Osaka Metro
 | |||
 | |||
|
Top: 10 series and 21 series trains on the Midōsuji Line. Bottom: A 30000 series train on the Tanimachi Line. | |||
| Overview | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Native name |
Osaka Metro Ōsaka Metoro | ||
| Locale | Osaka and Keihanshin region, Japan | ||
| Transit type | Metro | ||
| Number of lines | 8 (+ 1 People Mover) | ||
| Number of stations |
123[1] 133 (incl. People Mover)[1] | ||
| Daily ridership | 2,464,000 (FY2013)[2] | ||
| Operation | |||
| Began operation | May 20, 1933 | ||
| Operator(s) |
Osaka Municipal Transportation Bureau (1933–March 31, 2018) Osaka Rapid Electric Tramway, K.K. (April 1, 2018–present) | ||
| Technical | |||
| System length |
129.9 km (80.7 mi)[1] 137.8 km (85.6 mi) (incl. People Mover)[1] | ||
| Track gauge | 1,435 mm (4 ft 8 1⁄2 in) standard gauge | ||
| Electrification |
Third rail lines: 750 V DC, third rail Sakaisuji Line and linear motor metro lines: 1,500 V DC, overhead lines | ||
| Top speed | 70 km/h (43 mph) | ||
| |||
Osaka Metro (大阪メトロ Ōsaka Metoro) is the rapid transit network in the Osaka Metropolitan Area of Japan, operated by Osaka Metro Co., Ltd. (大阪市高速電気軌道株式会社 Ōsaka Kōsoku Denki Kidō Kabushiki-gaisha). It serves the city of Osaka and the adjacent municipalities of Higashiosaka, Kadoma, Moriguchi, Sakai, Suita, and Yao. Osaka Metro forms an integral part of the extensive mass transit system of Greater Osaka (part of the Kansai region), having 123[1] out of the 1,108 rail stations (2007) in the Osaka-Kobe-Kyoto region.[3] In 2010, the greater Osaka region had 13 million rail passengers daily (see Transport in Keihanshin) of which the Osaka Municipal Subway (as it was then known) accounted for 2.29 million.[4]
Osaka Metro is the only subway system in Japan to be legally classified as a tramway, whereas all other subway systems in Japan are legally classified as railways. Despite this, it has characteristics typical of that of a full-fledged metro system.[5]
Until March 31, 2018, the network was operated by the Osaka Municipal Transportation Bureau as Osaka Municipal Subway, and was the oldest publicly-operated subway network in Japan, having begun operations in 1933. A proposal to privatize the Osaka subway was sent to the city government in February 2013 and was given final approval in 2017. The rationale behind privatization is that it would bring private investors to Osaka and could help revive Osaka's economy. The new private operator took over operations on April 1, 2018.
Overview
The network's first service, the Midōsuji Line from Umeda to Shinsaibashi, opened in 1933.[6] As a north-south trunk route, it is the oldest and busiest line in the whole network.[7][8][1] Both it and the main east-west route, the Chūō Line, were later extended to the north and east, respectively. These extensions are owned by other railway companies, but both Osaka Metro and these private operators run their own set of trains through between the two sections.
All but one of the remaining lines of the network, including the Yotsubashi Line, Tanimachi Line, and Sennichimae Line, are completely independent lines with no through services. The lone exception is the Sakaisuji Line, which operates through trains to existing Hankyu Railway lines and is the only line to operate through services to existing railway lines that are not isolated from the national rail network (which is the case with the Midōsuji and Chūō Lines).
Nearly all stations have a letter number combination, the letter identifying the line served by the station and the number indicating the relative location of the station on the line. For example, Higobashi Station on the Yotsubashi Line is also known as Y12. This combination is heard in bilingual Japanese-English automated next-station announcements on board all trains, which also provide information on local businesses near the station. Only Hankyu stations served by the Sakaisuji Line do not follow this convention.
Branding
Osaka Metro stations are denoted by a white-on-dark-blue icon placed at ground-level entrances, depicting an "M" (for "Metro") based on a coiled ribbon, which would form an "O" (for "Osaka") when viewed from the side, with the "Osaka Metro" wordmark set in Gotham. "Osaka Metro" (in Latin characters) is the official branding in Japanese, and is always represented as such in official media. (News outlets have been seen to use 大阪メトロ, presumably to better flow with article text.) Individual lines are represented by a public-facing name (e.g. “Midōsuji Line” for Line No. 1) and a specific color, as well as a single Latin letter, which is paired with a different number at each station for easy identification (see below). Icons for each line (featured in station wayfinding signage) are represented by a solid roundel in the line color, superimposed with the line’s letter-designation in Parisine.
An older branding (also used on the tram network run by the city until 1969) is the “Mio-Den” mark, which depicts an old-fashioned depth-marker, ![]()
When it was run by the Osaka Municipal Transportation Bureau, the subway used a logo known as the “Circle-Ko” (マルコ Maru-Ko) symbol, which is a katakana “ko” (コ) for “transport” (交通 kōtsū) superimposed over a circular capital “O” for “Osaka” (see infobox, above). This remains on many trainsets and at stations, but is slated for replacement with the Osaka Metro logo as the changeover progresses.
