Butch Cassidy
Robert LeRoy Parker (April 13, 1866 – November 7, 1908), better known as Butch Cassidy,[1] was a U.S. train robber and bank robber, and the leader of a gang of criminal outlaws known as the "Wild Bunch" in the American Old West.
Butch Cassidy | |
|---|---|
 Fort Worth, Texas, 1900 | |
| Born | Robert LeRoy Parker April 13, 1866 Beaver, Utah Territory, United States |
| Died | November 7, 1908 (aged 42) San Vicente, Bolivia |
| Cause of death | Gunshot wounds |
| Nationality | U.S. |
| Other names | Butch Cassidy, Mike Cassidy, George Cassidy, Jim Lowe, Santiago Maxwell |
| Occupation | Farm hand, cowboy, butcher, thief, bank robber, train robber, gang leader, outlaw |
| Parent(s) |
|
| Allegiance | Butch Cassidy's Wild Bunch |
| Conviction(s) | Imprisoned in the state prison in Laramie, Wyoming for horse theft |
| Criminal charge | Horse theft, cattle rustling, bank and train robbery |
| Penalty | Served 18 months of two-year sentence; released January 1896 |
| Partner(s) | Harry Longabaugh a.k.a. the "Sundance Kid", Elzy Lay, Matt Warner |
Parker participated in criminal activity for more than a decade at the end of the 19th century, but the pressures of being pursued by law enforcement, notably the Pinkerton detective agency, forced him to flee the country. He fled with his accomplice Harry Alonzo Longabaugh, known as the "Sundance Kid", and Longabaugh's girlfriend Etta Place. The trio traveled first to Argentina and then to Bolivia, where Parker and Longabaugh are believed to have been killed in a shootout with the Bolivian army in November 1908; the exact circumstances of their fate continue to be disputed. Parker's life and death have been extensively dramatized in film, television, and literature, and he remains one of the most well-known icons of the "Wild West" mythos in modern times.
Early life
Robert LeRoy Parker was born on April 13, 1866 in Beaver, Utah, the first of 13 children of British immigrants Maximillian Parker and Ann Campbell Gillies.[2][3][4] The Parker and Gillies families had converted to the Mormon faith while still living in the UK. Maximillian Parker was 12 years old when his family arrived in Salt Lake City in 1856 as Mormon pioneers.[5] Ann Gillies was born and lived in Tyneside in northeast England before immigrating to the U.S. with her family in 1859 at age 14.[6][7][8] The couple were married in July 1865.[9] Robert grew up on his parents' ranch near Circleville, Utah, approximately 215 miles (346 km) south of Salt Lake City.

Parker fled his home as a teenager and while working on a dairy ranch he met Mike Cassidy, a horse and cattle thief. He subsequently worked on several ranches, in addition to a brief apprenticeship with a butcher in Rock Springs, Wyoming, where he got the nickname (by the word “butcher”, which morphed later into ”Butch”), to which he soon added the last name Cassidy in honor of his old friend and mentor.
Criminal career
Butch Cassidy's first criminal offence was minor. Around 1880, he journeyed to a clothier's shop in another town but found it closed. He entered the shop and stole a pair of jeans and some pie, leaving a note promising to pay on his next visit. The clothier pressed charges, but Cassidy was acquitted by a jury. He continued to work on ranches until 1884, when he moved to Telluride, Colorado, ostensibly to seek work but perhaps to deliver stolen horses to buyers. He led a cowboy's life in Wyoming and Montana before returning to Telluride in 1887 where he met Matt Warner, the owner of a racehorse. Cassidy and Warner raced the horse at various events, dividing the winnings between them.
1889–1895

Cassidy's first bank robbery took place on June 24, 1889 when he, Warner, and two of the McCarty brothers robbed the San Miguel Valley Bank in Telluride. The businessman L. L. Nunn had taken a controlling interest in the bank the previous year.[11] The robbers stole approximately $21,000 (equivalent to $598,000 in 2019), after which they fled to the Robbers Roost, a remote hideout in southeastern Utah.
