Same-sex marriage in Luxembourg
Same-sex marriage became legal in Luxembourg on 1 January 2015. A bill for the legalisation of such marriages was enacted by the Chamber of Deputies on 18 June 2014. Partnerships have also been available since 2004.
Partnerships
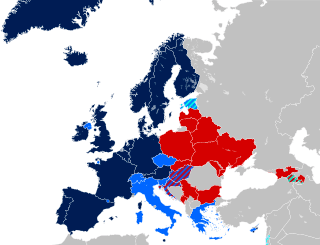
¹ May include recent laws or court decisions which have created legal recognition of same-sex relationships, but which have not entered into effect yet.
On 7 December 1995, MP Lydie Err introduced a private member's bill to create "free unions" (French: union libre).[1] Her party, the Luxembourg Socialist Workers' Party (LSAP), was part of the Juncker–Poos Government together with the Christian Social People's Party (CSV). A bill to legalise same-sex marriage was introduced as early as 9 May 1996 by MP Renée Wagener, of the opposition Greens.[2][3][4] Both proposals would not get a Council of State opinion until 13 June 2000.
The Juncker–Polfer Government consisting of the Christian Social People's Party (CSV) and the Democratic Party drafted a bill establishing partnerships, approving it in cabinet on 26 April 2002. The Council of State criticised in its opinion of 13 January 2004 taking the French civil solidarity pact (PACS) as basis rather than the Belgian statutory cohabitation, which was of superior legal quality. Furthermore, it recommended considering the legalisation of same-sex marriage, again taking neighbouring Belgium, which had then recently taken that step, as example.[5]
The government bill, along with the two earlier proposals, were debated and voted on together on 12 May 2004. The Chamber of Deputies approved the partnership bill, with 33 votes in favour (by the two governing parties), 7 votes against (by the ADR) and 20 abstentions (by the LSAP, the Greens, and The Left) while rejecting the bill creating free unions and the same-sex marriage bill, with the two governing parties voting against and the opposition parties voting in favour (except for ADR voting against the same-sex marriage bill).
The Act creating partnerships was signed on 9 July 2004 and took effect on 1 November 2004.[6] The partnerships, which are based on the French civil solidarity pact (PACS), are available for same-sex and opposite-sex couples. These partnerships provide many of the rights of marriage in relation to access to welfare benefits and fiscal advantages but not the same as marriage. They do not give the right to jointly adopt children.[7][8]
Same-sex marriage
The ruling Christian Social People's Party until 2009 was opposed to same-sex marriage, even though the Prime Minister, originating from the same party, has expressed his personal support.[9] In July 2007, a motion calling for the legalisation of same-sex marriage was rejected by Parliament, on a 38-22 vote.[10]
In July 2009, the newly formed Juncker–Asselborn Government announced its intention to legalise same-sex marriage.[11][12] During a debate on 19 January 2010, the Minister of Justice, François Biltgen, announced that a law to legalise same-sex marriage (with exception of certain adoption rights) would be finalized before the summer vacation break of Parliament.[13][14] On 9 July 2010, the Government accepted the bill;[15][16][17][18] on 10 August 2010, it was submitted to Parliament.[19]
In May 2012, the bill was re-drafted and the vote was not expected at least until 2013.[19][20][21] On 27 November 2012, the Council of State delivered a negative response to the bill, but asked Parliament to open a debate on the topic if it moved to vote on the bill. Some members of the Council submitted separate opinion supporting the bill.[22]
On 6 February 2013, the Chamber's Legal Affairs Committee agreed to approve the measure opening marriage for same-sex couples.[23] On 20 February, the committee initially backed the right to simple adoption for same-sex couples, but restricting plenary adoption to opposite-sex couples.[24][25] On 6 March 2013, the committee confirmed that position.[26][27] However, on 4 June, the Council of State issued a second review, rejecting the compromise to allow simple adoption for all couples while restricting plenary adoption to opposite-couples only.[28][29][30] On 19 June 2013, the Legal Affairs Committee decided to back full adoption rights for same-sex couples. The bill was expected to be voted on by Parliament in the autumn of 2013,[31][32] however, a further delay was caused by the elections in October 2013 following the resignation of the Luxembourgish Government.[33]
