College Park, Georgia
| College Park | |
|---|---|
| City | |
| City of College Park | |
 Downtown College Park | |
 Location in Fulton County and the state of Georgia | |
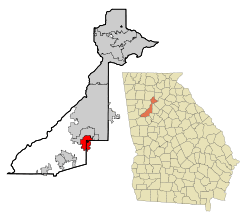
 College Park Location of College Park in Metro Atlanta | |
| Coordinates: 33°38′54″N 84°27′22″W / 33.64833°N 84.45611°WCoordinates: 33°38′54″N 84°27′22″W / 33.64833°N 84.45611°W | |
| Country | United States |
| State | Georgia |
| Counties | Fulton, Clayton |
| Area | |
| • Total | 10.1 sq mi (26.1 km2) |
| • Land | 10.1 sq mi (26.1 km2) |
| • Water | 0 sq mi (0 km2) |
| Elevation | 1,050 ft (320 m) |
| Population (2010) | |
| • Total | 13,942 |
| • Estimate (2016)[1] | 15,035 |
| • Density | 1,385/sq mi (534.7/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC-5 (Eastern (EST)) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC-4 (EDT) |
| ZIP codes | 30337, 30349 |
| Area code(s) | 404/678/470 |
| FIPS code | 13-17776[2] |
| GNIS feature ID | 0331435[3] |
| Website |
www |
College Park is a city in Fulton County and Clayton County, Georgia, United States, adjacent to the southern boundary of the city of Atlanta. As of the 2010 census, the population was 13,942.[4] Hartsfield–Jackson Atlanta International Airport is partially located in the city's boundaries (including the domestic terminal, Concourse T, Concourse A, and about two-thirds of Concourse B), and the Georgia International Convention Center, owned and operated by the City of College Park, is within the city limits.[5][6] The city is home to the fourth largest urban historical district registered with the National Register of Historic Places in the state of Georgia. [7][8]
Geography
College Park is located on the border of Fulton and Clayton counties at 33°38′54″N 84°27′22″W / 33.64833°N 84.45611°W (33.648209, -84.456007).[9] According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 10.1 square miles (26.1 km2), of which 0.019 square miles (0.05 km2), or 0.19%, is water.[4]
Infrastructure
College Park's City Hall is 8 miles (13 km) southwest of downtown Atlanta. Interstate 85 passes through the city and merges with Interstate 285, the perimeter highway around Atlanta, for a short distance in the southern part of College Park. I-85 exits 69 through 72 and I-285 exits 60 and 62 are located within the College Park city limits. The western part of Hartsfield–Jackson Airport, including its domestic terminal, occupies the eastern side of the city.
Transit systems
The Metropolitan Atlanta Rapid Transit Authority (MARTA) provides heavy rail and bus services in College Park.
Metro
The College Park Station is the primary station for College Park, located just south of Downtown, and is the third busiest station in the MARTA Rail System, with a weekday average of 9,023 entries.[10] It is serviced by both the Gold Line and the Red Line during the day,[11] and only the Gold Line after 9:00 PM.[12]
Buses
The following bus routes serve College Park:[13]
- Route 82 - Camp Creek / Welcome All
- Route 84 - East Point/Camp Creek (leaves via the East Point Station)[14]
- Route 89 - Old National Hwy./Union City
- Route 172 - Sylvan Road/Virginia Ave.
