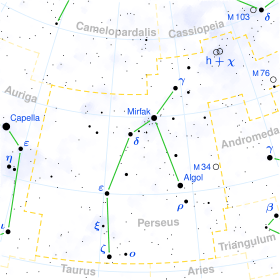
Eta Persei
 | |
| Observation data Epoch J2000 Equinox J2000 | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Perseus |
| Right ascension | 02h 50m 41.80959s[1] |
| Declination | +55° 53′ 43.7876″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 3.79[2] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | K3 Ib[3] |
| U−B color index | +1.90[2] |
| B−V color index | +1.69[2] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | −1.07 ± 0.27[4] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: +16.23[1] mas/yr Dec.: −13.54[1] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 3.71 ± 0.27[1] mas |
| Distance | 880 ± 60 ly (270 ± 20 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | −4.29[5] |
| Details | |
| Radius | 44[6] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 5,135[7] L☉ |
| Temperature | 4,047[7] K |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 5.8[3] km/s |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
Eta Persei (η Persei, abbreviated Eta Per, η Per), is a binary star and the 'A' component of a triple star system (the 'B' component is the star HD 237009)[8] in the constellation of Perseus . It is approximately 1331 light-years away from Earth.
The two components of Eta Persei itself are designated Eta Persei A (also named Miram[9]) and B.
Nomenclature

η Persei (Latinised to Eta Persei) is the binary star's Bayer designation. The designations of its two components as Eta Persei A and B derive from the convention used by the Washington Multiplicity Catalog (WMC) for multiple star systems, and adopted by the International Astronomical Union (IAU).[10]
Eta Persei mysteriously gained the named Miram in the 20th Century, though no source is known.[11][12] In 2016, the IAU organized a Working Group on Star Names (WGSN)[13] to catalog and standardize proper names for stars. The WGSN decided to attribute proper names to individual stars rather than entire multiple systems.[14] It approved the name Miram for the component Eta Persei A on 5 September 2017 and it is now so included in the List of IAU-approved Star Names.[9]
This star, together with Delta Persei, Psi Persei, Sigma Persei, Alpha Persei and Gamma Persei has been called the Segment of Perseus.[12].
In Chinese, 天船 (Tiān Chuán), meaning Celestial Boat, refers to an asterism consisting of Eta Persei, Gamma Persei, Alpha Persei, Psi Persei, Delta Persei, 48 Persei, Mu Persei and HD 27084. Consequently, Eta Persei itself is known as 天船一 (Tiān Chuán yī, English: the First Star of Celestial Boat.)[15]
Properties
Eta Persei A belongs to spectral class K3 and has an apparent magnitude of +3.76. It radiates with 35,000 times the luminosity of the Sun.[16]
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 Van Leeuwen, F. (2007). "Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 474 (2): 653. arXiv:0708.1752. Bibcode:2007A&A...474..653V. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078357.
- 1 2 3 Ducati, J. R. (2002). "VizieR Online Data Catalog: Catalogue of Stellar Photometry in Johnson's 11-color system". CDS/ADC Collection of Electronic Catalogues. 2237. Bibcode:2002yCat.2237....0D.
- 1 2 De Medeiros, J. R.; Udry, S.; Burki, G.; Mayor, M. (2002). "A catalog of rotational and radial velocities for evolved stars. II. Ib supergiant stars". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 395: 97. Bibcode:2002A&A...395...97D. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20021214.
- ↑ Famaey, B.; Jorissen, A.; Luri, X.; Mayor, M.; Udry, S.; Dejonghe, H.; Turon, C. (2005). "Local kinematics of K and M giants from CORAVEL/Hipparcos/Tycho-2 data. Revisiting the concept of superclusters". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 430: 165. arXiv:astro-ph/0409579. Bibcode:2005A&A...430..165F. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20041272.
- ↑ Ryon, Jenna; Shetrone, Matthew D.; Smith, Graeme H. (2009). "Comparing the Ca ii H and K Emission Lines in Red Giant Stars". Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific. 121 (882): 842. arXiv:0907.3346. Bibcode:2009PASP..121..842R. doi:10.1086/605456.
- ↑ Pasinetti Fracassini, L. E.; Pastori, L.; Covino, S.; Pozzi, A. (2001). "Catalogue of Apparent Diameters and Absolute Radii of Stars (CADARS) - Third edition - Comments and statistics". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 367 (2): 521. arXiv:astro-ph/0012289. Bibcode:2001A&A...367..521P. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20000451.
- 1 2 McDonald, I.; Zijlstra, A. A.; Boyer, M. L. (2012). "Fundamental parameters and infrared excesses of Hipparcos stars". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 427: 343. arXiv:1208.2037. Bibcode:2012MNRAS.427..343M. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2012.21873.x.
- ↑ "Washington Double Star Catalog". United States Naval Observatory. Retrieved 2 January 2018.
- 1 2 "Naming Stars". IAU.org. Retrieved 16 December 2017.
- ↑ Hessman, F. V.; Dhillon, V. S.; Winget, D. E.; Schreiber, M. R.; Horne, K.; Marsh, T. R.; Guenther, E.; Schwope, A.; Heber, U. (2010). "On the naming convention used for multiple star systems and extrasolar planets". arXiv:1012.0707 [astro-ph.SR].
- ↑ Kaler, Jim. "Eta Persei". Retrieved 2017-02-11.
- 1 2 Allen, R. H. (1963). Star Names: Their Lore and Meaning (Reprint ed.). New York: Dover Publications Inc. p. 331. ISBN 0-486-21079-0. Retrieved 2012-09-04.
- ↑ "IAU Working Group on Star Names (WGSN)". Retrieved 22 May 2016.
- ↑ "WG Triennial Report (2015-2018) - Star Names" (PDF). p. 5. Retrieved 2018-07-14.
- ↑ (in Chinese) AEEA (Activities of Exhibition and Education in Astronomy) 天文教育資訊網 2006 年 7 月 11 日
- ↑ Mallik, Sushma V. (December 1999), "Lithium abundance and mass", Astronomy and Astrophysics, 352: 495–507, Bibcode:1999A&A...352..495M