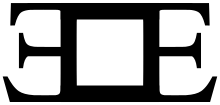
In 1890, Cassidy purchased a ranch on the outskirts of Dubois, Wyoming. This location is across the state from the notorious Hole-in-the-Wall, a natural geological formation and a popular hideout for outlaw gangs, including Cassidy's during the era. It is possible that Cassidy's ranching was a façade for clandestine activities, perhaps with Hole-in-the-Wall outlaws, as he was never financially successful at ranching.[12] His ranch used the "unmistakable brand" of "Reverse-E, Box, E".[10]
In early 1894, Cassidy became involved romantically with outlaw and rancher Ann Bassett. Her father was a rancher who did business with Cassidy, supplying him with fresh horses and beef. That same year, Cassidy was arrested at Lander, Wyoming for stealing horses and possibly for running a protection racket among the local ranchers there. He was imprisoned in the Wyoming State Prison in Laramie, Wyoming where he served 18 months of a two-year sentence; he was released and pardoned in January 1896 by Governor William Alford Richards.[13] He became involved briefly with Ann Bassett's older sister Josie before returning to Ann.
Formation of the Wild Bunch
Cassidy associated with a wide circle of criminals, most notably his closest friend William Ellsworth "Elzy" Lay, Harvey "Kid Curry" Logan, Ben Kilpatrick, Harry Tracy, Will "News" Carver, Laura Bullion, and George "Flat Nose" Curry, who collectively became the so-called "Wild Bunch". The gang assembled some time after Cassidy's release from prison in 1896 and took its name from the Doolin–Dalton gang, also known as the "Wild Bunch".[14]

On August 13, 1896, Cassidy, Lay, Logan, and Bob Meeks[15] robbed the bank at Montpelier, Idaho, escaping with approximately $7,000. Cassidy recruited Harry Alonzo Longabaugh into the gang soon after, who was also known as "The Sundance Kid".
Ann Bassett, Elzy Lay, and Lay's girlfriend Maude Davis all joined Cassidy at Robbers Roost in early 1897. The four hid there until early April when Lay and Cassidy sent the women home so that the men could plan their next robbery. They ambushed a small group of men carrying the payroll of the Pleasant Valley Coal Company on April 22, 1897, in the mining town of Castle Gate, Utah, stealing a sack containing $7,000 in gold with which they fled back to the Robbers Roost.
On June 2, 1899, the gang robbed a Union Pacific Overland Flyer passenger train near Wilcox, Wyoming, a robbery which earned them a great deal of notoriety and resulted in a massive manhunt.[16][17] Many notable lawmen took part in the hunt, but they did not find them. Kid Curry and George Curry had a shootout with lawmen following the train robbery, and they killed Sheriff Joe Hazen. Tom Horn was a killer-for-hire employed by the Pinkerton Agency, and explosives expert Bill Speck told him about the Hazen shooting. Pinkerton detective Charlie Siringo was then assigned the task of capturing the outlaws. He became friends with Elfie Landusky, who was using the last name Curry after becoming pregnant by Kid Curry's brother Lonny, and Siringo intended to locate the gang through her.
On July 11, 1899, Lay and others were involved in a Colorado and Southern Railroad train robbery near Folsom, New Mexico, which Cassidy might have planned and personally directed. A shootout ensued with local law enforcement, during which Lay killed Sheriff Edward Farr and Henry Love; Lay was convicted of murder and sentenced to life imprisonment at the New Mexico State Penitentiary.
The Wild Bunch would typically separate following a robbery and flee in different directions, later reuniting at a predetermined location such as the Hole-in-the-Wall hideout, Robbers Roost, or Fannie Porter's brothel in San Antonio, Texas.
1899 plea for amnesty
Cassidy approached Governor Heber Wells of Utah to negotiate an amnesty. Wells advised him to ask the Union Pacific Railroad to drop their criminal complaints against him, and Union Pacific Railroad chairman E. H. Harriman attempted to meet with Cassidy through Matt Warner. On August 29, 1900, Cassidy, Longabaugh, and others robbed Union Pacific train No. 3 near Tipton, Wyoming, violating Cassidy's earlier promise to the Governor of Wyoming and ending any chance for amnesty.