- Route 180 - Fairburn / Palmetto
- Route 181 - Buffington Rd./South Fulton P/R
- Route 189 - Flat Shoals Road/ Scofield Road
- Route 195 - Forest Parkway/Roosevelt Highway
- Route 196 - Church/Upper Riv./Mt. Zion
History
19th Century

The community that would become College Park was founded as Atlantic City in 1890 as a depot on the Atlanta and West Point Railroad. The town was renamed Manchester when it was incorporated as a city in 1891. It was renamed again as the city of College Park in 1896. The city's name came from being the home of Cox College (where the city hall and other buildings now stand) and Georgia Military Academy (now the Woodward Academy). The east-west avenues in College Park are named for Ivy League colleges, and the north-south streets are named for influential College Park residents.[15]
20th Century
Airport-Associated Changes
The history of College Park has been closely linked with what is now known as Hartsfield–Jackson Atlanta International Airport — airport development having spurred several radical changes to the landscape of the municipality over the course of the 20th century.[16] In 1966, a study funded by the Department of Housing and Urban Development suggested that the introduction and expansion of jet aircraft travel would place the airport and surrounding communities, including College Park, into conflict; ultimately, the study concluded that "the only effective way to control the use of land is to own it," suggesting that the airport would have to acquire the properties it would be in conflict with in order to expand.[17]
In the 1970s and 1980s, large swaths of property in College Park were purchased using information detailed in The Hartsfield-Jackson Atlanta International Airport Noise Land Reuse Plan, which allowed the airport to apply for federal funding to purchase property deemed to be in so-called "noise land."[18][19] The 1985 Chuck Norris film Invasion U.S.A. was notoriously filmed in these abandoned portions of College Park; houses owned by the City of Atlanta and the FAA were allowed to be blown up to simulate bazooka attacks, a decision that has faced modern day criticism due to the fact that nearby properties were still in the process of being purchased.[20][19] This site would eventually, in 2003, in part be home to the Georgia International Convention Center; the center officially opened in 1985 at a separate location, but was relocated to the area in response to planned airport runway expansions.[21]
In 1978, the College Park Historical Society was founded in order to combat proposed northward expansion of the airport; the society succeeded in lobbying against proposed flight paths over the neighborhood colloquially known as Historic College Park, as well as registered swaths of homes and the Main Street commercial district with the National Register of Historic Places, eventually resulting in the establishment of the College Park Historic District.[19]
Between the 1980s and the early 2000s, as part of continued execution of the FAA noise abatement program, the City of Atlanta and the FAA purchased roughly 320 acres of property (containing residential structures, churches, and some small commercial buildings) immediately adjacent to the west side of downtown College Park, resulting in a multitude of properties sitting abandoned for decades.[22] The totality of these eventually abandoned properties purchased between the 1970s and the 2000s have been described as a major player in shaping a negative public image of the city, second only to the perception of crime in the area.[23]
Recent History
Hip Hop
Although the Atlanta hip hop music scene in the 1980s and 1990s was largely credited to artists from nearby suburban Decatur, College Park and the adjacent city of East Point have been strongly associated with artists and record producers from "SWATS" ("Southwest Atlanta, too strong"), whom have substantially contributed to the evolution of the southern hip hop genre over the course of the 2000s.[24]
Gentrification
While the controversial process of gentrification started in the larger Atlanta Metropolitan Area in the 1970s, it was only in the latter 2010s that redevelopment substantially spread to College Park proper.[25] In 2016, the College Park government embarked on a 20 year development plan which included goals "to expand its economic base while keeping its small town historic characteristics," and to "make use of its available land to attract new employers and residential opportunities."[26] 2017 saw the construction of a mixed-use project which contained the first mid-rise apartments to be constructed in the city since 1969.[27] From the 1990s and into the 2010s, the City of College Park succeeded in repurchasing the entirety of the 320 acres adjacent to downtown; in 2018, concurrent with substantial commercial and residential development in the area, the City of College Park announced major redevelopment of this abandoned area, now referred to as "Airport City," as part of a larger transit-oriented revitalization plan referred to as "Aerotropolis."[28]
Historic District

The city center is part of the College Park Historic District, a 606 acre historic district listed with the National Register of Historic Places.[8] According to the federal agency, the district contains 853 recognized historical resources constructed in the late 19th and early 20th centuries.
