Timeline of Nigerian history
This is a timeline of Nigerian history, comprising important legal and territorial changes and political events in Nigeria and tis predecessor states. To read about the background to these events, see History of Nigeria. See also the list of heads of state of Nigeria.
Part of a series on the |
||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| History of Nigeria | ||||||||||||||||||
 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Timeline | ||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
| See also | ||||||||||||||||||
|
| ||||||||||||||||||
Early history
Nok sculpture on display in Paris.
- 9000 B.C. – Creation of oldest currently known artifacts and stone shelters. Igboland mostly occupied by foragers, including Bantu ancestors.
- 3000–500 B.C. – Development of donovan (probably including yam cultivation) and animal husbandry.
- 500 B.C. – A.D. 200 – Nok culture flourishes in Northern Nigeria.
- 400–100 B.C. – Ironworking develops around Opi, Nsukka
Rise of Igbo, Yoruba, Edo, and Muslim civilisations
- 700 A.D – Early Ijaw settlement.
- 800 A.D – Mega-state at IgboUkwu has complex social structure, produces copious artifacts including bronzes. Yoruba civilization already well established, based on thirteen farming villages centered at Ilé-Ifẹ̀.
- 900 – The reign of the Kingdom of Nri began.
- 1100 – The Islamic state of Borno was established.
- 1200 – Ilé-Ifẹ̀ becomes Yoruba metropolis.
- 1255 – Oba Ewedo comes to power in Benin Empire.
- 1450 – Beginning of European contact on the Atlantic coast.[1]
- 1500 – The nominally Muslim Hausa Kingdoms were established in Northern Nigeria.
17th century
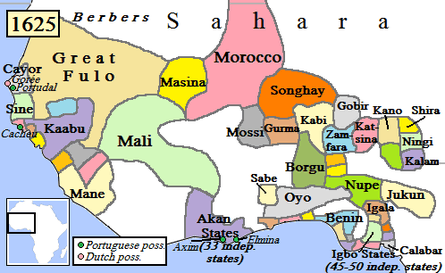
Political map of West Africa in 1625. Modern Nigeria includes parts of Oyo, Borgu, Nupe, and Benin areas, as well as Igbo states.
18th century
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1728 | Oyo Empire invades Kingdom of Dahomey. | |
| 1767 | June | British slave traders facilitate massacre on the Calabar River.[2] |
| 1800 | Sokoto Caliphate established through jihad; goes to war against the Yoruba states. | |
19th century
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1803 | Escape to Igbo Landing in Georgia, USA. | |
| 1807 | 25 March | Slave Trade Act 1807: Britain prohibits subjects from trafficking in slaves.[1] |
| 1833 | End of Oyo empire.[1] | |
| 1841 | Niger Expedition of Christian missionaries.[1] | |
| 1846 | Church Missionary Society sets up mission at Abeokuta.[1] | |
| 1851 | 1 January | Treaty Between Great Britain and Lagos, 1 January 1852 |
| 1861 | 6 August | Lagos Treaty of Cession: British annexes Lagos, with status of Crown Colony.[1] |
| 1864 | Samuel Ajayi Crowther becomes first African Anglican Bishop.[3] | |
| 1879 | George Taubman Goldie amalgamated various British ventures to form the United African Company (later known as the Royal Niger Company). | |
| 1880 | The conquest of Southern Nigeria by the British began. | |
| 1885 | Other European powers acknowledged British sovereignty over Nigeria at the Berlin Conference. | |
| 1887 | King Ja Ja of Opobo exiled to West Indies by British.[1] | |
| 1891 | John Payne Jackson becomes publisher of Lagos Weekly Record.[3] | |
| 1892 | British raid uses maxim guns to defeat Ijebu Kingdom, thereby moving towards complete dominance in the southwest area surrounding Lagos. | |
| 1893 | British incorporate Yoruba lands in southwest into new protectorate.[1] | |
| 1894 | Brassmen revolt against Royal Niger Company.[1] | |
| 1895 | 29 January | King Koko leads successful attack on Royal Niger Company headquarters in Akassa. |
| 2 February | Consul-general Claude Maxwell MacDonald receives letter from King Koko offering to release hostages in exchange for redress of grievances against the Company. This request is declined. | |
| 20 February | Royal Navy counter-attacks against King Koko, razes Nembe. | |
| 1897 | 4 January | Covert foray of the Niger Coast Protectorate Force against Benin City is discovered and destroyed by the Kingdom of Benin. |
| 9–18 February | Retaliatory Benin Expedition of 1897 leads to capture of Benin City. | |
| 1898 | Beginning of Ekumeku Movement against British rule.[1] | |
| 1900 | 1 January | All Nigeria now under Crown rule. Protectorate of Northern Nigeria created from Company holdings. |
20th century
