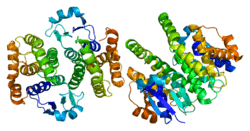PGDS
PGDS protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HPGDS gene.[5][6][7][8]
Prostaglandin-D synthase is a sigma class glutathione-S-transferase family member. The enzyme catalyzes the conversion of PGH2 to PGD2 and plays a role in the production of prostanoids in the immune system and mast cells. The presence of this enzyme can be used to identify the differentiation stage of human megakaryocytes.[8]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000163106 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000029919 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ Kanaoka Y, Ago H, Inagaki E, Nanayama T, Miyano M, Kikuno R, Fujii Y, Eguchi N, Toh H, Urade Y, Hayaishi O (Oct 1997). "Cloning and crystal structure of hematopoietic prostaglandin D synthase". Cell. 90 (6): 1085–95. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80374-8. PMID 9323136.
- ↑ Mahmud I, Ueda N, Yamaguchi H, Yamashita R, Yamamoto S, Kanaoka Y, Urade Y, Hayaishi O (Dec 1997). "Prostaglandin D synthase in human megakaryoblastic cells". J Biol Chem. 272 (45): 28263–6. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.45.28263. PMID 9353279.
- ↑ Jowsey IR, Thomson AM, Flanagan JU, Murdock PR, Moore GB, Meyer DJ, Murphy GJ, Smith SA, Hayes JD (Oct 2001). "Mammalian class Sigma glutathione S-transferases: catalytic properties and tissue-specific expression of human and rat GSH-dependent prostaglandin D2 synthases". Biochem J. 359 (Pt 3): 507–16. doi:10.1042/0264-6021:3590507. PMC 1222171. PMID 11672424.
- 1 2 "Entrez Gene: PGDS prostaglandin D2 synthase, hematopoietic".
Further reading
- Kanaoka Y, Urade Y (2004). "Hematopoietic prostaglandin D synthase". Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fatty Acids. 69 (2–3): 163–7. doi:10.1016/S0952-3278(03)00077-2. PMID 12895599.
- Suzuki T, Watanabe K, Kanaoka Y, et al. (1998). "Induction of hematopoietic prostaglandin D synthase in human megakaryocytic cells by phorbol ester". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 241 (2): 288–93. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1997.7803. PMID 9425264.
- Tokugawa Y, Kunishige I, Kubota Y, et al. (1998). "Lipocalin-type prostaglandin D synthase in human male reproductive organs and seminal plasma". Biol. Reprod. 58 (2): 600–7. doi:10.1095/biolreprod58.2.600. PMID 9475419.
- Pinzar E, Kanaoka Y, Inui T, et al. (2000). "Prostaglandin D synthase gene is involved in the regulation of non-rapid eye movement sleep". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 97 (9): 4903–7. doi:10.1073/pnas.090093997. PMC 18330. PMID 10781097.
- Kanaoka Y, Fujimori K, Kikuno R, et al. (2000). "Structure and chromosomal localization of human and mouse genes for hematopoietic prostaglandin D synthase. Conservation of the ancestral genomic structure of sigma-class glutathione S-transferase". Eur. J. Biochem. 267 (11): 3315–22. doi:10.1046/j.1432-1327.2000.01362.x. PMID 10824118.
- Fujimori K, Kanaoka Y, Sakaguchi Y, Urade Y (2001). "Transcriptional activation of the human hematopoietic prostaglandin D synthase gene in megakaryoblastic cells. Roles of the oct-1 element in the 5'-flanking region and the AP-2 element in the untranslated exon 1". J. Biol. Chem. 275 (51): 40511–6. doi:10.1074/jbc.M007688200. PMID 10998423.
- Sui D, Wilson JE (2000). "Interaction of insulin-like growth factor binding protein-4, Miz-1, leptin, lipocalin-type prostaglandin D synthase, and granulin precursor with the N-terminal half of type III hexokinase". Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 382 (2): 262–74. doi:10.1006/abbi.2000.2019. PMID 11068878.
- Noguchi E, Shibasaki M, Kamioka M, et al. (2002). "New polymorphisms of haematopoietic prostaglandin D synthase and human prostanoid DP receptor genes". Clin. Exp. Allergy. 32 (1): 93–6. doi:10.1046/j.0022-0477.2001.01261.x. PMID 12002745.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Inoue T, Irikura D, Okazaki N, et al. (2003). "Mechanism of metal activation of human hematopoietic prostaglandin D synthase". Nat. Struct. Biol. 10 (4): 291–6. doi:10.1038/nsb907. PMID 12627223.
- Ando M, Murakami Y, Kojima F, et al. (2003). "Retrovirally introduced prostaglandin D2 synthase suppresses lung injury induced by bleomycin". Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 28 (5): 582–91. doi:10.1165/rcmb.2002-0162OC. PMID 12707014.
- Inoue T, Okano Y, Kado Y, et al. (2005). "First determination of the inhibitor complex structure of human hematopoietic prostaglandin D synthase". J. Biochem. 135 (3): 279–83. doi:10.1093/jb/mvh033. PMID 15113825.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.