Isocyanate
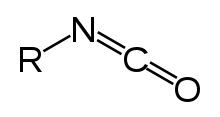
Isocyanate is the functional group with the formula R–N=C=O. Organic compounds that contain an isocyanate group are referred to as isocyanates. An isocyanate that has two isocyanate groups is known as a di-isocyanate. Di-isocyanates are manufactured for reactions with polyols in the production of polyurethanes, a class of polymers.
Isocyanates should not be confused with cyanate esters and isocyanides, whose behaviors are very different. The cyanate (cyanate ester) functional group (R–O–C≡N) is arranged differently from the isocyanate group (R–N=C=O). Isocyanides have the connectivity R-N≡C, lacking the oxygen of the cyanate groups.
Production
Isocyanates are produced by treating amines with phosgene:
- RNH2 + COCl2 → RNCO + 2 HCl
These reactions proceed via the intermediacy of a carbamoyl chloride (RNHC(O)Cl). Owing to the hazards associated with phosgene, the production of isocyanates requires special precautions.[1]
Reactivity
Reactions with nucleophiles
Isocyanates are electrophiles, and as such they are reactive toward a variety of nucleophiles including alcohols, amines, and even water. Upon treatment with an alcohol, an isocyanate forms a urethane linkage:[1]
If a di-isocyanate is treated with a compound containing two or more hydroxyl groups, such as a diol or a polyol, polymer chains are formed, which are known as polyurethanes. Isocyanates react with water to form carbon dioxide:
- RNCO + H2O → RNH2 + CO2
This reaction is exploited in tandem with the production of polyurethane to give polyurethane foams. The carbon dioxide functions as a blowing agent.[2]
Isocyanates also react with amines to give ureas:
- R2NH + R'NCO → R2NC(O)N(H)R'
The addition of an isocyanate to a urea gives a biuret:
- R2NC(O)N(H)R' + R"NCO → R2NC(O)NR'C(O)NHR"
Reaction between a di-isocyanate and a compound containing two or more amine groups, produces long polymer chains known as polyureas.
Cyclization
Isocyanates also can react with themselves. Aliphatic di-isocyanates can form trimers, which are structurally related to cyanuric acid. Isocyanates participate in Diels-Alder reactions, functioning as dienophiles.
Rearrangement reactions
Isocyanates are common intermediates in the synthesis of primary amines via hydrolysis:
- Hofmann rearrangement, a reaction in which a primary amide is treated with a strong oxidizer such as sodium hypobromite[3][4][5] or lead tetraacetate[6] to form an isocyanate intermediate.
- Schmidt reaction, a reaction where a carboxylic acid is treated with ammonia and hydrazoic acid yielding an isocyanate.
- Curtius rearrangement degradation of an acyl azide to an isocyanate and nitrogen gas.
- Lossen rearrangement, the conversion of a hydroxamic acid to an isocyanate via the formation of an O-acyl, sulfonyl, or phosphoryl intermediate.
Common isocyanates
The global market for diisocyanates in the year 2000 was 4.4 million tonnes, of which 61.3% was methylene diphenyl diisocyanate (MDI), 34.1% was toluene diisocyanate (TDI), 3.4% was the total for hexamethylene diisocyanate (HDI) and isophorone diisocyanate (IPDI), and 1.2% was the total for various others.[7] A monofunctional isocyanate of industrial significance is methyl isocyanate (MIC), which is used in the manufacture of pesticides.
Hazards
LD50s are typically several hundred milligrams per kilogram.[8] Despite this low acute toxicity, an extremely low short-term exposure limit (STEL) of 0.07 mg/m−3 is the legal limit for all isocyanates (except methyl isocyanate: 0.02 mg/m−3) in the United Kingdom.[9] These limits are set to protect workers from chronic health effects such as occupational asthma, contact dermatitis or irritation of the respiratory tract.[10]
Methyl isocyanate was the chemical released in the Bhopal disaster causing the death of nearly 4000 people.
Polyurethanes have variable curing times, and the presence of free isocyanates in foams vary accordingly.[11]
All major producers of MDI and TDI are members of the International Isocyanate Institute, whose aim is the promotion of the safe handling of MDI and TDI.
See also
References
- 1 2 Christian Six, Frank Richter "Isocyanates, Organic" in Ulmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 2005, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. doi:10.1002/14356007.a14_611
- ↑ Paul Painter and Michael Coleman. Fundamentals to Polymer Science, An Introductory Text (Second ed.). p. 39.
- ↑ http://alpha.chem.umb.edu/chemistry/orgchem/CH20Handout.pdf, Ch20Handout, University of Massachusetts Boston
- ↑ Mann, F. G.; Saunders, B. C. (1960). Practical Organic Chemistry, 4th Ed. London: Longman. p. 128. ISBN 9780582444072.
- ↑ Cohen, Julius (1900). Practical Organic Chemistry 2nd Ed. London: Macmillan and Co., Limited. p. 72.
- ↑ Baumgarten, Henry; Smith, Howard; Staklis, Andris (1975). "Reactions of amines. XVIII. Oxidative rearrangement of amides with lead tetraacetate". The Journal of Organic Chemistry. 40 (24): 3554–3561. doi:10.1021/jo00912a019. Retrieved 19 December 2013.
- ↑ Randall, D (2002). The Polyurethanes Book. Wiley. ISBN 0-470-85041-8.
- ↑ Allport DC, Gilbert, DS and Outterside SM (eds) (2003).MDI and TDI: safety, health & the environment: a source book and practical guide. Chichester, Wiley.
- ↑ http://www.hse.gov.uk/pUbns/priced/eh40.pdf
- ↑ http://www.hse.gov.uk/construction/healthrisks/hazardous-substances/isocyanates.htm
- ↑ Riedlich, C (2010). "Risk of isocyanate exposure in the construction industry" (PDF). CPWR - The Center for Construction Research and Training: 1–8.
External links
- NIOSH Safety and Health Topic: Isocyanates, from the website of the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH)
- Health and Safety Executive, website of the UK Health and Safety Executive, useful search terms on this site — isocyanates, MVR, asthma
- International Isocyanate Institute
- http://www.actsafe.ca/wp-content/uploads/resources/pdf/Isocyanates.pdf
- Isocyanates – Measurement Methodology, Exposure and Effects Isocyanates in Working Life Workshop Article (1999)
- Health and Safety Executive, Guidance Note (EH16) Isocyanates: Toxic Hazards and Precautions (1984)
- The Society of the Plastics Industry – Technical Bulletin AX119 MDI-Based Polyurethane
- Foam Systems: Guidelines for Safe Handling and Disposal (1993)
- An occupational hygiene assessment of the use and control of isocyanates in the UK by Hilary A Cowie et al. HSE Research Report RR311/2005. Prepared by the Institute of Occupational Medicine for the Health and Safety Executive