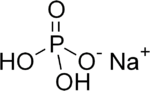
Monosodium phosphate
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Sodium dihydrogen phosphate | |
| Other names
monobasic sodium phosphate; sodium dihydrogen phosphate; sodium biphosphate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.028.591 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| NaH2PO4 | |
| Molar mass | 119.98 g/mol |
| Appearance | White powder or crystals |
| Density | 2.36 g/cm3 (anhydrous) |
| 59.90 g/100 mL (0°C) | |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 | |
| Flash point | Non-flammable |
| Related compounds | |
Other cations |
Monopotassium phosphate Monoammonium phosphate |
Related compounds |
Disodium phosphate Trisodium phosphate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Monosodium phosphate (MSP), also known as monobasic sodium phosphate and sodium dihydrogen phosphate, is an inorganic compound of sodium with a dihydrogen phosphate (H2PO4−) anion. One of many sodium phosphates, it is a common industrial chemical. The salt exists in an anhydrous form, as well as mono- and dihydrates.[1]
Production and reactions
The salt is obtained by partial neutralization of phosphoric acid. The pKa of monosodium phosphate is 6.8-7.2 (depending on the physicochemical characteristics during pKa determination).[2]
Heating this salt above 169 °C gives the corresponding sodium acid pyrophosphate:
- 2 NaH2PO4 → Na2H2P2O7 + H2O
Uses
Phosphates are often used in foods and in water treatment. The pH of such formulations is generally adjusted by mixtures of various sodium phosphates, such as this salt.[1] The sodium chloride equivalent value, or E-Value, is 0.49. It is soluble in 4.5 parts water.
Food additive
It is added in animal feed, toothpaste, and evaporated milk. It is used as a thickening agent and emulsifier.
Detection of magnesium
Monosodium phosphate is used to detect the presence of magnesium ions in salts. Formation of a white precipitate on the addition of ammonium chloride, ammonium hydroxide and monosodium phosphate to an aqueous or dilute HCl solution of the salt indicates presence of magnesium ions.
Notes
- 1 2 Klaus Schrödter, Gerhard Bettermann, Thomas Staffel, Friedrich Wahl, Thomas Klein, Thomas Hofmann "Phosphoric Acid and Phosphates" in Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 2008, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. doi:10.1002/14356007.a19_465.pub3
- ↑ Salaun, F.: "Influence of mineral environment on the buffering capacity of casein micelles", "Milchwissenschaft", 62(1):3