The coalition agreement of the new Government, sworn in on 4 December 2013 and led by gay Prime Minister Xavier Bettel, includes marriage and adoption rights for same-sex couples, scheduled for the first trimester of 2014.[34][lower-alpha 1] On 8 January 2014, the Minister of Justice, Felix Braz, stated that Parliament would vote on the bill in the summer of 2014, and if approved, it would take effect before the end of 2014.[35][36]
On 19 March 2014, the Chamber's Legal Affairs Committee completed its work on the marriage reform law, and sent it to the Council of State, which released its opinion on 20 May 2014.[37][38][39] On 28 May 2014, the Legal Affairs Committee approved the bill. All political parties except ADR were in favour.[40][41] On 18 June 2014, the bill was approved by the Chamber of Deputies, in a 56-4 vote.[42][43] On 24 June 2014, the Council of State gave its consent to skip the second vote, a formality.[44][45] It was promulgated by Grand Duke Henri on 4 July and published in the official gazette on 17 July 2014. The law took effect the first day of the sixth month after publication (i.e. 1 January 2015).[46][47][48]
| Party | Voted for | Voted against |
|---|---|---|
| G Democratic Party (DP) | 13
|
– |
| G Luxembourg Socialist Workers' Party (LSAP) | 13
|
– |
| G The Greens (Déi Gréng) | 6
|
– |
| Christian Social People's Party (CSV) | 22
|
1
|
| Alternative Democratic Reform Party (ADR) | – | 3
|
| The Left (Déi Lénk) | 2
|
– |
| Total | 56 | 4 |
The first same-sex marriage in Luxembourg was between Messrs Henri Lorenzo Huber and Jean-Paul Olinger, performed by Mayor Roberto Traversini at Differdange Town Hall on 1 January 2015.[50] On 15 May 2015, Prime Minister Xavier Bettel married his partner Gauthier Destenay in a private ceremony at the capital's town hall. Bettel became the first EU member state leader and just the second serving head of a government worldwide (after Iceland's Jóhanna Sigurðardóttir) to marry a person of the same sex.[51] In November 2016, Vice Prime Minister Etienne Schneider confirmed that he and his partner Jérôme Domange had married in a private ceremony sometime in 2016.[52]
In June 2014, the Chamber of Deputies invalidated a petition that demanded the repeal of the laws on marriage, adoption and assisted reproduction for same-sex couples.[53] On 16 November 2015, however, a court declared the petition valid.[54] The petition, called "Schutz fir d'Kand" in Luxembourgish ("Protection of the Child" in English), accompanied with about 4,500 signatures was then re-presented to the Chamber of Deputies, which rejected it again in November 2016.[55][56]
On 7 July 2015, a proposal by a member of the Alternative Democratic Reform Party (ADR) to organize a national referendum on opening marriage and adoption to same-sex couples was rejected by all members of every other political party in the Chamber of Deputies.[57]
On 19 November 2015, the Government introduced a bill to ensure recognition of same-sex marriages performed abroad before 1 January 2015. On 19 April 2016, it was approved by the Chamber of Deputies, in a 50-3 vote.[58][59][60] On 3 May, the Council of State gave its consent to skip the second vote in the Chamber.[61][62] The law was promulgated on 23 May, published in the official journal on 1 June, and took effect on 5 June 2016.[63]
Statistics
In 2015, approximately 120 same-sex marriages took place in Luxembourg. 49 and 11 of which occurred in Luxembourg City and Esch-sur-Alzette, respectively, the two biggest cities in the country.[64][65] 7% of all marriages performed in the country were between persons of the same sex. Additionally, about 69% of all same-sex couples that married that year were aged above 40 (74% for male couples and 61% for female couples).[66]
Public opinion
A 2006 Angus Reid Global Monitor poll found that 58% of Luxembourgers supported same-sex marriage.[67]
An April 2013 Polimonitor survey commissioned by the Luxemburger Wort and RTL found support for same-sex marriage at 83% and for same-sex adoption at 55%.[68]
The 2015 Eurobarometer found that 75% of Luxembourgers thought that same-sex marriage should be allowed throughout Europe, 20% were against.[69]
See also
Notes
- ↑ Page 12: La réforme sur le droit au mariage pour tous les couples, indépendamment de leur genre ou identité sexuelle sera adoptée au courant du premier trimestre 2014. translates to Reform on the right to marriage for all couples, regardless of their gender or sexual identity will be adopted in the first quarter of 2014.