The majority of the 852 historic structures are homes of the Queen Anne style, various Late 19th and 20th Century Revivals, and bungalows of the American Craftsman style, all dating from 1882 to 1946.[8] Other major historical structures include:[8] The College Park Woman's Clubhouse at Camellia Hall (1927);[29] the College Park First United Methodist Church (1904);[30]; a United States Postal Service Office (1937); four schools (constructed between 1914 and 1942); and the College Park Depot (pre-1900), part of the Atlanta & West Point Railroad.[31]
Recreation

College Park has four public recreation facilities: the Wayman & Bessie Brady Recreation Center, named in honor of its first Coordinators;[32] the Hugh C. Conley Recreation Center, named in honor of a former Mayor Pro-Tem;[33] the Tracey Wyatt Recreation Complex, named in honor of the current Ward III Councilperson, Tracey Wyatt;[34] and the College Park City Auditorium.[35]
The city has four parks: Barrett Park, which is located along Rugby Avenue; Brenningham Park, which surrounds the Brady Center; Jamestown Park; and Richard D. Zupp Park.[36]
College Park is home to the College Park Municipal Golf Course, a nine-hole course established in 1929.[37]
In February 2018, development began on the Gateway Center at College Park, a 5,000 seat multipurpose arena intended for public use, as well as to host the Atlanta Hawks NBA G League team, currently known as the Erie BayHawks.[38]
Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1900 | 517 | — | |
| 1910 | 2,173 | 320.3% | |
| 1920 | 3,622 | 66.7% | |
| 1930 | 6,604 | 82.3% | |
| 1940 | 8,213 | 24.4% | |
| 1950 | 14,535 | 77.0% | |
| 1960 | 23,469 | 61.5% | |
| 1970 | 18,203 | −22.4% | |
| 1980 | 24,632 | 35.3% | |
| 1990 | 20,457 | −16.9% | |
| 2000 | 20,382 | −0.4% | |
| 2010 | 13,942 | −31.6% | |
| Est. 2016 | 15,035 | [1] | 7.8% |
| U.S. Decennial Census[39] | |||
At the time of the 2010 census[40], there were 13,942 people, 5,595 households, and 3,208 families residing in the city. The population density was 2,099.8 people per square mile (810.5/km²). There were 7,159 housing units at an average density of 860.3 per square mile (332.1/km²). The racial makeup of the city was 81.1% Black, 14.1% White, 1.2% Native American, 1.1% Asian, 4.7% from other races, and 2.0% from two or more races. Hispanic or Latino people of any race were 6.9% of the population.
Population Decline, 2000-2010
Between 2000 and 2010, College Park saw a 31.6% reduction in their population. The city government has suggested that this was due to the combined effects of airport expansion and the difficult nature of having housing constructed in areas previously considered to be "high noise." [41]
Government and Politics
The city of College Park is governed by a mayor and four council members. The current mayor is Jack Longino, and the council members are: Ward 1, Ambrose Clay; Ward 2, Joe Carn; Ward 3, Tracey Wyatt; and Ward 4, Roderick Gay.[42]
The mayor is elected at-large, on a nonpartisan basis, for 4 year terms.[43] The incumbent mayor, Jack Longino, has held the office since 1996.[44]
Four council members are elected on a nonpartisan basis for 4 year terms, and each represents one of the four wards that make up the city.[43] Legislative authority is placed in the city council, wherein each member is afforded one vote; the mayor oversees the deliberations of the council and is only entitled to a vote in the case of a tie.[45]
Crime
For much of the 2000s, College Park – along with the other so-called Tri-Cites, East Point and Hapeville – has been popularly associated with crime[46]; for example, a comedy/travel book originally published in 2005 describes College Park as "a nightmarish southern ghetto."[47] Over the course of the 2010s, this reputation has been publicly challenged in the media, by Tri-Cities residents, and by the College Park Police Department.[48][49][50]
The Federal Bureau of Investigation's annual Uniform Crime Report reveals that the College Park Police Department has historically reported a high crime rate per 100,000 persons as compared to other US jurisdictions.[51] In 2008, College Park had one of the highest crime rates in Georgia, with reports including 13 homicides. However, 2008 was an outlier with respect to the rest of that decade and homicide; for the rest of the years between 2000 and 2010, between 1 and 3 homicides were reported annually.
