Operation Herkules
| Operation Herkules | |
|---|---|
Part of Mediterranean and Middle East Theatre
| |
 | |
| Type | Invasion |
| Location |
Malta, 80 km (50 mi) south of Sicily Coordinates: 35°53′N 14°30′E / 35.883°N 14.500°E |
| Planned by | Generalmajor Kurt Student |
| Objective |
|
| Date | Planned for mid-July 1942 |
| Outcome | Cancelled in November 1942 |
Operation Herkules (German: Unternehmen Herkules; Italian: Operazione C3) was the German code-name given to an abortive plan for the invasion of Malta during World War II. Through air and sea landings, the Italians and Germans hoped to eliminate Malta as a British air and naval base and secure an uninterrupted flow of supplies across the Mediterranean Sea to Axis forces in Libya and Egypt.
Extensive preparations were made for the invasion, but the Axis victory at the Battle of Gazala (26 May to 21 June 1942), the capture of Tobruk on 21 June and Operation Aïda, the pursuit of the British as they retreated into Egypt, led to the plan being postponed and then cancelled in November 1942.
Origins
The Axis plan to invade Malta had its origin in Italian military studies conducted in the mid-1930s during Second Italo-Abyssinian War. By 1938, the Italian army command had estimated the amount of sea transport it would require to move significant military forces into North Africa, and identified the seizure of Malta as a prerequisite. An outline plan for a seaborne assault was drawn up and periodically revised, but the Regia Marina initially showed little interest in it.[1] The concept was approved at a meeting between Adolf Hitler and Benito Mussolini from 29 to 30 April 1942.
Axis plans and preparations
Airborne forces

Command of the airborne component of Herkules was given to Generalmajor Kurt Student and Fliegerkorps XI. Student had planned and executed the German airborne assault in the Battle of Crete in May 1941. In contrast with the hasty planning for that operation, Student now had months to prepare and avoid the mistakes made on Crete. Knowledge of British defensive positions on Malta was extensive, thanks to meticulous aerial mapping by the Italians. Every fortification, artillery emplacement and AA battery was carefully noted and scrutinised. Student claimed later that "We even knew the calibre of the coastal guns, and how many degrees they could be turned inland".[2] Ten Gruppen of Junkers Ju 52 transports with 500 aircraft were allocated for the air landings, along with 300 DFS 230 gliders (carrying ten men each) and 200 larger Go 242 gliders (each carrying twenty-three men or a light vehicle/gun).[2] Also to be included were two dozen Messerschmitt Me 321 Gigant gliders capable of carrying up to 200 fully equipped paratroopers or a 25 long tons (25 t) tank. These were to be towed by the new He 111Z (Zwilling) five-engined modification of the He 111 medium bomber.[3]

The Regia Aeronautica would contribute approximately 180–220 transport aircraft, mostly three-engined SM.75s (carrying 24–28 men each), SM.81s (carrying 12–14 men each) and SM.82s (carrying 30–34 men each).[4] Given the 90 mi (140 km) distance between Axis airfields on Sicily and the drop zones over Malta, it was possible for the motorised transports to make four round-trips per day.[2] They were to drop one Italian and one German airborne division onto the southern side of the island. The paratroopers had to secure the high ground behind the invasion beaches, and seize a nearby airfield for Axis transport aircraft to land on with another division and supplies.[5] Airborne units for the invasion included the German Fliegerdivision 7 (11,000 men) plus the Italian 185th Airborne Division Folgore (7,500 men) and 80th Infantry Division La Spezia airlanding division (10,500 men); approximately 29,000 airborne troops.[5] Preparations for the airborne assault included construction of three glider strips 25 mi (40 km) south of Mount Etna on Sicily.