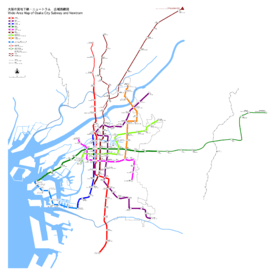
Lines
Currently, there are eight lines, operating on 129.9 kilometers (80.7 mi) and serving 123 stations; there is also a 7.9-kilometer (4.9 mi)-long, 10-station automated people mover line known as the "New Tram".[1]
| Line color |
Mark | Line number |
Name | Japanese | Opened | Last extension | Length[1] | Stations[1] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Red | Via trackage rights | Kitakyū Namboku Line | 北大阪急行電鉄 | 1970 | 1970 | 5.9 km (3.7 mi) | 4[Note 1] | |
| Line 1 | Midōsuji Line | 御堂筋線 | 1933 | 1987 | 24.5 km (15.2 mi) | 20 | ||
| Purple | Line 2 | Tanimachi Line | 谷町線 | 1967 | 1983 | 28.1 km (17.5 mi) | 26 | |
| Blue | Line 3 | Yotsubashi Line | 四つ橋線 | 1942 | 1972 | 11.4 km (7.1 mi) | 11 | |
| Green | Line 4 | Chūō Line (Yumehanna) | 中央線 | 1997[Note 2] | – | 2.4 km (1.5 mi) | 1[Note 3] | |
| 1961[Note 4] | 1985 | 15.5 km (9.6 mi) | 13 | |||||
| Via trackage rights | Keihanna Line (Yumehanna) | 近鉄けいはんな線 | 1986 | 2006 | 18.8 km (11.7 mi) | 8[Note 5] | ||
| Pink | Line 5 | Sennichimae Line | 千日前線 | 1969 | 1981 | 12.6 km (7.8 mi) | 14 | |
| Brown | Via trackage rights | Hankyu Senri Line | 阪急千里線 | 1969 | – | 13.6 km (8.5 mi) | 11[Note 6] | |
| Hankyu Kyoto Main Line | 阪急京都本線 | 1969[Note 7] | – | 41.1 km (25.5 mi) | 22[Note 8] | |||
| Line 6 | Sakaisuji Line | 堺筋線 | 1969 | 1993 | 8.5 km (5.3 mi) | 10 | ||
| Lime | Line 7 | Nagahori Tsurumi-ryokuchi Line | 長堀鶴見緑地線 | 1990 | 1997 | 15.0 km (9.3 mi) | 17 | |
| Gold | Line 8 | Imazatosuji Line | 今里筋線 | 2006 | – | 11.9 km (7.4 mi) | 11 | |
| TOTAL (Subway only – not incl. trackage rights portions): | 129.9 km (80.7 mi) | 123 | ||||||
| Automated people mover | ||||||||
| Light blue |
New Tram | Nankō Port Town Line | 南港ポートタウン線 | 1997[Note 9] | – | 0.7 km (0.43 mi) | 1[Note 10] | |
| 1981[Note 11] | 2005 | 7.2 km (4.5 mi) | 9 | |||||
| TOTAL (Subway, incl. People Mover): | 137.8 km (85.6 mi)[1] | 133[1] | ||||||
- Table notes
- ↑ Including Esaka Station
- ↑ Owned by Osaka Port Transport System between Cosmosquare Station and Ōsakakō Station
- ↑ Including Ōsakakō Station
- ↑ Between Ōsakakō Station and Nagata Station
- ↑ Including Nagata Station
- ↑ Including Tenjimbashisuji Rokuchōme Station
- ↑ Between Awaji Station and Kawaramachi Station
- ↑ Including Awaji Station
- ↑ Owned by Osaka Port Transport System between Cosmosquare Station and Trade Center-mae Station
- ↑ Including Trade Center-mae Station
- ↑ Between Trade Center-mae Station and Suminoekoen Station
Planned line and extensions
In addition, there are four line extensions and one new line that are planned. However, on August 28, 2014, the Osaka Municipal Transportation Bureau met about creating the extensions of the later four of the five lines listed below, and have stated considering the current cost of the new extensions (and the possibly of privatization at the time), the government has also thought creating light rail transit or bus rapid transit instead.[9] With Osaka as an Expo 2025 candidate city, there are also tentative plans to extend the Chuo Line northwest onto Yume-shima (the event's planned site), with a terminus on Sakura-jima north of Universal Studios Japan. Provisions were put in place for such an extension when the existing road tunnel between Cosmosquare and Yume-shima was built, but the current state of the artificial island (with only industrial facilities and a lone convenience store for workers) mean it is unlikely to be built if Osaka loses its bid.