The Uniform Crime Report and data released by the College Park Police Department suggests that the 2010s have brought a substantial decline in total crime, particularly in the latter half; in 2017, a total of 1,334 crimes were reported (compared to 2,695 in 2001, 2,530 in 2010, and 1,964 in 2015), 85% of which were property crimes.[50]
Economy

ExpressJet Airlines is headquartered in College Park, near Hartsfield-Jackson Atlanta International Airport.[52] Chick-fil-A, a fast food chicken chain, is headquartered in College Park.[5][53] Atlantic Southeast Airlines had its headquarters in College Park until December 31, 2011; its final headquarters facility was a hangar at Hartsfield-Jackson Atlanta International Airport.[54]
As of the 2016 American Community Survey, 35.7% of College Park residents are predicted to live in poverty.[55]
Top employers
According to College Park's 2017 Comprehensive Annual Financial Report,[56] the top employers in the city are:
| # | Employer | Employees |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Chick-Fil-A | 1,599 |
| 2 | Federal Aviation Administration | 1,300 |
| 3 | Sysco | 768 |
| 4 | Southwest Airlines | 664 |
| 5 | Woodward Academy | 630 |
| 6 | Express Jet Airlines | 532 |
| 7 | Logisticare Solutions | 403 |
| 8 | VXI global | 360 |
| 9 | Marriott Hotels, Hotel #481 | 238 |
| 10 | Marriott Hotels, Hotel #11005 | 206 |
Education
Primary and secondary schools
Fulton County
Residential areas within College Park are served by the Fulton County School System.
College Park Elementary School,[57] Love T. Nolan Elementary School, G.W. Northcutt Elementary School and the Main Street Academy[58] are in College Park and serve College Park.[5][59][60] Other schools serving sections of College Park with residences include Hapeville Elementary School in Hapeville,[61] Heritage Elementary School in an unincorporated area,[62] and Oak Knoll Elementary School in East Point.[63]
Middle schools serving College Park include the Main Street Academy, located in College Park,[58] and Paul D. West Middle School[64] and Woodland Middle School, both in East Point.
Benjamin Banneker High School, in an unincorporated area, and Tri-Cities High School in East Point, both serve sections of College Park.[65][66] Frank S. McClarin Alternative High School[67] is located in College Park.[5]
Clayton County
The section in Clayton County is served by Clayton County Public Schools.[5]
Private schools
Woodward Academy is located in College Park.[68]
Public libraries
Atlanta-Fulton Public Library System operates the College Park Branch.[69]
Notable people
- 2 Chainz, rap artist
- Morgan Burnett, safety for the Pittsburgh Steelers
- Kandi Burruss, member of the singing quartet Xscape
- Tameka Cottle, member of singing quartet Xscape and wife of rapper T.I.
- Bill Curry, football coach and analyst, former head coach for Georgia State University
- Creflo Dollar, teacher, pastor, and founder of World Changers Church International
- Jermaine Dupri, rapper, songwriter, record producer
- Keyaron Fox, Pittsburgh Steelers
- Trinidad James, rap artist
- Kap G, rapper
- Ludacris, rapper
- Margaret Martin, professional bodybuilder
- Mr. Collipark, record producer
- Monica, R&B singer
- Cam Newton, professional football player, Carolina Panthers
- OG Maco, rapper
- Greg Patton, quarterback at Dartmouth College; broke the single-game rushing record in his first varsity appearance[70][71]
- Playaz Circle, rap group
- Rich The Kid, rapper
- LaTocha Scott, member of singing quartet Xscape
- Tamika Scott, member of singing quartet Xscape
- Josh Smith, professional basketball player
- Fletcher Thompson, politician
- V.I.C., rapper
- Yung Joc, rapper
See also
References
- 1 2 "Population and Housing Unit Estimates". Retrieved June 9, 2017.
- ↑ "American FactFinder". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on 2013-09-11. Retrieved 2008-01-31.
- ↑ "US Board on Geographic Names". United States Geological Survey. 2007-10-25. Retrieved 2008-01-31.
- 1 2 "Race, Hispanic or Latino, Age, and Housing Occupancy: 2010 Census Redistricting Data (Public Law 94-171) Summary File (QT-PL), College Park city, Georgia". U.S. Census Bureau, American FactFinder 2. Archived from the original on September 11, 2013. Retrieved October 28, 2011.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "City Maps Archived 2011-10-23 at WebCite." City of College Park. Retrieved on May 25, 2009.
- ↑ "Contact the GICC." Georgia International Convention Center. Retrieved on May 25, 2009.