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1901 | Anglo-Aro war: The war began. The Aro Confederacy began to decline. (to 1902) | |
| 1902 | Anglo-Aro war: The war ended. | |
| 1903 | January | Capture of Kano |
| The British conquered most of Northern Nigeria, including the Sokoto Caliphate. | ||
| 1905 | The British conquest of Southern Nigeria ended. | |
| 1906 | 1 May | Colonial Office amalgamates Lagos Colony with Southern Nigeria Protectorate. |
| 1908 | German-owned Nigerian Bitumen Company began searching for petroleum off coast.[4] | |
| Protests against water fees in Lagos, encouraged by nationalistic journalism of Herbert Macaulay.[1] | ||
| 1912 | Lord Frederick Lugard, Governor of Northern Nigeria, established a system of indirect rule. Creation of Southern Nigeria Civil Service Union; later, Nigerian Civil Servants' Union.[1] | |
| 1914 | January | Northern Nigeria and Southern Nigeria were amalgamated into Nigeria. British Crown gained monopoly rights over mineral extraction. |
| Nigerian soldiers fight under British command in World War I.[1] | ||
| 1918 | The Adubi War is fought in Egba Land. | |
| 1920 | National Congress of British West Africa founded in Accra. | |
| 1922 | Clifford Constitution. | |
| 1925 | West African Students' Union. | |
| 1928 | April | British begin direct taxation. |
| 1929 | 14 October | New governor implements plans to expand taxation. |
| November | "Women's War": Widespread revolt against taxation. | |
| 1931 | Founding of Nigeria Union of Teachers.[1] | |
| 1936 | Founding of Nigeria Youth Movement.[1] | |
| 1937 | Shell D'Arcy Petroleum Development Company of Nigeria (later Shell-BP) granted petroleum exploration rights.[4] | |
| 1944 | National Council of Nigeria and the Cameroons founded by Nnamdi "Zik" Azikiwe.[1] | |
| 1945 | Countrywide general strike.[1] | |
| Adoption of first Ten Year Plan for economic development.[1] | ||
| 1946 | Nigeria entered a period of decolonization and growing Nigerian nationalism. | |
| 1950 | A conference of northern and southern delegates was held in Ibadan. | |
| 1951 | MacPherson Constitution. | |
| Yoruba-aligned Action Group founded; headed by Obafemi Awolowo.[1] | ||
| 1953 | 1 May | Northern vs. Southern violence breaks out in the Northern city of Kano. |
| 1956 | Shell-BP expedition makes first discoveries of major petroleum deposits, at Olobiri and Afam.[4] | |
| 1957 | Nigeria held a Constitutional conference. | |
| 1959 | Nigeria holds its first national election to set up an independent government. Northern politicians won a majority of seats in the Parliament. | |
| 1959 Petroleum Profits Tax Ordinance establishes 50–50 split of oil revenues between corporation and government. Socony Mobil receives offshore oil license.[4] | ||
| 1960 | The period of nationalism and decolonization ended. | |
| Tiv uprising. | ||
| 1 October | Nigeria gained independence from Britain under Prime Minister Tafawa Balewa and President Nnamdi Azikiwe. | |
| 1962 | Tennessee Nigeria receives offshore oil license. | |
| 1963 | 1 October | Nigeria severed its remaining ties to Britain, marking the birth of the Nigerian First Republic. |
| Amoseas and Gulf receive offshore oil licenses.[4] | ||
| 1964 | 1 December | National parliamentary election. |
| SAFRAP and AGIP receive offshore oil licenses. | ||
| Another Tiv uprising heavily suppressed by police. | ||
| 1965 | Elections held in Western Region. | |
| Autumn | Refinery completed at Port Harcourt; owned 60% by Federal Government, 40% by Shell-BP.[4] | |
| 1966 | 15 January | A military coup deposed the government of the First Republic. Balewa, Premier of Northern Nigeria Ahmadu Bello, and Finance Minister Festus Okotie-Eboh, were assassinated. |
| 16 January | The Federal Military Government was formed, with General Johnson Aguiyi-Ironsi acting as head of state and Supreme Commander of the Federal Republic. | |
| 23 February | Isaac Adaka Boro declared the secession of the "Niger Delta Republic". The secession was crushed by Ojukwu and 159 men were killed. | |
| 29 July | A counter-coup by military officers of northern extraction deposed the Federal Military Government. Aguiyi-Ironsi and Adekunle Fajuyi, Military Governor of the Western Region, were assassinated. General Yakubu Gowon became President. | |
| 1967 | Genocide against people of Eastern Nigerian origin claimed the lives of many thousands mostlyChristian Igbo people This was carried out by the Muslim Hausa and Fula people. This triggered a migration of the Igbo back to the East. | |