References
- ↑ (in French) 4110 - Proposition de loi sur l'union libre
- ↑ (in French) 4162 - Proposition de loi sur la réforme du mariage
- ↑ ILGA Euroletter 42, June 1996
- ↑ (in French) Mariage et adoption - L’égalité, c’est maintenant
- ↑ (in French) Avis du Conseil d'Etat (13.1.2004)
- ↑ (in French) 4946 - Projet de loi relative aux effets légaux de certains partenariats
- ↑ (in French) Loi du 9 juillet 2004 relative aux effets légaux de certains partenariats
- ↑ The Partenariat (PACS)
- ↑ (in French) Question de mariage
- ↑ (in French) Résolution Sujet : Mariage des couples homosexuels
- ↑ (in French) Le Luxembourg devrait autoriser les mariages homosexuels
- ↑ Luxembourg Considers Legalizing Gay Marriage and Adoption
- ↑ "Luxemburg will Ehe öffnen" (in German). Queer.de. 22 January 2010.
- ↑ (in German) Homo-Ehe auch in Luxemburg
- ↑ (in French) Conseil de gouvernement Résumé des travaux du 9 juillet 2010
- ↑ (in French) Ouverture du mariage aux couples de même sexe et réforme de l'adoption Archived 2010-09-24 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ "Les gays pourront bientôt se marier et adopter" (in French). L'essentiel. 9 July 2010.
- ↑ Is gay marriage on the way for Luxembourg?
- 1 2 (in French) 6172
- ↑ (in French) 6172A
- ↑ (in French) Des dossiers en attente au Conseil d'État
- ↑ (in French) Avis du Conseil d'Etat (27.11.2012)
- ↑ (in French) Vers le mariage homosexuel
- ↑ (in French) Les couples homosexuels pourront adopter
- ↑ (in French) Adoption pour couples de même sexe bientôt possible
- ↑ (in French) L'adoption simple pour couples homosexuels
- ↑ "Une adoption simple pour les couples gay?" (in French). L'essentiel. 6 March 2013.
- ↑ (in French) Avis complémentaire du Conseil d'Etat (4.6.2013)
- ↑ State Council objects to new adoption law
- ↑ "Luxembourg: Le Conseil d'État balaie le compromis" (in French). Le Quotidien. 6 June 2013. Archived from the original on November 13, 2014.
- ↑ "Breakthrough in adoption law reform for same-sex couples". Wort.lu. 19 June 2013.
- ↑ "L'adoption plénière pour les couples homosexuels?" (in French). L'essentiel. 19 June 2013.
- ↑ "Adoption et mariage gay devront attendre" (in French). L'essentiel. 25 July 2013.
- ↑ "Programme gouvernemental" (PDF) (in French). Government of Luxembourg. p. 12.
- ↑ (in French) La loi sur le mariage gay votée d'ici cet été
- ↑ Luxembourg LBGT community welcomes same sex marriage before end of year
- ↑ Amendements adoptés par la Commission juridique
- ↑ (in French) Deuxième avis complémentaire du Conseil d'Etat (20 mai 2014)
- ↑ State Council warns of gay adoption legal challenges
- ↑ (in French) Rapport de la commission juridique (28.5.2014)
- ↑ "Green light for same-sex marriage in Luxembourg". Wort.lu. 28 May 2014.
