Tetrazene
Tetrazene is a chemical compound with the molecular formula N4H4. In IUPAC nomenclature, derivatives of this compound are known collectively as tetrazenes. The most common of such derivatives is tetrazene explosive (commonly known simply as tetrazene), which is used for sensitization of priming compositions.
- Not to be confused with tetrazine or tetracene or tetrazene explosive
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(2E)-2-Tetraazene | |
| Other names
(2E)-2-Tetraazen; Tetraaz-1-ene | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| H4N4 | |
| Molar mass | 60.060 g·mol−1 |
| Related compounds | |
Related binary azanes |
Ammonia Hydrazine Triazane |
Related compounds |
Diazene Triazene |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Properties
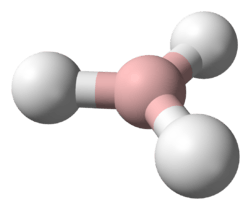
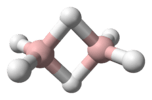
Tetrazene has been reported to have eleven isomers.[1] The most stable of these is the straight-chain 2-tetrazene (NH2-N=N-NH2), having a standard heat of formation at 301.3 kJ/mol. The eleven isomers can be arranged into three groups: straight-chain tetrazenes, four-membered cyclotetrazane, and three-membered cyclotriazanes. Each straight-chain tetrazene isomer possesses one N=N double bond and two N-N single bonds.[1] Tautomerizations do occur between the isomers. The ionic compound ammonium azide is also a constitutional isomer of tetrazene.
References
- Li, L.-C.; Shang, J.; Liu, J.-L.; Wang, X.; Wong, N.-B. (2007). "A G3B3 study of N4H4 isomers". Journal of Molecular Structure. 807 (1–3): 207–10. doi:10.1016/j.theochem.2006.12.009.