1900–01

On February 28, 1900, lawmen attempted to arrest Kid Curry's brother Lonny at his aunt's home. Lonny was killed in the shootout that followed, and his cousin Bob Lee was arrested for rustling and sent to prison in Wyoming. On March 28, Curry and News Carver were pursued by a posse from St. Johns, Apache County, Arizona after using currency which they had stolen in the Wilcox, Wyoming train robbery. The posse engaged them in a shootout, during which Deputies Andrew Gibbons and Frank LeSueur were killed, while Carver and Curry escaped. On April 17, George Curry was killed in a shootout with Grand County, Utah Sheriff John Tyler and Deputy Sam Jenkins. On May 26, Kid Curry rode into Moab, Utah and killed both Tyler and Jenkins in another shootout in retaliation for the deaths of George and Lonny.
In December, Cassidy posed alongside Longabaugh, Logan, Carver, and Ben Kilpatrick in Fort Worth, Texas for the now-famous "Fort Worth Five" photograph. The Pinkerton Detective Agency obtained a copy of the photograph and began to use it for wanted posters.
On July 3, 1901, Curry and a group of men robbed a Great Northern train near Wagner, Montana,[18] stealing more than $60,000 in cash (equivalent to $1,840,000 in 2019). The gang split up, but a posse led by Sheriff Elijah Briant caught up with News Carver and killed him. Ben Kilpatrick was captured in St. Louis, Missouri on Nov.5 at Josie Blakey's resort on Chestnut St. In his pocket, they found a key to a room at The Laclede Hotel. The next morning, they found Laura Bullion in the lobby, checking out with her luggage. In her valise was $8500 in unsigned banknotes from The Great Northern Train robbery. Curry killed Knoxville policemen William Dinwiddle and Robert Saylor in another shoot out on December 13, then escaped. He returned to Montana, pursued by Pinkertons and other law enforcement officers, where he shot and killed rancher James Winters in retaliation for killing his brother Johnny years before.[19]
Escape to South America

Cassidy and Longabaugh fled to New York City, feeling continuous pressure from the numerous law enforcement agencies pursuing them and seeing their gang falling apart. They departed from there to Buenos Aires, Argentina aboard the British steamer Herminius on February 20, 1901,[20][21][22][23] along with Longabaugh's companion Etta Place. Cassidy posed as James Ryan, Place's fictitious brother. They settled in a four-room log cabin on a 15,000-acre (61 km2) ranch that they purchased on the east bank of the Rio Blanco near Cholila, just east of the Andes in the Chubut.
1905
Two English-speaking bandits held up the Banco de Tarapacá y Argentino in Río Gallegos on February 14, 1905, 700 miles (1,100 km) south of Cholila near the Strait of Magellan, and the pair vanished north across the Patagonian grasslands. Cassidy and Longabaugh sold the Cholila ranch on May 1, fearing that law enforcement had located them. The Pinkerton Agency had known their location for some time, but the snow and the hard winter of Patagonia had prevented their agent Frank Dimaio from making an arrest. Governor Julio Lezana issued an arrest warrant, but Sheriff Edward Humphreys tipped them off, a Welsh-Argentine who was friendly with Cassidy and enamored of Etta Place. The trio then fled north to San Carlos de Bariloche where they embarked on the steamer Condor across Nahuel Huapí Lake and into Chile; they returned to Argentina by the end of the year. Cassidy, Longabaugh, Place, and an unknown male associate robbed the Banco de la Nación Argentina branch in Villa Mercedes on December 19, 400 miles (640 km) west of Buenos Aires, taking 12,000 pesos. They fled across the Andes to reach the safety of Chile.
On June 30, 1906, Etta Place decided that she had enough of life on the run, so Longabaugh took her back to San Francisco. Cassidy obtained honest work under the alias James "Santiago" Maxwell at the Concordia Tin Mine in the Santa Vera Cruz range of the central Bolivian Andes, where Longabaugh joined him upon his return. Their main duties included guarding the company payroll. The two traveled to Santa Cruz in late 1907, a frontier town in Bolivia's eastern savannah, still wanting to settle down as respectable ranchers.
