Châteaux of the Loire Valley
| Châteaux of the Loire Valley | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Location | France (Centre, Pays de la Loire) |
| Built | Renaissance |
| Architectural style(s) | French Renaissance architecture |
| Type | Cultural |
| Designated | 2000 |
| Part of | The Loire Valley between Sully-sur-Loire and Chalonnes |
| Reference no. | 933 |
| Country | France |
| Region | Europe and North America |
The Châteaux of the Loire Valley (French: Châteaux de la Loire) are part of the architectural heritage of the historic towns of Amboise, Angers, Blois, Chinon, Montsoreau, Nantes, Orléans, Saumur, and Tours along the Loire River in France. They illustrate Renaissance ideals of design in France.[1]
The châteaux, numbering more than three hundred, are the achievement of a nation of builders, starting with practical fortified castles in the 10th century to splendid residences built half a millennium later. When the French kings began constructing their huge châteaux in the Loire Valley, the nobility, drawn to the seat of power, followed suit, attracting the finest architects and landscape designers. The châteaux and their surrounding gardens are cultural monuments which stunningly embody the ideals of the Renaissance and Enlightenment. Many of the châteaux were built on hilltops, such as the Château d'Amboise, while the only one built in the riverbed is the Château de Montsoreau. Many had exquisite churches on the grounds or within the château.
History
As the wars of the 15th century wound down, Kings Charles VII, Louis XI, and their successors preferred to spend the bulk of their time in the "garden of France" along the banks of the Loire. In the late 15th century, Tours, then Blois, and later Amboise became the preferred locations of the French royal court. Many courtiers bought dilapidated castles built by the medieval Counts of Blois and Anjou, and had them reconstructed in the latest Italianate fashion. Leonardo da Vinci and other Italian artists arrived to design and beautify these residences.
By the middle of the 16th century, King François I had shifted his throne from the Loire back to the ancient capital of Paris. With him went the great architects, but the Loire Valley continued to be the place where most of the French royalty preferred to spend the bulk of their time. King Louis XIV in the middle of the 17th century made Paris the permanent locale for great royal châteaux when he built the Palace of Versailles. Nonetheless, those who gained the king's favour and the wealthy bourgeoisie continued to renovate existing châteaux or build lavish new ones in the Loire as summer residences.
The French Revolution saw a number of the great châteaux destroyed and many ransacked, their treasures stolen. The overnight impoverishment of many of the deposed nobility, usually after one of its members lost his or her head to the guillotine, saw many châteaux demolished. During World War I and World War II, some chateaux were commandeered as military headquarters. Some of these continued to be so used after the end of World War II.
Today, the remaining privately owned châteaux serve as homes, a few open their doors to tourists, while others operate as hotels or bed-and-breakfasts. Many others have been taken over by local governments, and the grandest, like those at Chambord, are owned and operated by the national government and are major tourist sites, attracting hundreds of thousands of visitors each year.
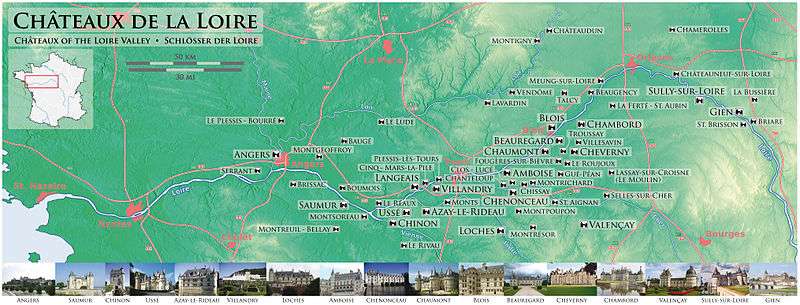
List of châteaux of the Loire
Though there is no universally accepted definition for the designation, the main criterion is that the château must be situated close to the Loire or one of its tributaries (such as the Maine, Cher, Indre, Creuse or Loir). Châteaux further upstream than Gien are generally not included, with the possible exception of the Bastie d'Urfé for its historical significance.
Royal châteaux
Châteaux of the nobility
Other châteaux
See also

- List of châteaux in France
- Tuffeau, principal building material of the Loire Valley
References
- ↑ The Loire Valley: A Phaidon Cultural Guide. New York: Prentice Hall Press. 1986.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Peregrine, Anthony (21 May 2014). "The best chateaux of the Loire Valley, France". The Daily Telegraph. Retrieved 15 November 2016.
- 1 2 Lounes, Allison (4 December 2012). "Chateaux spectacular: 5 best Loire Valley castles | CNN Travel". CNN. Retrieved 15 November 2016.
- ↑ Gleadell, Colin (23 June 2015). "Largest Collection of Radical Conceptualists ART & LANGUAGE Finds a Home in French Chateau | artnet news". artnet. Retrieved 24 April 2018.
External links

- Châteaux de la Loire, Finest France





















_-_2.jpg)










.jpg)











.jpg)






.jpg)