- ↑ "City of College Park Comprehensive Plan 2016-2036". www.collegeparkga.com. Retrieved 14 August 2018.
- 1 2 3 4 "National Register of Historic Places Form - College Park Historic District". npgallery.nps.gov. Retrieved 14 August 2018.
- ↑ "US Gazetteer files: 2010, 2000, and 1990". United States Census Bureau. 2011-02-12. Retrieved 2011-04-23.
- ↑ "2014 Transportation Fact Book" (PDF). Atlanta Regional Commission. Retrieved 11 May 2015.
- ↑ "College Park". itsmarta. Metropolitan Atlanta Rapid Transit Authority. Retrieved 22 July 2015.
- ↑ "Red Line Map: Red Line". itsmarta. Metropolitan Atlanta Rapid Transit Authority. Retrieved 22 July 2015.
- ↑ "Bus Information by Nearest Station". itsmarta. Metropolitan Atlanta Rapid Transit Authority. Retrieved 22 July 2015.
- ↑ "Bus Information by Nearest Station". itsmarta. Metropolitan Atlanta Rapid Transit Authority. Retrieved 22 July 2015.
- ↑ Hellmann, Paul T. (May 13, 2013). Historical Gazetteer of the United States. Routledge. p. 224. Retrieved 30 November 2013.
- ↑ "Airport History". web.archive.org. Retrieved 15 August 2018.
- ↑ "Atlanta metropolitan region comprehensive plan: airports". library.gsu.edu. Retrieved 15 August 2018.
- ↑ stumptown.typepad.com http://stumptown.typepad.com/stumptown_ga/. Retrieved 15 August 2018. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - 1 2 3 "BLOWING UP BUNGALOWS TO MAKE WAY FOR AIRPORTS, ON ANOTHER KIND OF URBAN DISPLACEMENT IN ATLANTA". lithub.com. Retrieved 15 August 2018.
- ↑ Zita, Josef (Director) (May 15, 2003). The Making of Invasion USA (Motion picture). United States: Cannon Films.
- ↑ Kemp, Kathryn (2009). Historic Clayton County: The Sesquicentennial History. p. 80-81.
- ↑ "Exclusive: 320-acre development set to take off by airport". www.bizjournals.com. Retrieved 15 August 2018.
- ↑ "City of College Park Comprehensive Plan 2016-2036". www.collegeparkga.com. Retrieved 14 August 2018.
- ↑ "Revolution Rock: Atlanta's Goodie Mob fight for truth, justice, but not necessarily the American Way", Vibe, June-July 1998
- ↑ "Gentrification Changing Face of New Atlanta". www.nytimes.com. Retrieved 15 August 2018.
- ↑ "City of College Park Comprehensive Plan 2016-2036". www.collegeparkga.com. Retrieved 14 August 2018.
- ↑ "5 things to know about the Pad on Harvard, College Park's first new mid-rise in 40 years". www.atlantamagazine.com. Retrieved 15 August 2018.
- ↑ "The Aerotropolis Atlanta Blueprint" (PDF). aeroatl.org. Retrieved 15 August 2018.
- ↑ "cpwc - HISTORY". www.collegeparkwomansclub.org. Retrieved 14 August 2018.
- ↑ "Our Stained Glass Windows". cpfirstumc.org. Retrieved 14 August 2018.
- ↑ "College Park Depot". cpfirstumc.org. Retrieved 14 August 2018.
- ↑ "WAYMAN & BESSIE BRADY RECREATION CENTER". www.atldistrict.com. Retrieved 15 August 2018.
- ↑ "Hugh C. Conley Recreation Center". www.collegeparkga.com. Retrieved 15 August 2018.
- ↑ "Tracey Wyatt Recreation Complex". www.collegeparkga.com. Retrieved 15 August 2018.
- ↑ "Recreation and Cultural Arts". www.collegeparkga.com. Retrieved 14 August 2018.
- ↑ "Recreation and Cultural Arts FAQ". www.collegeparkga.com. Retrieved 15 August 2018.
- ↑ "Historic College Park Golf Course". www.atldistrict.com. Retrieved 14 August 2018.