Death
A courier was carrying the payroll for the Aramayo Franke and Cia Silver Mine on November 3, 1908, near San Vicente in southern Bolivia, when he was attacked by two masked American bandits believed to be Cassidy and Longabaugh. Witnesses saw them three days later in the small mining town of San Vicente, where they lodged in a small boarding house owned by a miner named Bonifacio Casasola.[24] Casasola became suspicious of them because they had a mule from the Aramayo Mine, identifiable from the company's brand. He notified a nearby telegraph officer, who notified the Abaroa cavalry regiment stationed nearby. The unit dispatched three soldiers under the command of Captain Justo Concha, and they notified the local authorities.
The soldiers, the police chief, the local mayor, and some of his officials all surrounded the lodging house on the evening of November 6, intending to arrest the Aramayo robbers. But as they approached the house, the bandits opened fire, killing one of the soldiers and wounding another and starting a gunfight. The mayor heard a man scream three times inside the house, then two successive shots were fired from inside the house.[24]
The authorities entered the house the next morning where they found two bodies with numerous bullet wounds to the arms and legs. The man assumed to be Longabaugh had a bullet wound in the forehead, and the man thought to be Cassidy had a bullet hole in the temple. The local police report speculated that, judging from the positions of the bodies, Cassidy had probably shot the fatally wounded Longabaugh to put him out of his misery, then killed himself. The Tupiza police identified the bandits as the men who robbed the Aramayo payroll transport, but the Bolivian authorities didn't know their real names, nor could they positively identify them.[24]
The bodies were buried at the small San Vicente cemetery, near the grave of a German miner named Gustav Zimmer. American forensic anthropologist Clyde Snow and his researchers attempted to find the graves in 1991, but they did not find any remains with DNA matching the living relatives of Cassidy and Longabaugh.[24] In 2017, a new search was launched for Cassidy's grave which zeroed in on a mine outside Goodsprings, Nevada. The dig found human remains, but they did not match the DNA provided.[25]
Rumors of survival
John McPhee's Annals of the Former World repeats a story that Dr. Francis Smith told to geologist David Love in the 1930s. Smith stated that he had seen Cassidy, who told him that his face had been altered by a surgeon in Paris, and he showed Smith an old bullet wound which Smith recognized as work that he had done.[26]
Josie Bassett claimed in 1960 that Cassidy came to visit her in the 1920s "after returning from South America," and that he "died in Johnnie, Nevada[27] about 15 years ago."[28] Residents in Cassidy's hometown of Circleville, Utah claimed in an interview that he worked in Nevada until his death.[29] Western historian Charles Kelly observed in his 1938 book The Outlaw Trail: A History of Butch Cassidy and His Wild Bunch that "it seems exceedingly strange" that Cassidy never returned to Circleville, Utah to visit his father if he was in fact still alive.[30]
Bruce Chatwin in his classic travel book, “In Patagonia” says “I went to see the star witness; his sister, Mrs. Lulu Parker Betenson, a forthright and energetic woman in her nineties .... She has no doubts: her brother came back and ate blueberry pie with family at Circleville in the of 1925. She believes he died of pneumonia in Washington State in the late 1930s.” P. 63-64; published Vintage 2005.
