Languages of Spain
| Languages of Spain | |
|---|---|
| Official languages | Spanish (aka Castilian) |
| Regional languages |
|
| Main immigrant languages |
Spanish, Arabic, Romanian, English, German, French, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese, Bulgarian, Ukrainian, Russian. (see immigration to Spain) |
| Sign languages |
Spanish Sign Language Catalan/Valencian Sign Language |
| Common keyboard layouts | |
| Source | [1] |
The languages of Spain (Spanish: lenguas de España), or Spanish languages (Spanish: lenguas españolas),[2] are the languages spoken or once spoken in Spain. Romance languages are the most widely spoken in Spain; of which Spanish, or Castilian, is the only language which has official status for the whole country.[3] Various other languages have co-official or recognised status in specific territories,[4] and a number of unofficial languages and dialects are spoken in certain localities.
Present-day languages
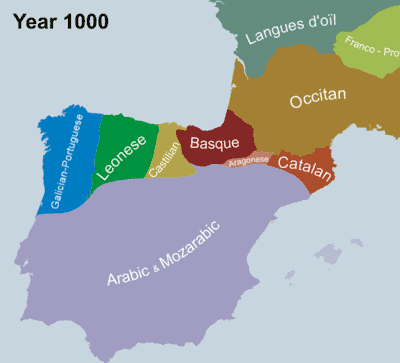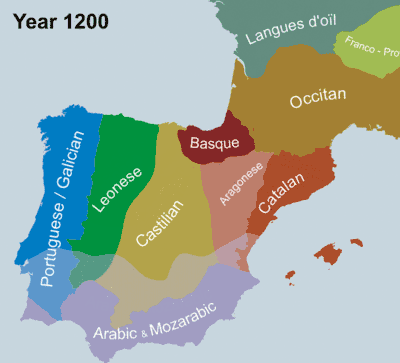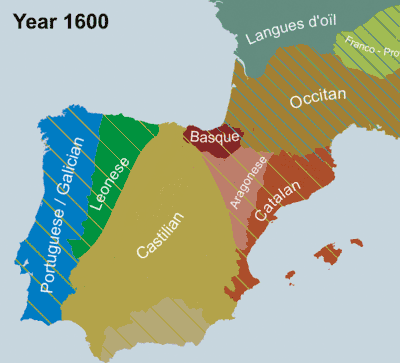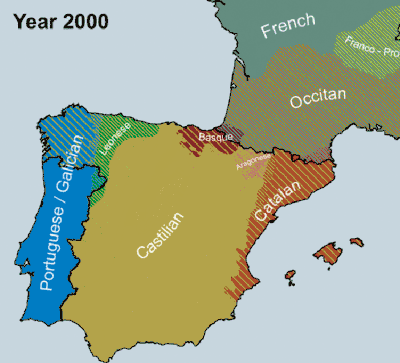
In terms of the number of speakers and dominance, the most prominent of the languages of Spain is Spanish (Castilian), spoken by about 99% of Spaniards as a first or second language.[5] Catalan (or Valencian) is spoken by 19%, Galician by 5%, and Basque by 2% of the population.[6]
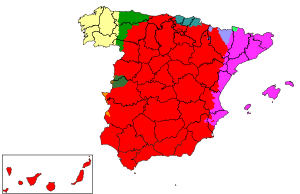
Distribution of the regional co-official languages in Spain:
- Aranese, co-official in Catalonia.[7] It is spoken mainly in the Pyrenean comarca of the Aran Valley (Val d'Aran), in north-western Catalonia. It is a variety of Gascon, which in turn is a variety of the Occitan language.
- Basque, co-official in the Basque Country and northern Navarre (see Basque-speaking zone). Basque is the only non-Romance language (as well as non-Indo-European) with an official status in mainland Spain.
- Catalan, co-official in Catalonia and in the Balearic Islands (sometimes referred to as Balearic). It is recognised—but not official—in Aragon in the area of La Franja.