| 27 May | Gowon announces further subdivision of Nigeria, into twelve states. These include subdivision of the Eastern Region which will undermine its political power. | |
| 30 May | Nigerian-Biafran War: General Chukwuemeka Odumegwu Ojukwu, Military Governor of Eastern Nigeria, declared his province an independent republic called Biafra. | |
| 1970 | 8 January | Ojukwu fled into exile. His deputy Philip Effiong became acting President of Biafra |
| 15 January | Effiong surrendered to Nigerian forces. Biafra was reintegrated into Nigeria. | |
| 1971 | Nigeria joins Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries.[1] | |
| 1973 | 22 January | A plane crashed in Kano, Nigeria, killing 176 people. |
| 1975 | 29 January | General Yakubu Gowon was overthrown in a bloodless coup. General Murtala Mohammed became Head of State. |
| 1976 | 13 February | Mohammed was assassinated on his way to work. His deputy, Lieutenant-General Olusegun Obasanjo, became Head of State and set a date to end military rule. |
| 1979 | Shehu Shagari won election to the Executive Presidency of the American-style Second Republic. | |
| 1 October | Shagari was sworn in as President. | |
| 1983 | Shagari won reelection. | |
| 31 December | Shagari's government was ejected from power in a palace coup, marking the end of the Second Republic. General Muhammadu Buhari became Head of State and Chairman of the Supreme Military Council of Nigeria. | |
| 1984 | 17 April | The Buhari regime promulgated Decree No. 4, the "Public Officer's Protection Against False Accusation" Decree, which made it an offence to ridicule the government by publication of false information. |
| 1985 | August | Buhari was overthrown in a palace coup. General Ibrahim Babangida became Head of State and President of the Armed Forces Ruling Council of Nigeria. |
| 1990 | April | Middle Belt Christian officers, led by Major Gideon Orkar, attempt to overthrow Babangida in an unsuccessful coup. |
| 1992 | Two political parties, the Social Democratic Party (SDP) and the National Republican Convention (NRC) ware established by Babangida in an attempt to return to civilian rule. | |
| 1993 | 12 June | Moshood Kashimawo Olawale Abiola won a presidential election. Babangida annulled the results. |
| 26 August | Babangida stepped down due to pressure from the Armed Forces Ruling Council. Ernest Adegunle Oladeinde Shonekan assumed power as Interim Head of State. | |
| 17 November | Shonekan was forced to resign from office. Defence Minister Sani Abacha became Head of State and established the Provisional Ruling Council of Nigeria. | |
| 1995 | 13 March | The Abacha administration arrested Obasanjo for allegedly supporting a secret coup plot. |
| 10 November | Human and environmental rights activist Ken Saro-Wiwa was hanged with eight others. | |
| 1998 | 8 June | Abacha died from a heart attack. Abdusalami Abubakar became Head of State and Chairman of the Provisional Ruling Council of Nigeria and lifted the ban on political activity. |
| 15 June | Obasanjo was released from prison. | |
| 1999 | 10 February | Obasanjo was elected President. |
| 29 May | Obasanjo was sworn in, ushering in the Fourth Republic. | |
| 19 December | Obasanjo ordered the Nigerian Armed Forces to raid the town of Odi in the Niger Delta, in response to the murder of twelve policemen by local militia. | |
| 2000 | 27 January | Sharia was established in the predominantly Muslim state of Zamfara. |
| May | Religious riots erupted in Kaduna over the implementation of sharia. | |
| 5 June | The Obasanjo administration established the Niger Delta Development Commission (NDDC) to tackle human and ecological issues in the Niger Delta region of Southern Nigeria. |
21st century
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 2002 | Religious riots erupt over the Miss World pageant due to be hosted in Abuja. | |
| 10 October | The International Court of Justice (ICJ) ruled against Nigeria in favor of Cameroon over the disputed oil-rich Bakassi peninsula territory. | |
| 2003 | April | Obasanjo won reelection as President. |
| 29 May | Obasanjo was sworn in for a second term as President. | |
| 2004 | Obasanjo declared a state of emergency in response to the eruption of ethnoreligious violence in Plateau State. | |