An episode of the television series In Search of... (1978) examines the claims and possible evidence for Butch Cassidy's return to America during the 1920s in a series of interviews with residents of Baggs, Wyoming, a popular destination for the Wild Bunch during their raiding years. Residents claimed that Cassidy had visited for several days in 1924, driving a Ford Model T. Cassidy's sister Lula Parker Betenson states that he returned to the family home in Circleville during this period and picked up his brother Mark in a Ford, then drove to their father's home[31] where she also lived. Her father allegedly said to her, "I'll bet you don't know who this is. This is your brother Robert Leroy." She stated that Cassidy was full of regrets, particularly at having disappointed his mother. She quoted him lamenting that "all I done is make a wreck of my life." Betenson claims that Cassidy lived out his years in "the Northwest" and died in 1937, and that the family had agreed not to disclose his final resting place since "they had chased him all his life, and now he's going to rest in peace." This story is also recounted by W. C. Jameson in Butch Cassidy: Beyond the Grave,[32] referencing the 1975 book Betenson co-authored with Dora Flack, Butch Cassidy, My Brother.[14]
On an episode of the series Mission Declassified (2019), investigative journalist Christof Putzel met with local researcher Marilyn Grace at Cassidy's childhood home, the Parker Ranch in Circleville, Utah, to talk about the alleged burial of Cassidy at the Ranch on 20 July 1937. Grace explains that Cassidy was secretly buried at Toms Cabin, a former sheep herders cabin located in a remote area of the property, a favorite camping spot for Cassidy and his brothers. Grace says an eyewitness, neighbor Dee Crosby, saw the burial take place at the cabin. Earlier Putzel spoke to Alta Orton, another Parker family ranch neighbor who described the family having been dressed in funeral like attire on that same day. Grace goes on to say cadaver dogs had been brought to the cabin in an attempt to locate remains and lead to a positive indication. The underside of the cabin was later dug and two bones discovered, identified as a human spinal bone and toe bone. Putzel had forensic scientist Suzanna Ryan at Pure Gold Forensics in Redlands, California, conduct a DNA test on the bones, Ryan confirmed they were in fact human but lacked enough DNA for a complete profile. It's since believed that as the site may have become public knowledge, the Parker family had excavated Cassidy's remains at the cabin and moved them to a different burial site leaving the spinal and toe bone behind in the process.[33]
Aliases
Alleged friends
William T. Phillips claimed to have known Butch Cassidy since childhood.[36] In his book In Search of Butch Cassidy,[37] Larry Pointer speculated that Phillips was actually Butch Cassidy, based upon stories in Phillip's unpublished manuscript, The Bandit Invincible, and a resemblance between Phillips and Cassidy. However, in 2012, Pointer obtained a copy of the Wyoming Territorial Prison mugshot of William T. Wilcox, a previously unknown associate of Butch Cassidy. Observing the similarities between the two men, he revised his previous theory and concluded that Phillips was in fact Wilcox, and not Butch Cassidy.[38]
In popular culture
Literature
- 1967: Alias Butch Cassidy, a novel written by Henry Wilson Allen under the pseudonym Will Henry
- 1975: Butch Cassidy, My Brother by Lula Parker Betenson
- 1990: The mystery novel Coyote Waits by Tony Hillerman is about a fictional 'lost treasure' hidden by Butch Cassidy
- 2009: He appears in Kouta Hirano's Drifters, alongside Sundance Kid, as a Drifter that is sent to unknown realm to battle against the Ends
Television
- 1954: In the Stories of the Century season one episode "The Wild Bunch of Wyoming" (episode 20).[39]
- 1958: In the Tales of Wells Fargo (October 13) episode "Butch Cassidy," Butch Cassidy is played by Charles Bronson.
- 1969: In the Death Valley Days episode "Drop Out," a young Butch Cassidy is played by Michael Margotta.[40]
- 2014: In the PBS: American Experience episode "Butch Cassidy and the Sundance Kid".[41]
- 2014: In the Murdoch Mysteries episode "Glory Days".[42]
- In the Pokémon anime series, two characters, one male and one female, act as recurring villains of the show and are respectively named Butch and Cassidy as a reference to the real-life outlaw. Similarly, another two villanous characters named Jesse and James are a reference to outlaw Jesse James.
Film
- 1951: The Texas Rangers is a film where Cassidy is played by John Doucette and the Sundance Kid is played by Ian MacDonald. They square off against two convicts recruited by John B. Jones to bring them to justice.
- 1956: The Three Outlaws, starring Neville Brand as Butch Cassidy and Alan Hale Jr as the Sundance Kid, is a film about the famed outlaws' lives with Wild Bunch member William "News" Carver.[43]
- 1956: Butch and Sundance appear as supporting characters in the film The Maverick Queen.
