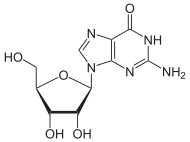
Guanosine
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-Amino-9-[3,4-dihydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-2-yl]-3H-purin-6-one | |
| Other names
Guanine riboside | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.844 |
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | Guanosine |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H13N5O5 | |
| Molar mass | 283.241 |
| -149.1·10−6 cm3/mol | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Guanosine is a purine nucleoside comprising guanine attached to a ribose (ribofuranose) ring via a β-N9-glycosidic bond. Guanosine can be phosphorylated to become guanosine monophosphate (GMP), cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP), guanosine diphosphate (GDP), and guanosine triphosphate (GTP). These forms play important roles in various biochemical processes such as synthesis of nucleic acids and proteins, photosynthesis, muscle contraction, and intracellular signal transduction (cGMP). When guanine is attached by its N9 nitrogen to the C1 carbon of a deoxyribose ring it is known as deoxyguanosine.
The antiviral drug acyclovir, often used in herpes treatment, and the anti-HIV drug abacavir, are structurally similar to guanosine.
Guanosine is required for an RNA splicing reaction in mRNA, when a "self-splicing" intron removes itself from the mRNA message by cutting at both ends, re-ligating, and leaving just the exons on either side to be translated into protein.[1]
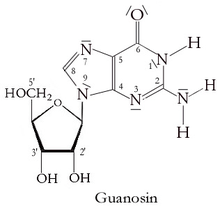
Guanosine was used to make Regadenoson.
References
- ↑ Splicing (JPG) Archived June 13, 2010, at the Wayback Machine.