Amphibious forces
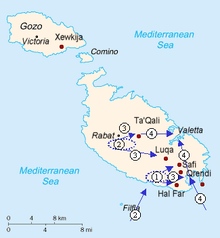
1 – First airborne landings
2 – Second airborne landing and seaborne landings
3 – Breakout
4 – Capture of Valetta and landing of additional troops
The seaborne assault force comprised 70,000 Italian ground troops who were to make amphibious landings at two points on the south-eastern side of the island, in Marsaxlokk bay, with the main effort falling upon a site named "Famagosta beach", and a smaller secondary landing at "Larnaca beach". Also to be seized were the lesser islands of Gozo and Comino. Amphibious feints would be directed at St. Paul's Bay, Mellieha Bay, and north-west of Valletta near the old Victoria Lines, to draw British attention away from the real landing sites.[6] The main assault convoy was scheduled to begin landing on Malta just before midnight on the first day, after the airborne forces had landed in the afternoon and secured the heights above the beaches. The bulk of the first-wave assault troops would come from the Friuli Infantry Division (10,000 men) and Livorno Infantry Division (9,850) of the Italian XXX Corps. Also included were 1,200 men from the 1st Assault Battalion and Loreto Battalion (both drawn from the Regia Aeronautica) two battalions of San Marco Marines (2,000) three battalions of Blackshirts (1,900) and 300 Nuotatori (a commando unit of San Marco marines specially trained in ocean swimming and beach assault). Armoured support comprised nineteen Semovente 47/32 and eight Semovente 75/18 self-propelled guns plus thirty L3 tankettes (comparable in size and armament to the British Bren Gun Carrier).[7]
The follow-up convoy would be mainly made up of troops from the Italian XVI Corps: the Assieta Infantry Division (9,000) and the Napoli Infantry Division (8,900) along with attached artillery assets (3,200). It would also include the remainder of the 10th Armour Regiment (3,800). The Superga Infantry Division (9,200) plus a battalion of Blackshirts and a small detachment of San Marco Marines (1,000) were to be in position to land on the smaller island of Gozo in the early morning hours of the second day.[7] Additional armour intended for Herkules included 2.Kompanie/Panzerabteilung z.b.V.66 (zur besonderen Verwendung [for special use]), a German unit partly equipped with captured Russian tanks. Ten assorted KV-1 [46 long tons (47 t)] and KV-2 [53 long tons (54 t)] heavy tanks were made available. At least ten Italian motozattere (landing craft) were modified with reinforced flooring and internal ramps to carry and off-load the Russian vehicles. Other tanks in the unit included captured Russian T-34 medium tanks, up-armoured German light tanks (five VK 1601s and five VK 1801s) plus twelve German Panzer IVGs armed with 75 mm guns.[8][9] Twenty German Panzer III tanks were also offered for use in the invasion but it is not known what unit these were to be drawn from.[6] Two days were allowed for the main amphibious assault and landing of the follow-up convoy, though this was dependent on quickly securing Marsaxlokk Bay to land heavier artillery pieces and a much higher tonnage of supplies.[10]
Landings

Lacking enough landing craft for an amphibious assault, the Regia Marina secured plans from the German Kriegsmarine to build copies of the Marinefährprahm Type A (MFP) in Italian shipyards. These 220 long tons (220 t) shallow-draught vessels were capable of transporting up to 200 fully equipped infantry, 2–3 medium tanks, or an equivalent weight in cargo, and could unload directly onto an open beach via a drop-down bow ramp. Sixty-five of these motozattere (MZs) were completed by July 1942, and about fifty were available for the invasion.[11] Twenty German MFPs were transferred to the Mediterranean via the river Rhone to make up for an expected shortfall of Italian-built landing craft.
German-operated landing craft were sent to Italy via rail for the invasion, including twelve Siebel ferries (catamaran rafts powered by automobile engines driving water screws and armed with 88 mm and 20 mm flak guns), six Type 39 Pionierlandungsboote (carrying 20 long tons (20 t) of cargo, two light vehicles or 45 infantry, unloaded via clamshell doors at the bow), six Type 40 Pionierlandungsboote (a larger version of the Type 39, carrying 40 long tons (41 t) of cargo, three or four light vehicles or 80–90 fully equipped infantry), a company of eighty-one Sturmboote (Type 39 Stormboats, small plywood boats carrying up to six infantrymen and powered by 30 hp outboard motors) plus an assortment of large inflatable rafts (carrying 25 troops each). Some rafts were powered by outboard motors, but some had to be rowed.[4]
The Italians assembled a varied collection of other naval craft to transport the amphibious forces. These included two former Strait of Messina railway ferries (converted to carry four to eight tanks each); ten passenger ships (800–1,400 men each), six former passenger ferries (400 men each), six cargo ships (3,000 tons of supplies each), 30 ex-trawlers (300 men each); five converted minelayers (500 men each) and 74 assorted motorboats (30–75 men each). The Italians also requested the use of 200 additional German Sturmboote to quickly transfer men from ship to shore.[4] The Italian landing flotilla and the supporting ships formed the "Special Naval Force" (Forza Navale Speciale) under Admiral Vittorio Tur.