| Line color |
Mark | Line number |
Name | Start | Terminus | Length |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Line 3 | Yotsubashi Line | Nishi-Umeda | Jūsō, later towards Shin-Ōsaka | 2.9 km (to Jūsō) | ||
| Line 5 | Sennichimae Line | Minami-Tatsumi | towards Mito | (TBD) | ||
| Line 7 | Nagahori Tsurumi-ryokuchi Line | Taishō | Tsurumachi Yonchōme (vicinity) | 5.5 km | ||
| Line 8 | Imazatosuji Line | Imazato | Yuzato Rokuchōme | 6.7 km | ||
| (TBD) | - | Line 9 | Shikitsu–Nagayoshi Line (provisional) | Suminoekōen | Kire-Uriwari | 6.9 km |
Technology and rolling stock
Osaka Municipal Subway rolling stock use two types of propulsion systems. The vast majority of lines use trains with conventional electric motors, but the two newest lines, the Nagahori Tsurumi-ryokuchi Line and Imazatosuji Line, use linear motor-powered trains, which allow them to use smaller trains and tunnels, reducing construction costs. These two lines have half-height automatic platform gates installed at all station platforms, as does the Sennichimae Line.[10]
Also, unlike other rapid transit networks in Japan, most Osaka subway lines use a third rail electrification system for trains. Only three lines use overhead catenary: the Sakaisuji Line, to accommodate through services on Hankyu trackage; and the linear-motor Nagahori Tsurumi-ryokuchi and Imazatosuji Lines. Also unusually, all lines use standard gauge; there are no narrow gauge sections of track due to the network being almost entirely self-enclosed.
Electric motored
- 10 series: Midōsuji Line
- 20 series: Chūō Line
- 21 series ("New 20 series"): Midōsuji Line
- 22 series ("New 20 series"): Tanimachi Line
- 23 series ("New 20 series"): Yotsubashi Line
- 24 series ("New 20 series"): Chūō Line (A variant of the 24 series is used on the Chūō Line in Osaka Port Transport System livery.)
- 25 series ("New 20 series"): Sennichimae Line
- 66 series: Sakaisuji Line
- 30000 series: Tanimachi Line and Midōsuji Line
Linear motored
- 70 series: Nagahori Tsurumi-ryokuchi Line
- 80 series: Imazatosuji Line
Fares
Osaka Metro charges five types of fares for single rides, based on the distance traveled in each journey.[11] Some discount fares exist.
| Distance travelled | Rates (yen)[11] |
|---|---|
| 1–3 km |
|
| 4–7 km |
|
| 8–13 km |
|
| 14–19 km |
|
| 20–25 km |
|
Incidents
On April 8, 1970, a gas explosion occurred during the construction of the Tanimachi Line at Tenjimbashisuji Rokuchōme Station, killing 79 people and injuring 420.[12][13] The gas leaked out from a detached joint and filled the tunnel and exploded, creating a fire pillar of over 10 meters and destroying 495 houses and buildings.[14]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 営業線の概要 [Overview of operating lines] (in Japanese). 大阪市営交通局 [Osaka Municipal Transportation Bureau]. Archived from the original on January 11, 2014. Retrieved June 7, 2014.
- ↑ "交通局の予算・決算について" [For budget and balance sheet of Transportation Bureau] (in Japanese). 大阪市営交通局 [Osaka Municipal Transportation Bureau]. Retrieved December 18, 2014.
- ↑ MiSoL ASP会員サービス・アプリケーション概要 Archived 2007-10-27 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ http://www.mlit.go.jp/kisha/kisha07/01/010330_3/01.pdf
- ↑ Kokudo Kōtsū Shō Tetsudō Kyoku (2005). Tetsudō Yōran (Heisei 17 Nendo) (in Japanese). Tokyo: Denkisha Kenkyūkai. p. 228. ISBN 4-88548-106-6.
- ↑ "公営地下鉄在籍車数ビッグ3 大阪市交通局 (One of the big three public subway operators: Osaka Municipal Subway)". Japan Railfan Magazine. Vol. 49 no. 576. April 2009. pp. 88–99.
- ↑ Rogers, Krista. "The most crowded train lines during rush hour in Tokyo, Osaka, and Nagoya are…". Rocket News 24. Retrieved September 8, 2014.
- ↑ 大阪府内で働く人の通勤時間は「52分」――理想の路線は?. bizmakoto.jp (in Japanese). September 9, 2014. Retrieved September 8, 2014.
- ↑ 地下鉄4線延伸「採算厳しい」 有識者審議会. Yomiuri Online (in Japanese). August 29, 2014. Retrieved September 1, 2014.
- ↑ "Osaka subway's Sennichimae Line to have platform screen doors installed in every station Chinese translation to follow". Asian Public Transport. February 13, 2014. Retrieved September 8, 2014.
- 1 2 "Tickets". Osaka Metro. Retrieved April 14, 2018.
- ↑ 市会のあゆみ. Osaka City Council Website (in Japanese). Retrieved August 3, 2014.
- ↑ Pulvers, Roger (November 4, 2012). "Beware the parallels between boom-time Japan and present-day China". The Japan Times. Retrieved August 3, 2014.
- ↑ "Gas Explosion at a Subway Construction Site". Failure Knowledge Center. Retrieved August 3, 2014.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Ōsaka Metro. |