- Valencian (variety of Catalan), co-official in the Valencian Community. Not all areas of the Valencian Community, however, are historically Valencian-speaking, particularly the western side. It is also spoken without official recognition in the municipality of Carche, Murcia.
- Galician, co-official in Galicia. It is also spoken without official recognition in the adjacent western parts of the Principality of Asturias and Castile and León.
Spanish is official throughout the country; the rest of these languages have legal and co-official status in their respective communities, and (except Aranese) are widespread enough to have daily newspapers and significant book publishing and media presence in those communities. In the cases of Catalan and Galician, they are the main languages used by the Catalan and Galician regional governments and local administrations. A number of citizens in these areas consider their regional language as their primary language and Spanish as secondary.
In addition to these, there are a number of seriously endangered and recognised minority languages:
- Aragonese, recognised—but not official—in Aragon.
- Asturian, recognised—but not official—in Asturias.
- Leonese, recognised—but not official—in Castile and León. Spoken in the provinces of León and Zamora.
Spanish itself also has distinct dialects around the country; for example, the Andalusian or Canarian dialects, each of these with their own subvarieties, some of them being partially closer to the Spanish of the Americas, which they heavily influenced at different degrees, depending on the regions or periods, and according to different and non-homogeneous migrating or colonisation processes.
Five very localised dialects are of difficult filiation: Fala, a nearly extinct variety of its own mostly adscribed to the Galician-Portuguese group; Cantabrian and Extremaduran, two Astur-Leonese dialects also regarded as Spanish dialects; Eonavian, a dialect between Asturian and Galician, closer to the latter according to several linguists; and Benasquese, a Ribagorçan dialect that was formerly classified as Catalan, later as Aragonese, and which is now often regarded as a transitional language of its own. Asturian and Leonese are closely related to the local Mirandese which is spoken on an adjacent territory but over the border into Portugal. Mirandese is recognised and has some local official status.
With the exception of Basque, which appears to be a language isolate, all of the languages present in mainland Spain are Indo-European languages, specifically Romance languages.
Afro-Asiatic languages, such as Arabic (including Ceuta Darija) or Berber (mainly Riffian), are spoken by the Muslim population of Ceuta and Melilla and by recent immigrants (mainly from Morocco and Algeria) elsewhere.
Portuguese and Galician
In Galicia, the mutual relationship between Galician and Portuguese has caused some controversy, since some linguists, such as Lindley Cintra,[8] consider that they are still dialects of a common language, in spite of the differences in phonology and vocabulary (see reintegrationism).
Others, such as Pilar Vázquez Cuesta,[9] argue that they have become separate languages due to major differences in phonetics and vocabulary usage, and, to a lesser extent, morphology and syntax.
In any case, the respective written standards are noticeably different one from another, partly because of the divergent phonological features and partly due to the usage of Spanish orthographic conventions over the Portuguese ones at the time of Galician standardisation by the early 20th century.
The official (delegated onto both the Galician Language Institute and the Royal Galician Academy standard) and widespread position is that Galician and Portuguese should be considered independent languages.
A Galician-Portuguese-based dialect known as Fala is locally spoken in an area sometimes called Valley of Jálama/Xálima, which includes the towns of San Martín de Trevejo (Sa Martin de Trevellu), Eljas (As Elhas) and Valverde del Fresno (Valverdi du Fresnu), in the northwestern corner of Cáceres province, Extremadura.
Portuguese proper is still spoken by local people in three border areas:
- The town of La Alamedilla, in Salamanca province.
- The so-called Cedillo-horn, including Cedillo (in Portuguese Cedilho) and Herrera de Alcántara (in Portuguese Ferreira de Alcântara).
- The town of Olivenza (in Portuguese Olivença), in Badajoz province, and its surrounding territory, which used to be Portuguese until the 19th century and is still claimed by Portugal.