Specialised landing equipment slated for Herkules included the Seeschlange (Sea Snake), a floating ship-to-shore bridge originally developed by the German Army for Operation Sea Lion. It was formed from a series of joined modules that could be towed into place and act as a temporary jetty. Moored ships could then unload their cargo either directly onto the "roadway" or lower it down onto the Seeschlange via their cranes. The Seeschlange had been tested by the Army Training Unit at Le Havre in the fall of 1941 and was easily transportable by rail.[12]
Naval escort
The Regia Marina had to protect the invasion convoys from attacks by the British Mediterranean Fleet and provide gunfire support during the landings. The force assigned to accomplish this included four battleships (Littorio, Vittorio Veneto, Caio Duilio and Andrea Doria), four heavy cruisers, eight light cruisers and 21 destroyers. These ships would assemble and sortie from the ports of Messina, Reggio Calabria, Augusta and Cagliari. The two older Andrea Doria-class battleships would carry approximately 200 rounds each for shore bombardment.[6]
Italian and German submarines were to scout for and intercept British naval forces attempting to interfere with the seaborne landings. One submarine was to be stationed midway between Sicily and Malta, to act as a guide beacon for the transport aircraft on their way to and from the drop zones.[6]
The Italians were confident they could defeat any daylight incursions by the Mediterranean Fleet, especially given the Luftwaffe's ability to dominate the daytime skies, but there were concerns the Italian fleet would face serious difficulties if the British attacked at night.[10] Lacking ship-borne radar and having neglected night-fighting training and equipment, the Regia Marina had been defeated at the Battle of Cape Matapan in March 1941. A similar encounter off Malta might wreak havoc on the slow-moving Axis invasion convoys, leaving the airborne forces cut off and imperilling Axis chances of taking the island.[13]
_starboard_bow_view.jpg)
The Regia Marina had made some efforts to rectify this situation by equipping the battleship Littorio with an experimental E.C.-3/bis Gufo (Owl) radar apparatus in August 1941, but the unit was considered unreliable (not until September 1942 did Littorio receive a standardised production-version Gufo with better performance; this set could detect surface ships at a range of 17 nmi (31 km; 20 mi) and aircraft out to a range of 45 nmi (83 km; 52 mi)).[13] In September 1941, while awaiting production of Italian-made radar units in quantity, the Regia Marina requested from the Kriegsmarine installation of a FuMO 24/40 G DeTe unit on the new destroyer, Legionario (then still under construction). DeTe units could detect surface ships up to 14 nmi (26 km; 16 mi) away. By March 1942, the set had been delivered and installed and a small group of Italian ratings had been trained in Germany on its use. Operational testing began that spring and by May, the fleet commander Vice-Admiral Angelo Iachino had submitted a report praising its performance.[13]
Malta defences
In 1942 the garrison of Malta consisted of 15 infantry battalions (11 Commonwealth, 4 Maltese) organised into four brigades totalling 26,000 men. Tank support was provided by the 1st Independent Troop of the Royal Tank Regiment, disembarked in November 1940, which was initially equipped with four Matilda II "Infantry Tanks", armed with 2-pounder (40 mm) guns, and two Vickers Mk.VIC light tanks, armed with two machine guns (all tanks as part of detachments from the 7th Royal Tank Regiment and the 3rd The King's Own Hussars). These were reinforced in January 1942 by an additional eight tanks (four Cruiser Mk I and three Cruiser Mk IV tanks, and one Vickers Mk.VIC light tank), with the cruiser tanks armed with 2-pounder (40 mm) guns (all additional tanks were as part of a detachment from the 6th Royal Tank Regiment).[14][15][16][17] Artillery support came from the 12th Field Regiment, Royal Artillery with twenty-four 25-pounder 3.45 in (88 mm) field guns, capable of providing fire support out to a range of 6.8 mi (11 km) and covering most of the island while remaining in protected static positions.[18] Malta's fixed defences included nineteen heavy coastal guns (varying in size from 12-inch to 16-inch - although these Victorian era weapons were all decommissioned), 130 smaller coastal guns (6-pounder to 9.2-inch), and 112 heavy and 144 light anti-aircraft guns.[19][20][1][4]
The smaller coastal guns were composed of:[21]
- 10 × BL 6 in (150 mm) Mk XXIV, on Mounting, 6 in (150 mm) Mk 5 or 6
- 7 × BL 9.2 in (230 mm) gun Mk X, on Mounting Mk 7
- QF 4.5 in (110 mm) gun Mk II, on Mounting Mk I
- 18 × QF 6 pounder 10 cwt gun (9 × 2) [20]
- ~30 × Ordnance QF 18 pounder
Aftermath
A date near mid-July 1942 was set for the invasion, partly to allow time to bring troops from other front line positions. Field Marshal Erwin Rommel supported the Malta plan and asked Hitler for command of the invasion forces. His reasons for supporting an invasion were to hinder the Allied troops fighting in Africa, as well as to remove the threat to the convoys heading to Italian-German forces with supplies, oil and men, all of which they were desperately low on. He prioritised the attack to such an extent that he was willing to move units from his front for the attack. The head of the Luftwaffe, Hermann Göring, opposed the invasion, fearing it would turn into another near-disaster for his paratroops, as had happened on Crete. Generalfeldmarschall Albert Kesselring tirelessly promoted Unternehmen Herkules but even he was eventually dissuaded when it became apparent that too many air and ground units had been siphoned off to support the Axis drive into Egypt, diminishing any chance of success. With Hitler lacking faith in the parachute divisions after the Invasion of Crete, and in the ability of the Italian Navy to protect the invasion fleet from British naval attacks, the plan was cancelled.