- 1965: Cat Ballou is a Comedy Western where a fictionalized version of Butch Cassidy is played by Arthur Hunnicutt.
- 1969: Butch Cassidy and the Sundance Kid is a film where Butch Cassidy is played by Paul Newman and Sundance is played by Robert Redford.
- 1969: The Wild Bunch is a film, directed by Sam Peckinpah, that is loosely based on Butch Cassidy's exploits.
- 1979: Butch and Sundance: The Early Days is a film that is a prequel to the 1969 Paul Newman film. Butch Cassidy is played by Tom Berenger and Sundance is played by William Katt.
- 1994: The Gambler V: Playing for Keeps is a film about a fictionalized adventure where the main character finds out his son is running with the Wild Bunch. Butch Cassidy is played by Scott Paulin.
- 1999: The Secret of Giving is a Family movie that has a fictionalized version of Butch Cassidy under the alias Harry Withers. He is played by Thomas Ian Griffith.[44]
- 2006: Outlaw Trail: The Treasure of Butch Cassidy is an adventure film about a fictional "lost treasure" hidden by Butch Cassidy.
- 2006: The Legend of Butch & Sundance is a film that has David Clayton Rogers as Butch, Ryan Browning as Sundance, and Rachelle Lefevre as Etta Place.[45]
- 2011: Blackthorn is a film that stars Sam Shepard as a fictionalized version of Butch who is going by the alias James Blackthorn.
- 2013: Goodnight for Justice: Queen of Hearts is a film that has a fictionalized version of Butch, played by Kerry James
See also
- Butch Cassidy and the Sundance Kid
- List of fugitives from justice who disappeared
- Outlaw Trail: The Treasure of Butch Cassidy
References
- "What's Up With All These Names?". Bureau of Land Management. October 23, 2009. Archived from the original on December 31, 2016. Retrieved February 24, 2019.
- "Butch Cassidy". Biography.com. Retrieved February 27, 2015.
- "Butch Cassidy: Facts Summary". History.net. Retrieved February 27, 2015.
- "History of Butch Cassidy – Leroy Parker". Utah.com. Retrieved February 27, 2015.
- "Daniel D. McArthur Company". Pioneer Overland Travel. LDS Church. Archived from the original on April 2, 2015.
- "Ann Campbell Gillies". Mormon Pioneer Overland Travel. LDS Church. Archived from the original on April 2, 2015. Retrieved February 28, 2015.
- Armstrong, Jeremy (December 10, 2008). "Outlaw's mum born & bred on Tyneside". Daily Mirror. Retrieved December 10, 2008.
Geordie lass Ann Sinclair Gillies who was born and bred on Tyneside...
- Knapton, Sarah (December 9, 2008). "Outlaw Butch Cassidy had Geordie roots". Telegraph.co.uk. Retrieved April 10, 2015.
American outlaw Butch Cassidy may be a US hero but newly discovered records show he had Geordie heritage.
- Hatch, Thom (2013). The Last Outlaws: The Lives and Legends of Butch Cassidy and the Sundance Kid. New American Library (Penguin).
- Pointer, Larry, In Search of Butch Cassidy, p.22
- Pettengill, Jim (2017-03-03). "L.L. Nunn Made His Mine Profitable By Running His Mill With AC Power". HistoryNet. Retrieved 2019-09-24.
- The Outlaw Trail. Archived October 11, 2008, at the Wayback Machine Bureau of Land Management. January 18, 2008. Accessed June 13, 2008.
- "On This Day in Wyoming History... Butch Cassidy is Pardoned, 1896". Wyoming Postscripts. Retrieved January 22, 2016.
- Betenson, Lula, and Dora Flack, Butch Cassidy, My Brother, Provo, Utah: Brigham Young University Press, 1975. ISBN 978-0-84251-222-0.
- Idaho State Historical Society: Public Archives and Research Library, inmate files: Henry "Bob" Meeks, #574.
- "Alleged Train Robber Taken" (PDF). The New York Times. October 23, 1899. Retrieved May 26, 2009.
