Miami-Dade Transit
 Metrorail (top), Metromover (middle), and Metrobus (bottom) at Government Center | |
| Overview | |
|---|---|
| Locale | Greater Miami |
| Transit type | Rapid transit, Downtown people mover, transit bus |
| Number of lines |
2 Metrorail lines 3 Metromover loops 90 Metrobus routes 1 Transitway |
| Number of stations |
Miami Central Station Government Center 23 (Metrorail) 22 (Metromover) 28 (South Dade Transitway) |
| Daily ridership | 391,000+ daily |
| Chief executive | Alice Bravo (Director) |
| Headquarters |
701 NW 1st Court Miami, Florida, 33132 |
| Operation | |
| Began operation | August 2, 1960[1] |
| Operator(s) | Miami-Dade Transit |
| Number of vehicles |
817 buses 136 Metrorail cars 42 Metromover cars |
| Technical | |
| System length | 31 miles (50 km) (Elevated metro; 2012) |
| Track gauge | 1,435 mm (4 ft 8 1⁄2 in) (standard gauge) |
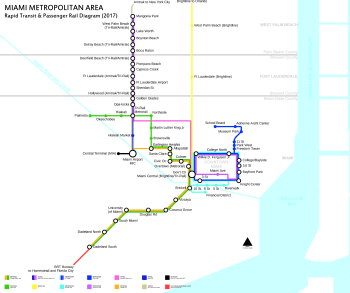
Miami-Dade Transit (MDT) is the primary public transit authority of Miami, Florida, United States and the greater Miami-Dade County area. It is the largest transit system in Florida and the 15th-largest transit system in the United States.[2]
MDT operates the rapid transit Metrorail, the Downtown Metromover people mover, Metrobus, and Paratransit (STS) systems. Metrorail is composed of two rail lines (Green and Orange lines) with 23 stations radiating from the city center towards outlying neighborhoods north and south of Downtown. Metromover operates throughout the Downtown and Brickell neighborhoods, and is composed of three rail loops and 22 stations. Metrobus operates over 93 routes, including the South Dade Transitway. [3] MDT's main transit stations are Government Center in Downtown, and the new Miami Central Station in Grapeland Heights, near Miami International Airport.[4]
As of 2011, MDT has a daily passenger ridership of 336,067, and accounts for over 15% of Miamians' daily transportation. MDT has seen growing passenger ridership since 1998, with ridership increasing 79% since then. The opening of the new Metrorail Orange Line in April 2012 is expected to significantly increase usage of the system.[5] Although not under the control of MDT, Tri-Rail is Miami's commuter rail system, and connects Miami north to Fort Lauderdale and West Palm Beach.[6]
Currently, the Director of the authority is former City of Miami Manager Alice Bravo. The MDT headquarters are located in the Overtown Transit Village in Downtown Miami.[7]
History
In 1960, the Dade County Commission passed an ordinance creating the Metropolitan Transit Authority (MTA) to unify the different transit operations into one countywide service. This ordinance provided for the purchase, development, and operation of an adequate mass transit system by the County. These companies included the Miami Transit Company, Miami Beach Railway Company, South Miami Coach Lines, and Keys Transit Company on Key Biscayne and would be managed by National City Management Company. Over the years and under various administrations, MTA evolved into the Metro-Dade Transportation Administration, the Metro-Dade Transit Agency, the Miami-Dade Transit Agency, and is now known simply as Miami-Dade Transit (MDT).
Miami-Dade Transit, a county department of more than 4,000 employees, is the largest transit agency in the state of Florida and accounts for more than half of the trips taken on public transit in the state. MDT operates an accessible, integrated system of 93-plus Metrobus routes; the 22-mile (35 km) Metrorail rapid transit system; Metromover, a free downtown people mover system; and the Paratransit division's Special Transportation Service. Metrobus routes cover more than 35-million miles annually, including limited service to Broward and Monroe counties. In 2004, MDT's Metrorail, Metromover, and Metrobus transported more than 96 million passengers, compared to 85 million the previous year.
2011 federal investigation
Miami-Dade Transit is undergoing a federal investigation by the Federal Transit Administration that includes several audits and a criminal investigation of the transit agency due to concerns over money mismanagement within the agency.[8] This caused a freezing of federal funds being granted to the county agency. In late 2010 the county manager claimed that it was 'not fraud' but rather accounting errors, poor management, and erroneous information given to the auditors that triggered the investigation, including a withdrawal of $15 million through the ECHO program that was made by a transit official two hours after a letter arrived in September 2010 from the FTA telling them withdrawals had been restricted.[9] The investigation and lack of funding let to emergency service cuts to Metrorail, Metrobus, and Metromover being considered by the agency by the middle of 2011, six months into the investigation and lack of funding which began in November 2010, causing MDT to lose $185 million in grant money. Assistant county manager Ysela Llort became responsible for Miami-Dade Transit after director Harpal Kapoor left in April 2011. Additionally, funding for the Metrorail airport link was jeopardized by the funding freeze. The FTA decided to continue funding under strict control in order to keep service cuts from happening.[10]
Improvement projects
- The Miami-Dade County Government has received federal money in order to purchase new railcars from Hitachi Rail Italy at a cost of $325 million.
- Technology and Corridor Improvements: Two corridors, totaling 24.4 miles (39.3 km) of rapid transit, have completed the planning phase and are ready to enter into final design and construction—the North Corridor, Earlington Heights-MIC Connection, and East-West Corridor.
Fares