References
- 1 2 Greene/Massignani, p. 64
- 1 2 3 Bekker, p.352
- ↑ Green, p.648
- 1 2 3 4 "Could Royal Navy save Malta?". groups.google.com. 2013. Retrieved 12 August 2013.
- 1 2 Greene/Massignani, p. 67
- 1 2 3 4 Greene/Massignani, p. 70
- 1 2 Greene/Massignani, p. 66
- ↑ Ref
- ↑ Ritgen, p.7
- 1 2 Greene/Massignani, p. 71
- ↑ Marcon, p.221-224
- ↑ Schenk, p.139
- 1 2 3 Greene/Massignani, p. 209–213
- ↑ "RTR Independent Troop - Malta". Axis History Forum. 2011. Retrieved 21 May 2017.
- ↑ "British Tanks on Malta". World War 2 Mailing List. 2007. Retrieved 21 May 2017.
- ↑ "British Forces – MkVIc on Malta". ww2incolor.com. 2013. Retrieved 12 August 2013.
- ↑ "British Tanks on Malta". robomod.net. 2007. Retrieved 12 August 2013.
- ↑ Greene/Massignani, p. 68
- ↑ "The place of Malta in British strategic Policy". University College London. 2002. Retrieved 21 May 2017.
- 1 2 "Malta Garrison 1942". axis history forum. 2008. Retrieved 21 May 2017.
- ↑ Hogg
Bibliography
- Ansel, Walter (1972). Hitler and the Middle Sea. Duke University Press. ISBN 978-0-8223-0224-7.
- Bekker, Cajus (1975). The Luftwaffe War Diaries. Ballantine Books. ISBN 978-0-306-80604-9.
- Gabriele, Mariano (1965). Operazione C3: Malta. Roma: Ufficio Storico della Marina Militare. OCLC 560391306.
- Green, William (1979). Warplanes of the Third Reich. New York: Doubleday. ISBN 978-0-356-02382-3.
- Greene, Jack; Massignani, Alessandro (1998). The Naval War in the Mediterranean 1940–1943. Chatham Publishing. ISBN 978-1-86176-057-9.
- Greene, Jack; Massignani, Alessandro (Jan–Feb 1993). "The Summer of '42: The Proposed Axis Invasion of Malta" (20). Conshohocken, PA: Command Magazine. ISSN 0198-7313.
- Heckmann, Wolf (1981). Rommel's War in Africa. Doubleday. ISBN 978-0-385-14420-9.
- Hogg, Ian (2002). British & American Artillery of World War Two (rev. ed.). Greenhill Books. ISBN 978-1-85367-478-5.
- Kitchen, Martin (2009). Rommel's Desert War: Waging World War II in North Africa, 1941–1943. London: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-50971-8.
- Lucas, Laddie (1994). Malta: The Thorn in Rommel's Side (Large Print ed.). Leicester: Ulverscroft Large Print. ISBN 978-0-7089-3169-1.
- Levine, Alan J. (2008). The War Against Rommel's Supply Lines, 1942–43. Mechanicsburg, PA: Stackpole Books. ISBN 978-0-8117-3458-5.
- Marcon, Tullio (1998). I Mule del Mare [The Mule of the Sea]. Storia militare. Parma: Albertelli. ISBN 978-88-87372-02-1.
- O'Hara, Vincent P. (2009). Struggle for the Middle Sea: The Great Navies at War in the Mediterranean Theater, 1940–1945. Naval Institute Press. ISBN 978-1-59114-648-3.
- Ritgen, Helmut (1995). The Western Front 1944: Memoirs of a Panzer Lehr Officer. J.J. Fedorowicz. ISBN 978-0-921991-28-1.
- Sadkovich, James J. (1994). The Italian Navy in World War II. Greenwood Press. ISBN 978-0-313-28797-8.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Operation Herkules. |