Ioflupane (123I)
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
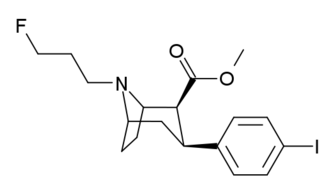
Ioflupane (FPCIT); [I-123] N-ω-fluoropropyl- 2β-carbomethoxy- 3β-(4-iodophenyl) nortropane |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Intravenous |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | N/A |
| Excretion | Renal and fecal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C18H23FINO2 |
| Molar mass | 427.285 g/mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Ioflupane (123I) is the International Nonproprietary Name of a phenyltropane compound which is a neuro-imaging radiopharmaceutical drug, used by nuclear medicine physicians for the diagnosis of Parkinson's disease and the differential diagnosis of Parkinson's disease over other disorders presenting similar symptoms. It is injected into a patient and viewed with a gamma camera in order to acquire SPECT images of the brain with particular respect to the striatum, a subcortical region of the basal ganglia.[2] The drug is sold under the tradename DaTSCAN and is manufactured by GE Healthcare, formerly Amersham plc. It is not marketed outside Europe and the United States.[1]
Pharmacology
DaTSCAN is a solution of ioflupane (123I) for injection into a living test subject.
The iodine introduced during manufacture is a radioactive isotope, I-123, and it is the properties of this isotope that makes the solution visible to a gamma camera. I-123 has a half life of approximately 13 hours and a gamma photon energy of 159 keV making it an appropriate radionuclide for medical imaging. The solution also contains 5% ethanol to aid solubility and is supplied sterile since it is intended for intravenous use.
Ioflupane has a high binding affinity for presynaptic dopamine transporters (DAT) in the brains of mammals, in particular the striatal region of the brain. A feature of Parkinson's disease is a marked reduction in dopaminergic neurons in the striatal region. By introducing an agent that binds to the dopamine transporters a quantitative measure and spatial distribution of the transporters can be obtained.
Method of administration
The DaTSCAN solution is supplied ready to inject with a certificate stating the calibration activity and time. The nominal injection activity is 185 MBq[2] and a scan should not be performed with less than 111 MBq.
Thyroid blocking via oral administration of 120 mg potassium iodide is recommended to minimize unnecessary excessive uptake of radioiodine.[3][4] One dose is given 2 hours before the injection and a further dose 24 hours later.
The most convenient way to administer the IV dose is via a peripheral intravenous cannula. The scan is carried out 3 to 6 hours post injection.[3][4]
Risks
Common side effects of ioflupane (123I) are headache, vertigo, increased appetite and formication. Less than 1% of patients experience pain at the injection site.[2]
The radiation risks are reported as low. The committed effective dose for a single investigation on a 70 kg individual is 4.35 mSv.[5] Pregnant patients should not undergo the test and breast feeding patients must cease since I-123 is secreted in breast milk.
See also
References
- 1 2 "Removal of [123I]Ioflupane From Schedule II of the Controlled Substances Act". DEA Diversion Control Division. Archived from the original on 13 May 2017. Retrieved 2016-02-09.
- 1 2 3 GE Healthcare Ltd. DaTSCAN - Prescribing information
- 1 2 Djang, D. S. W.; Janssen, M. J. R.; Bohnen, N.; Booij, J.; Henderson, T. A.; Herholz, K.; Minoshima, S.; Rowe, C. C.; Sabri, O.; Seibyl, J.; Van Berckel, B. N. M.; Wanner, M. (8 December 2011). "SNM Practice Guideline for Dopamine Transporter Imaging with 123I-Ioflupane SPECT 1.0". Journal of Nuclear Medicine. 53 (1): 154–163. doi:10.2967/jnumed.111.100784. PMID 22159160.
- 1 2 Darcourt, Jacques; Booij, Jan; Tatsch, Klaus; Varrone, Andrea; Vander Borght, Thierry; Kapucu, Özlem L.; Någren, Kjell; Nobili, Flavio; Walker, Zuzana; Van Laere, Koen (17 October 2009). "EANM procedure guidelines for brain neurotransmission SPECT using 123I-labelled dopamine transporter ligands, version 2". European Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging. 37 (2): 443–450. doi:10.1007/s00259-009-1267-x. PMID 19838702.
- ↑ Administration of Radioactive Substances Advisory Committee (2006). Notes for Guidance on the Clinical Administration of Radiopharmaceuticals and Use of Sealed Radioactive Sources. Archived 2009-01-05 at the Wayback Machine.