- ↑ Luxembourg passes same-sex marriage and adoption bill in landslide vote
- ↑ Luxembourg legislature votes to legalize same-sex marriage, adoption
- ↑ (in French) Séances publique et plénière du 24 juin 2014
- ↑ (in French) Dispense du second vote consitutionnel par le Conseil d'Etat (24.6.2014)
- ↑ (in French) Loi du 4 juillet 2014 portant a) réforme du Titre II.- du Livre Ier du Code civil «Des actes de l'état civil» et modifiant les articles 34, 47, 57, 63, 70, 71, 73, 75, 76, 79, 79-1 et 95; b) réforme du Titre V.- du Livre Ier du Code civil «Du mariage», rétablissant l'article 143, modifiant les articles 144, 145, 147, 148, 161 à 164, 165 à 171, 173 à 175, 176, 177, 179, 180 à 192, 194 à 199, 201, 202, 203 à 206, 212 à 224, 226, 227, introduisant les articles 146-1, 146-2, 175-1, 175-2 nouveaux et abrogeant les articles 149 à 154, 158 à 160bis, 178, le Chapitre VIII et l'article 228; c) modification des articles 295, 351, 379, 380, 383, 390, 412, 496, alinéa 1, 509-1, alinéa 2, 730, 791, 847 à 849, 852, alinéa 3, 980, alinéa 2, 1405, 1409 et 1676, alinéa 2, et abrogation des articles 296 et 297 et 1595 du Code civil; d) modification de l'article 66 du Code de commerce; e) modification des articles 265, alinéa 1er, 278 et 521 du Nouveau Code de procédure civile; f) introduction d'un Titre VI.bis nouveau dans la Deuxième Partie du Nouveau Code de procédure civile; g) introduction d'un Chapitre VII.-I nouveau au Titre VII du Livre Ier du Code pénal; h) abrogation de la loi du 23 avril 1827 concernant la dispense des prohibitions du mariage prévues par les articles 162 à 164 du Code civil; et i) abrogation de la loi du 19 décembre 1972 portant introduction d'un examen médical avant mariage
- ↑ Same-sex marriages from January 1
- ↑ Same-Sex Marriage in Luxembourg from 1 January 2015
- ↑ "Bulletin de Vote (Vote Public) - Projet de loi 6172A" (PDF) (in French). Retrieved 2 December 2016.
- ↑ "First same-sex marriage in Luxembourg: Jean Olinger and Henri Huber say 'I do'". Luxemburger Wort. 1 January 2015. Retrieved 2 January 2015.
- ↑ "Xavier Bettel and Gauthier Destenay say 'I do'". Luxemburger Wort. 15 May 2015.
- ↑ (in French) Etienne Schneider a épousé son compagnon dans l'intimité
- ↑ Pas de débat sur la pétition contre le mariage gay
- ↑ Les anti-mariage gay ont le droit à leur débat public, 20 November 2015, L'essentiel
- ↑ (in French) Les députés ne toucheront pas au mariage et à l'adoption
- ↑ (in German) Nur zwei Petitionen angenommen
- ↑ "Bulletin de Vote (Vote Public) - Proposition de loi 6699" (PDF) (in French). Retrieved 2 December 2016.
- ↑ (in French) 6908 - Projet de loi sur la reconnaissance du mariage au Grand-Duché de Luxembourg et modifiant le Code civil
- ↑ (in French) Mariages gay : l’injustice réparée
- ↑ (in French) Luxembourg : les mariages gay célébrés à l’étranger reconnus
- ↑ (in French) Séances publique et plénière du mardi 3 mai 2016
- ↑ (in French) Dispense du second vote consitutionnel par le Conseil d'Etat (3.5.2016)
- ↑ (in French) Loi du 23 mai 2016 sur la reconnaissance du mariage au Grand-Duché de Luxembourg et modifiant le Code civil
- ↑ Lambert, Frédéric (10 March 2016). "Plus d'une centaine de mariages gay en 2015" (in French). L'essentiel.
- ↑ Moins de naissances et 49 mariages homos
- ↑ (in French) À quel âge se marie-t-on le plus au Luxembourg ?
- ↑ "Eight EU Countries Back Same-Sex Marriage". Angus Reid Global Monitor. 24 December 2006. Archived from the original on 27 February 2010. Retrieved 13 October 2009.
- ↑ Majority in Luxembourg supports gay marriage
- ↑ Special Eurobarometer 437