- ↑ "College Park Breaks Ground on Multipurpose Arena". www.ajc.com. Retrieved 14 August 2018.
- ↑ "Census of Population and Housing". Census.gov. Archived from the original on May 12, 2015. Retrieved June 4, 2015.
- ↑ "Decennial Census of Population and Housing". Retrieved August 14, 2018.
- ↑ "City of College Park Comprehensive Plan 2016-2036". www.collegeparkga.com. Retrieved 14 August 2018.
- ↑ "College Park, GA - Official Website - Mayor & Council". Collegeparkga.com. Retrieved 4 August 2018.
- 1 2 "Sec. 5-8. - Same—Election by ward; terms of office". library.municode.com. Retrieved 15 August 2018.
- ↑ "Mayor Longino Senior Living Residences". www.collegeparkga.com. Retrieved 15 August 2018.
- ↑ "Sec. 1-8. - Mayor; constituted chief executive, exceptions; constituted presiding officer of council". library.municode.com. Retrieved 15 August 2018.
- ↑ "College Park has to battle image and crime". www.ajc.com. Retrieved 14 August 2018.
- ↑ Gilmartin, Dave (April 7, 2015). The Absolutely Worst Places to Live in America. St. Martin's Press. Retrieved 14 August 2015.
- ↑ "Wandering Atlanta's charming Historic College Park in 15 photos". atlanta.curbed.com. Retrieved 14 August 2018.
- ↑ "I Live in America's Most Dangerous Suburb". tropicsofmeta.com. Retrieved 14 August 2018.
- 1 2 "VERIFY: Is this metro Atlanta city among the most dangerous in the U.S.?". www.11alive.com. Retrieved 14 August 2018.
- ↑ "Uniform Crime Reporting Statistics". www.ucrdatatool.gov. Retrieved 14 August 2018.
- ↑ "Contact Us." ExpressJet. Retrieved on July 28, 2012. "100 Hartsfield Center Pkwy Suite 700 Atlanta, GA 30354"
- ↑ Chick-fil-A: Company Fact Sheet Retrieved July 30, 2012
- ↑ Tobin Ramos, Rachel and Douglas Sams. "ASA lands headquarters at Hartsfield hangar." Atlanta Business Chronicle. Monday December 10, 2007. Retrieved on July 28, 2012.
- ↑ "Population estimates, July 1, 2015, (V2015)". Census.gov. Retrieved 2018-08-14.
- ↑ "City of College Park CAFR". Collegeparkga.com. Retrieved 4 August 2018.
- ↑ "College Park Elementary School". Fultonschools.org. Retrieved 4 August 2018.
- 1 2 "The Main Street Academy - A Fulton County Charter School". tmsa.org. Retrieved 4 August 2018.
- ↑ "College Park Elementary Attendance Zone 2009-2010 School Year." Fulton County School System. Retrieved on June 21, 2009.
- ↑ "." Fulton County School System. Retrieved on June 21, 2009.
- ↑ "Hapeville Elementary Attendance Zone 2009-2010 School Year." Fulton County School System. Retrieved on June 21, 2009.
- ↑ "Heritage Elementary Attendance Zone 2009-2010 School Year." Fulton County School System. Retrieved on June 21, 2009.
- ↑ "Oak Knoll Elementary Attendance Zone 2009-2010 School Year." Fulton County School System. Retrieved on June 21, 2009.
- ↑ "Fulton County Schools". Fultonschools.org. Retrieved 4 August 2018.
- ↑ "Banneker High Attendance Zone 2009-2010 School Year." Fulton County School System. Retrieved on June 21, 2009.
- ↑ "Tri-Cities High Attendance Zone 2009-2010 School Year." Fulton County School System. Retrieved on June 21, 2009.
- ↑ Frank S. McClarin Alternative High School Archived 2008-07-19 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ "Private School Near Atlanta - Day School - Woodward Academy, GA". Woodward.edu. Retrieved 4 August 2018.
- ↑ "College Park Branch." Atlanta-Fulton Public Library System. Retrieved on February 24, 2010.
- ↑ Dartmouth Sports Bio - Greg Patton
- ↑ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2011-07-17. Retrieved 2009-11-09. Greg Patton Breaks Record