Ancient languages
In addition to the languages which continue to be spoken in Spain to the present day, other languages which have been spoken within what are now the borders of Spain include:
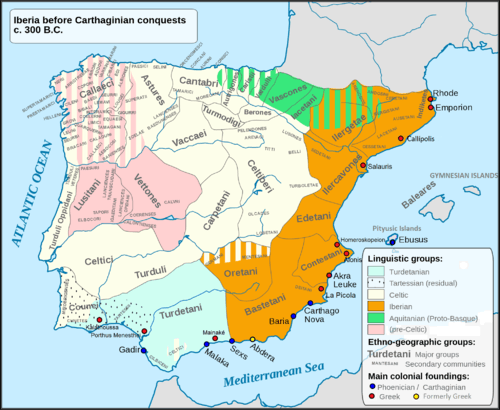
- Tartessian language
- Iberian language
- Celtic languages
- Lusitanian language
- Punic language
- Latin language
- Guanche language
- Galician-Portuguese
- Gothic language
- Vandalic language
- Frankish language
- Andalusi Arabic
- Classical Arabic
- Mozarabic languages
- Romani language
Languages that have been spoken outside Spain but which have roots in Spain are:
Variants
There are also variants of these languages proper to Spain, either dialect, cants or pidgins:
Further information
- Aragonese (aragonés)
- Astur-Leonese
- Asturian (asturianu, bable)
- Leonese (llionés)
- Extremaduran (estremeñu)
- Cantabrian (cántabru, montañés)
- Basque (euskara)
- Catalan (català), known as Valencian (valencià) in the Valencian Community
- Galician (galego)
- Gascon (Occitan dialect)
- Aranese (aranés)
- Spanish (español), also known as Castilian (castellano)
- Judaeo-Spanish (djudeo-espanyol, judezmo, ladino, sefardi, etc.)
- Dialects of the Spanish in Spain
- Andalusian Spanish
- Canarian Spanish
- Castilian Spanish
- Castrapo (Galicia)
- Castúo (Extremadura)
- Murcian Spanish
- Spanish spoken by Catalan-speakers
- Sign languages
- Spanish Sign Language (lengua de signos española, LSE).
- Catalan Sign Language (llengua de signes catalana, LSC) and Valencian Sign Language (llengua de signes valenciana, LSV).
- Language politics in Francoist Spain
See also
References
- ↑ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 14 April 2016. Retrieved 3 February 2007.
- ↑ The term lenguas españolas appears in the Spanish Constitution, referrering to all the languages spoken within Spain (those are Basque, Spanish, Catalan/Valencian, Galician, Asturian, Leonese, etc.).
- ↑ Promotora Española de Lingüística - Lengua Española o Castellana Archived 27 November 2010 at the Wayback Machine.. (Spanish)
- ↑ M. Teresa Turell (2001). Multilingualism In Spain: Sociolinguistic and Psycholinguistic Aspects of Linguistic Minority Groups. Multilingual Matters. p. 121. ISBN 978-1-85359-491-5.
- ↑ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 27 September 2010. Retrieved 15 January 2016.
- ↑ "CIA – The World Factbook – Spain". Cia.gov. Archived from the original on 19 May 2009. Retrieved 30 April 2011.
- ↑ (in Catalan)(in Occitan) Llei 35/2010, d'1 d'octubre, de l'occità, aranès a l'Aran
- ↑ Lindley Cintra, Luís F. "Nova Proposta de Classificação dos Dialectos Galego-Portugueses" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2 November 2006. (469 KB) Boletim de Filologia, Lisboa, Centro de Estudos Filológicos, 1971 (in Portuguese).
- ↑ Vázquez Cuesta, Pilar «Non son reintegracionista» Archived 8 December 2011 at the Wayback Machine., interview given to La Voz de Galicia on 22 February 2002 (in Galician).
External links
- Detailed Ethno-Linguistic map of Pre-Roman Iberia (around 200 BC)
- Detailed linguistic map of Spain
- Languages in Spain - Find out information about the Official languages of Spain.