The "EASY Card" system is a regional fare collection system with interoperable smartcards and equipment. The following information is specific to Miami-Dade Transit:
Since October 1, 2009, Miami-Dade Transit has used the EASY Card system[11] for fare collection.
On December 13, 2009 paper-based bus transfers were discontinued, and bus-to-bus transfers are now free only when using an EASY Card or EASY Ticket.
- An EASY Card can be purchased for $2 at EASY Card sales outlets, vending machines in Metrorail stations, calling 3-1-1 in Miami-Dade County, or online. Money can be reloaded on to the card at the same places and locations. The card is durable plastic and lasts for 20 years from first use since 2013.
- Alternatively an EASY Ticket may be purchased with no sales charge. However EASY Tickets are limited to the fare type initially loaded onto it, and expire 60 days after purchase.[12] EASY Tickets also may not be purchased online or via telephone.
- With the change, paper transfers are being eliminated on transit. People paying fares in cash will need to pay full fare when transferring.[13] Transfers will be available only by paying with an EASY Card or Ticket and using the card again within 3 hours of boarding transit.
The current standard fare is $2.25 and reduced fare is $1.10. A standard monthly pass costs $112.50 and $56.25 for reduced fare. The monthly Metropass is loaded onto the EASY Card. Turnstile equipment at all Metrorail stations does not accept any type of cash,[11] and require an EASY Card or Ticket to both enter and exit the boarding area.
Reduced fares are available only to Medicare recipients, people with disabilities, and Miami-Dade students in grades 1-12. No fare to kids below 42 inches (110 cm) tall with fare-paying rider; limit is 3.
All Miami-Dade senior citizens aged 65 years and older and with Social Security benefits ride free with a Golden Passport pass. Veterans residing in Miami-Dade and earning less than $22,000 annually ride free with the Patriot Passport pass.
Passenger ridership

In February 2011, Miami-Dade Transit ridership totaled 336,067 passengers, including all Metrorail, Metromover and Metrobus lines. With a population of about 2.5 million in Miami-Dade County, Miami-Dade Transit accounts for 15% of the population's daily mode of transportation. Note: This figure does not include Tri-Rail, Miami's commuter rail operator.
Annual passenger ridership
| Year | Metrobus | Metrorail | Metromover | Total ridership |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1995 | 61,516,400 | 14,445,400 | 4,168,600 | 80,130,400 |
| 1996 | 60,466,700 | 14,245,000 | 3,847,400 | 78,559,100 |
| 1997 | 62,344,200 | 13,923,700 | 4,175,200 | 80,443,100 |
| 1998 | 62,358,100 | 13,298,900 | 4,064,900 | 79,721,900 |
| 1999 | 64,252,400 | 13,769,400 | 4,069,700 | 82,091,500 |
| 2000 | 65,689,800 | 14,023,600 | 4,256,500 | 83,969,900 |
| 2001 | 65,067,100 | 13,678,000 | 4,951,800 | 83,696,900 |
| 2002 | 63,423,500 | 13,932,100 | 5,171,700 | 82,527,300 |
| 2003 | 65,046,900 | 14,318,500 | 6,978,900 | 86,344,300 |
| 2004 | 77,909,300 | 15,987,600 | 8,686,300 | 102,583,200 |
| 2005 | 78,373,000 | 17,001,000 | 8,537,500 | 103,911,500 |
| 2006 | 83,080,500 | 17,388,100 | 8,389,500 | 108,858,100 |
| 2007 | 84,218,300 | 17,672,000 | 8,838,800 | 110,729,100 |
| 2008 | 86,409,200* | 19,075,900* | 8,723,700 | 114,208,800* |
| 2009 | 73,104,900 | 17,792,100 | 7,986,100 | 98,883,100 |
| 2010 | 70,942,000 | 17,438,400 | 8,121,000 | 96,501,400 |
| 2011 | 76,858,200 | 18,295,500 | 9,219,600* | 104,373,300 |
* Record highs
Weekday passenger ridership averages
| Year | Metrobus | Metrorail[14] | Metromover | Total daily passengers |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1998 | 207,048 | 44,871 | 13,269 | 265,188 |
| 1999 | 209,111 | 46,774 | 13,880 | 269,765 |
| 2000 | 212,927 | 47,256 | 14,383 | 274,566 |
| 2001 | 211,823 | 46,664 | 16,849 | 275,336 |
| 2002 | 204,941 | 47,064 | 16,444 | 268,449 |
| 2003 | 215,306 | 51,248 | 25,521 | 292,076 |
| 2004 | 234,109 | 55,294 | 28,192 | 317,595 |
| 2005 | 246,023 | 59,700 | 28,473 | 334,195 |
| 2006 | 259,375 | 58,358 | 27,042 | 344,775 |
| 2007 | 264,467 (record high) | 59,708 | 28,058 | 352,233 (record high) |
| 2008 | 259,018 | 63,710 (record high) | 26,682 | 349,410 |
| 2009 | 233,858 | 59,992 | 25,883 | 319,733 |
| 2010 | 227,883 | 59,900 | 27,175 | 314,958 |
| 2011 | 245,358 | 62,559 | 29,775 (record high) | 337,692 |
Metrorail