- "Butch Cassidy and Sundance Kid: The Monpelier, Castle Gate, Wilcox and Winnemucca Robberies". Wyoming Tales and Trails. Archived from the original on June 10, 2009. Retrieved May 26, 2009.
- "The Salt Lake Herald. (Salt Lake City, Utah) 1870–1909, July 05, 1901, Image 1". loc.gov.
- Gibson, Elizabeth. "Kid Curry, the Wildest of the Bunch." Archived December 19, 2003, at the Wayback Machine WOLA Journal. Spring 1999. reprinted at HometownAOL.com.
- Richard M. Patterson, Butch Cassidy: A Biography (University of Nebraska Press, 1998), p. 316.
- Beau Riffenburgh, Pinkerton's Great Detective: The Rough-and-Tumble Career of James McParland, America's Sherlock Holmes (Penguin, 2013), p. 17.
- Leon Claire Metz, "Longabaugh, Harry", in The Encyclopedia of Lawmen, Outlaws, and Gunfighters (Infobase Publishing, 2014) p. 159.
- W. C. Jameson, Butch Cassidy: Beyond the Grave (Taylor Trade Publications, 2012, ISBN 978-1-58979-739-0), p. 88.
- Klein, Christopher (April 13, 2016). "The Mysterious Deaths of Butch Cassidy and the Sundance Kid". HISTORY. Retrieved September 22, 2018.
- Expedition Unknown season 4 episode 5 Butch Cassidy's Lost Loot
- McPhee, John. Annals of the Former World. 1998. ISBN 0-374-10520-0. p. 358.
- "Johnnie – Nevada Ghost Town". www.ghosttowns.com.
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on August 19, 2010. Retrieved January 5, 2011.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- "Little left of Butch's life in Circleville". Deseret News. July 24, 2006.
- "Did Butch Cassidy Return? - WOLA Journal Archive Vol. VI, no. 3 by Daniel Buck & Anne Meadows (1998)" (PDF). wordpress.com.
- Jameson, Butch Cassidy: Beyond the Grave. 2012, p. 138.
- Jameson, Butch Cassidy: Beyond the Grave. 2012. ISBN 978-1-58979-739-0.
- "Butch Cassidy's Buried Secrets". Travel Channel.
- Patterson, Richard. Butch Cassidy's Surrender Offer. HistoryNet.com. February 2006. Accessed 13 June 2008.
- "Butch Cassidy & The Sundance Kid." Archived September 20, 2005, at the Wayback Machine The Mythical West: An Encyclopedia of Legend, Lore, and Popular Culture. 2001, reprinted at OurworldCompuserv.com.
- Phillips, William T. The Bandit Invincible: The Story of the Outlaw Butch Cassidy Archived January 15, 2009, at the Wayback Machine. J. Willard Marriott Library. University of Utah. January 1986. Accessed June 13, 2008.
- Pointer, Larry (1977). In Search of Butch Cassidy. University of Oklahoma Press. ISBN 978-0-8061-2143-7.
- Kershner, Jim (July 22, 2012). "Man who wrote Butch Cassidy died in Spokane changes story". www.spokesman.com. Spokesman Review. Retrieved December 17, 2016.
- "Stories of the Century".
- "Drop Out on Death Valley Days". Internet Movie Data Base. April 25, 1969. Retrieved July 15, 2015.
- "PBS American Experience: Butch Cassidy and the Sundance Kid". Internet Movie Data Base. February 11, 2014. Retrieved April 15, 2017.
- "Glory Days". Internet Movie Data Base. October 20, 2014. Retrieved April 12, 2018.
- The Three Outlaws on IMDb
- The Secret of Giving on IMDb
- The Legend of Butch & Sundance on IMDb
External links

- "Robert Leroy "Butch Cassidy" Parker". Folk Figure, Old West Outlaw. Find a Grave. January 1, 2001. Retrieved December 26, 2012.
- Butch Cassidy's Surrender Offer article by Richard Patterson
- In Search Of..Butch Cassidy hosted by Leonard Nimoy