke
- Rogaland fylke
- Bergen fylke, merged into Hordaland fylke in 1972
- Hordaland fylke
- Sogn and Fjordane fylke
- Møre and Romsdal fylke
- Sør-Trøndelag fylke, merged into Trøndelag fylke in 2018
- Nord-Trøndelag fylke, merged into Trøndelag fylke in 2018
- Trøndelag fylke, created in 2018[9]
- Nordland fylke
- Troms fylke
- Finnmark fylke
The county numbers are from the official numbering system ISO 3166-2:NO, which originally was set up to follow the coastline from the Swedish border in the southeast to the Russian border in the northeast, but with the numbering has changed with county mergers. The number 13, 16 and 17 were dropped, and the number 50 was added to account for changes over the years. The lack of a county number 13 is due to the city of Bergen no longer being its own county, and is unrelated to fear of the number 13.
In 2018, Sør-Trøndelag was merged with Nord-Trøndelag into the new county of Trøndelag, and several followed.
| ISO-code | County | Administrative centre | Area (km2) | Population (2016) | County after 1 January 2020 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 01 | Sarpsborg | 4,180.69 | 290,412 | ||
| 02 | Oslo | 4,917.94 | 596,704 | ||
| 06 | Drammen | 14,910.94 | 278,028 | ||
| 03 | City of Oslo | 454.07 | 660,987 | ||
| 04 | Hamar | 27,397.76 | 195,443 | ||
| 05 | Lillehammer | 25,192.10 | 188,945 | ||
| 07 | Tønsberg | 2,225.08 | 245,160 | ||
| 08 | Skien | 15,296.34 | 172,527 | ||
| 09 | Arendal | 9,157.77 | 115,873 | ||
| 10 | Kristiansand | 7,276.91 | 182,922 | ||
| 11 | Stavanger | 9,375.97 | 470,907 | ||
| 12 | Bergen | 15,438.06 | 517,601 | ||
| 13 | Not in use from 1972 and onwards [lower-alpha 1] | ||||
| 14 | Hermansverk | 18,623.41 | 109,623 | ||
| 15 | Molde | 15,101.39 | 265,181 | ||
| 16 | Not in use from 2018 and onwards [lower-alpha 2] | ||||
| 17 | Not in use from 2018 and onwards [lower-alpha 2] | ||||
| 18 | Bodø | 38,482.39 | 241,948 | ||
| 19 | Tromsø | 25,862.91 | 164,613 | ||
| 20 | Vadsø | 48,631.04 | 75,886 | ||
| 50 | Steinkjer[lower-alpha 3] | 41,254.29 | 450,496 |
- Formerly used for Bergen county, merged into Hordaland on 1 January 1972
- Formerly used for Nord-Trøndelag (#17) and Sør-Trøndelag (#16) counties, merged as Trøndelag on 1 January 2018
- Steinkjer is the administrative centre, but the county mayor is seated in Trondheim. Steinkjer and Trondheim are sometimes named as co-capitals
Fylke (3rd period)
In 2017 the Norwegian government announced the merge of the existing 19 fylker into 11 fylkeskommuner (regions) by 2020. As a result, several government tasks will be transferred to the new regions.[10]
- New fylkeskommuner (regions)
- Troms og Finnmark, by merging Finnmark and Troms counties in 2020
- Nordland, no change, same as Nordland county
- Trøndelag, no change, same as Trøndelag county
- Møre og Romsdal, no change, same as Møre og Romsdal county
- Vestland, by merging Hordaland and Sogn og Fjordane counties in 2020
- Rogaland, no change, same as Rogaland county
- Agder, by merging Aust-Agder and Vest-Agder counties in 2020
- Vestfold og Telemark, by merging Vestfold and Telemark counties in 2020
- Innlandet, by merging Hedmark and Oppland counties in 2020
- Viken, by merging Akershus, Buskerud, and Østfold counties in 2020
- Oslo, no change, same as Oslo county
See also
- Ranked list of Norwegian counties
- Municipalities of Norway
- Regions of Norway
- Traditional districts of Norway
- Metropolitan regions of Norway
- Subdivisions of the Nordic countries
- Lists of County Governors of Norway
References
Footnotes
- "Dette er Norges nye regioner". vg.no. Archived from the original on 9 March 2018. Retrieved 28 April 2018.
- "Lagting og lagsogn frem til 1797". Borgarting lagmannsrett. Archived from the original on 2011-11-21.
- "Frå lagting til allting". Gulatinget. Archived from the original on 2015-04-09.
- Danielsen (et al.), 1991, p. 77
- Christian III, king of Denmark-Norway, carried out the Protestant Reformation in Norway in 1536.
- Kavli, Guthorm (1987). Norges festninger. Universitetsforlaget. ISBN 82-00-18430-7.
- Jesperson, Leon (Ed.) (2000). A Revolution from Above? The Power State of 16th and 17th Century Scandinavia. Odense University Press. ISBN 87-7838-407-9.CS1 maint: extra text: authors list (link)
- Danielsen (et al.), 1991, p. 153
- "Fylkespolitikerne sier ja til Trøndelag fylke" (in Norwegian). NRK. Archived from the original on 2016-08-28.
- moderniseringsdepartementet, Kommunal- og (7 July 2017). "Regionreform". Regjeringen.no. Archived from the original on 23 March 2018. Retrieved 28 April 2018.
Bibliography
- Danielsen, Rolf; Dyrvik, Ståle; Grønlie, Tore; Helle, Knut; Hovland, Edgar (2007) [1991]. Grunntrekk i norsk historie (1 ed.). Oslo: Universitetsforlaget. ISBN 978-82-00-21273-7.