Metrorail is an elevated heavy rail rapid transit system. It has two lines on 24.4 mi (39 km) of track with termini west of Hialeah, at Miami International Airport, and in Kendall.
Metrorail serves the urban core of Miami, connecting the urban centers of Miami International Airport, the Civic Center, Downtown Miami, and Brickell with the northern developed neighborhoods of Hialeah and Medley to the northwest, and to suburban The Roads, Coconut Grove, Coral Gables, and South Miami, ending at urban Dadeland in Kendall.
Metromover

Metromover is a free, elevated, automated mass transit people mover that runs on three loops: the Downtown Inner Loop, Brickell Loop, and the Omni Loop. The systems total 4.4 miles with 22 stations at roughly every two blocks in the greater Downtown area. Metromover serves the neighborhoods of Downtown, Brickell, Omni, Park West, and Overtown.
Metrobus
_bus_at_Adrienne_Arsht_Center_Bus_Terminal.jpg)
The Metrobus network provides bus service throughout Miami-Dade County 365 days a year. It consists of about 93 routes and 846 buses, which connect most points in the county and part of southern Broward County as well. Seven of these routes operate around the clock: Routes 3, 11, 27, 38, 77 (last bus from Downtown Miami 1:10am, first bus from Downtown Miami 4:10am), L (No 24-hour service to Hialeah, all trips terminate at Northside Station) and S. Routes 246 Night Owl & Route 500 Midnight Owl operate from 12am to 5am. Most other routes operate from 4:30am to 1:30am. All Metrobuses are wheelchair accessible, in compliance with the Americans with Disabilities Act of 1990 and equipped with Bicycle racks.
Bus route 301 (Dade-Monroe Express) extends into Monroe County, reaching Marathon, where a transfer is available to a Key West Transit bus proceeding further into the Keys. With the appropriate bus transfers, one can travel all the way from Key West to Jupiter entirely on public-transit buses.
Paratransit (STS)
Paratransit/Special Transportation Services (STS) is available for people with a mental or physical disability who cannot ride Metrobus, Metrorail, or Metromover. For $3 per one-way trip, STS offers shared-ride, door-to-door travel in accessible vehicles throughout most of Miami-Dade County, in some parts of south Broward County, and in the middle and northern Keys. STS operates 24 hours a day, 7 days a week, including most holidays.
See also
References
- ↑ http://scholar.library.miami.edu/miamidigital/1960s.php
- ↑ "Transit Development Plan" (PDF). Miami-Dade County. September 2011. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-12-15. Retrieved 2012-01-04.
- ↑ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2012-01-28. Retrieved 2012-01-15.
- ↑ http://www.micdot.com/miami_central_station.html
- ↑ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2011-12-15. Retrieved 2012-01-14.
- ↑ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2011-11-18. Retrieved 2011-11-20.
- ↑ "Contact Us." Miami-Dade Transit. Retrieved on September 14, 2011. "Miami-Dade Transit Administrative Offices Overtown Transit Village 701 NW 1st Court Miami, Florida 33136"
- ↑ Martha Brannigan and Alfonso Chardy (July 7, 2011). "Miami-Dade to weigh $100M loan for ailing Transit Agency". The Miami Herald. Retrieved 2011-07-07.
- ↑ Alfonso Chardy (December 8, 2010). "Miami-Dade Transit's federal funding freeze `not fraud'". Miami Herald. Retrieved 2011-07-07.
- ↑ Martha Brannigan, Alfonso Chardy and Matthew Haggman (May 10, 2011). "Miami-Dade transit agency eyes service cuts as feds hold back money". Miami Herald. Retrieved 2011-07-07.
- 1 2 http://www.miamidade.gov/transit/library/pdfs/misc/english_easy_card_brochure_july2009.pdf
- ↑ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2012-01-04. Retrieved 2012-01-14.
- ↑ http://www.miamidade.gov/transit/library/easy_card/transfers_poster.pdf%5Bpermanent+dead+link%5D
- ↑ http://www.miamidade.gov/transit/news_technical_reports_archive.asp%5Bpermanent+dead+link%5D
External links

- Miami-Dade Transit
- Citizens' Independent Transportation Trust
- APTA ridership information