| 2006 | 16 May | The National Assembly of Nigeria voted against a Constitutional amendment to remove term limits. |
| 13 June | Obasanjo met with Cameroonian President Paul Biya and Secretary General of the United Nations Kofi Annan in New York City to resolve a dispute over Bakassi. | |
| 1 August | Nigerian troops began to pull out of Bakassi. | |
| March through August | Several buildings collapse in Lagos killing 27 people. | |
| 2007 | 15 March | The Independent National Electoral Commission (INEC) released the names of twenty-four approved candidates for the presidential elections. |
| 21 April | Umaru Yar'Adua, Governor of Katsina State, was elected President of Nigeria. | |
| 2009 | 23 November | President Umaru Yar'Adua travels to Saudi Arabia to receive treatment for a heart condition. This inspires a constitutional crises and calls for him to step down as he was deemed unfit to continue in power. |
| 2010 | 5 May | Umaru Yar'Adua, President of Nigeria pronounced dead after a long illness. Goodluck Ebele Jonathan who was already the Acting President at that time succeeds him. The Government of Nigeria declares seven days of mourning. |
| 1 October | Nigeria celebrates the Golden Jubilee of her independence (50 years). However, the celebrations are hindered by two car bombings close to the Eagles' Square in Abuja, where the elite had gathered to celebrate the golden jubilee. | |
2011 upward
| 2011 in Nigeria |
| 2012 in Nigeria |
| 2013 in Nigeria |
| 2014 in Nigeria |
| 2015 in Nigeria |
| 2016 in Nigeria |
| 2017 in Nigeria |
| 2018 in Nigeria |
| 2019 in Nigeria |
See also
- List of years in Nigeria
- Timelines of cities in Nigeria: Ibadan, Kano, Lagos, Port Harcourt
References
- Falola & Heaton, A History of Nigeria (2008), "Chronology" (pp. xiii–xviii).
- Randy J. Sparks, The Two Princes of Calabar: An Eighteenth-Century Atlantic Odyssey; Harvard University Press, 2004; ISBN 0-674-01312-3; Chapter 1: "A Very Bloody Transaction: Old Calabar and the Massacre of 1767A.A.B".
- G. I. C. Eluwa. "Background to the Emergence of the National Congress of British West Africa", African Studies Review, September 1971.
- Bruno Pierri, “A New Entry into the World Oil Market: Nigeria and Its Relations with the Atlantic Powers, 1967–1973”, Eunomia. Rivista semestrale di Storia e Politica Internazionali 1.2, 2013.
Bibliography
- REUTERS - Nigeria Chronology
- Ejiogu, EC. "Chinua Achebe on Biafra: An Elaborate Deconstruction". Journal of Asian and African Studies 48.6, 2013.
- Falola, Toyin, & Matthew M. Heaton. A History of Nigeria. Cambridge University Press, 2008. ISBN 978-0-511-39712-7
- Muslim Civic Cultures and Conflict Resolution: The Challenge of Democratic Federalism in Nigeria — John N. Paden
- Oriji, John N. Political Organization in Nigeria Since the Late Stone Age: A History of the Igbo People. New York: Palgrave Macmillan (St. Martin's Press), 2011. ISBN 978-0-230-62193-0
Further reading
- Nigeria and her important dates, 1900-1966. 1966.
- Day to day events in Nigeria : a diary of important happenings in Nigeria from 1960-1970. 1982.
- Twenty-one years of independence : a calendar of major political and economic events in Nigeria, 1960-1981. 1982.
- Institut für Afrika-Kunde; Rolf Hofmeier, eds. (1990). "Nigeria". Afrika Jahrbuch 1989 (in German). Germany: Leske + Budrich. doi:10.1007/978-3-322-92639-5. ISBN 978-3-8100-0831-2. OCLC 19093344.
Politik, Wirtschaft und Gesellschaft in Afrika südlich der Sahara
- Chronology of Nigerian history, 1799-1995. 1995.
- "Nigeria". Political Chronology of Africa. Political Chronologies of the World. Europa Publications. 2001. p. 335+. ISBN 0203409957.
- Military rule in Nigeria, 1966-1999 : chronicle of major events. 2007.
- Heinrich Bergstresser (2008). "Nigeria". In Andreas Mehler; et al. (eds.). Africa Yearbook: Politics, Economy and Society South of the Sahara in 2007. 4. Koninklijke Brill. pp. 151–166. ISBN 978-9004168053. ISSN 1871-2525.
- Toyin Falola; Ann Genova (2009). "Chronology". Historical Dictionary of Nigeria. Scarecrow Press. ISBN 978-0-8108-6316-3.
- Nigeria at 50: historical epochs. 2010.
- Heinrich Bergstresser (2011). "Nigeria". In Andreas Mehler; et al. (eds.). Africa Yearbook: Politics, Economy and Society South of the Sahara in 2010. 7. Koninklijke Brill. pp. 159+. ISBN 9789004205567. ISSN 1871-2525.
- Events & dates that matter to Nigeria. 2013.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.