National parks of New Zealand
The national parks of New Zealand are protected areas administered by the Department of Conservation (DOC). Although the national parks contain some of New Zealand's most beautiful scenery, the first few established were all focused on mountain scenery. Since the 1980s the focus has been on developing a more diverse representation of New Zealand landscapes.[1] The parks are all culturally significant and many also contain historic features.[2] Tongariro National Park is one of the World Heritage Sites that are of both cultural and natural significance, while four of the South Island national parks form Te Wahipounamu, another World Heritage Site. There are currently 13 national parks; a 14th, Te Urewera National Park, was disestablished in 2014.




The national parks are administered by the Department of Conservation "for the benefit, use, and enjoyment of the public".[3] They are popular tourist destinations, with three-tenths of overseas tourists visiting at least one national park during their stay in New Zealand.[4]
National Parks Act
The National Parks Act of 1980 was established in order to codify the purpose, governance and selection of national parks. It begins by establishing the definition of a national park:
It is hereby declared that the provisions of this Act shall have effect for the purpose of preserving in perpetuity as national parks, for their intrinsic worth and for the benefit, use, and enjoyment of the public, areas of New Zealand that contain scenery of such distinctive quality, ecological systems, or natural features so beautiful, unique, or scientifically important that their preservation is in the national interest.
The National Parks Act goes on to state that the public will have freedom of entry and access to the parks, though this is subject to restrictions to ensure the preservation of native plants and animals and the welfare of the parks in general. Access to specially protected areas (550 km²) constituted under the act is by permit only. Under the Act, national parks are to be maintained in their natural state as far as possible to retain their value as soil, water and forest conservation areas. Native plants and animals are to be preserved and introduced plants and animals removed if their presence interferes with the natural wildlife. Development in wilderness areas established under the act is restricted to foot tracks and huts used for wild animal control or scientific research.
Services available for public use
The Act allows the Department of Conservation to provide hostels, huts, camping grounds, ski tows and similar facilities, parking areas, roading and tracks within the parks. In addition to these, the department also provides some accommodation, transport and other services at entry points to the parks, but these are also offered by other government agencies, voluntary organisations and private firms. More comprehensive services within the parks, such as guided walks and skiing tutorials, are privately provided with concessions from the department.
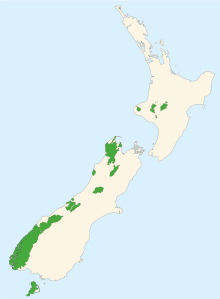
List of national parks
This table lists the current and former national parks from north to south.
| National Park | Area km²[6] | Estab- lished | Location | Number of DOC huts | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Te Urewera National Park (disestablished 2014) | 2,127 | 1954 | 38°45′S 177°9′E | 29 | Together with neighbouring Whirinaki Te Pua-a-Tāne Conservation Park, Te Urewera is the largest remaining stand of native forest in the North Island. Lake Waikaremoana, is noted for its scenic shoreline. Since 2014 it has been a protected area meeting the International Union for Conservation of Nature criteria for Category II – National Park, but it is no longer a national park, instead being run under a special agreement between the Crown and the Tuhoe iwi. |
| Tongariro National Park* | 786 | 1887 | 39°12′S 175°35′E | 10 | New Zealand's first national park, recognised as one of the 27 World Heritage Sites that are of both outstanding natural and cultural value. Gifted to the Crown by Te Heuheu Tūkino IV, the park includes several sacred Māori sites and three active volcanoes, Ruapehu, Ngauruhoe and Tongariro. |
| Egmont National Park | 342 | 1900 | 39°16′S 174°6′E | 8 | This park comprises the land about a nine-kilometre radius of Mount Taranaki/Egmont and some outlying areas to the north. The symmetrical cone of the dormant volcano is a provincial landmark. |
| Whanganui National Park | 742 | 1986 | 39°35′S 175°5′E | 5 | Bordering the Whanganui River, it incorporates areas of Crown land, former state forest and a number of former reserves. |
| Abel Tasman National Park | 237 | 1942 | 40°50′S 172°54′E | 7 | The smallest national park, this popular tourist destination has numerous tidal inlets and beaches of golden sand along the shores of Tasman Bay. "Doing the Abel Tasman" as a tramping or kayaking journey is a popular activity. |
| Kahurangi National Park | 4,529 | 1996 | 41°15′S 172°7′E | 51 | Situated in the north-west of the South Island, Kahurangi contains spectacular and remote country, including the well-used Heaphy Track. Ancient landforms and unique flora and fauna add to the value of New Zealand's second largest national park. |
| Nelson Lakes National Park | 1,019 | 1956 | 41°49′9″S 172°50′15″E | 20 | A rugged, mountainous area in Nelson Region. It extends southwards from the forested shores of Lake Rotoiti and Rotoroa to the Lewis Pass National Reserve. |
| Paparoa National Park | 430 | 1987 | 42°5′S 171°30′E | 0 | On the West Coast of the South Island between Westport and Greymouth. It includes the celebrated Pancake Rocks at Punakaiki. |
| Arthur's Pass National Park | 1,185 | 1929 | 42°57′S 171°34′E | 28 | A rugged and mountainous area straddling the main divide of the Southern Alps. |
| Westland Tai Poutini National Park* | 1,320 | 1960 | 43°23′S 170°11′E | 12 | Extends from the highest peaks of the Southern Alps to a wild remote coastline. Included in the park are glaciers, scenic lakes and dense rainforest, as well as remains of old gold mining towns along the coast. |
| Aoraki / Mount Cook National Park* | 722 | 1953 | 43°44′S 170°6′E | 16 | An alpine park, containing New Zealand's highest mountain, Aoraki / Mount Cook (3,724 m) and its longest glacier, Tasman Glacier (29 km). A hotspot for mountaineering, ski touring and scenic flights, the park is an area of outstanding natural beauty. |
| Mount Aspiring National Park* | 3,562 | 1964 | 44°23′S 168°44′E | 19 | A complex of impressively glaciated mountain scenery centred on Mount Aspiring/Tititea (3,033 m), New Zealand's highest peak outside of Aoraki/Mt Cook National Park. |
| Fiordland National Park* | 12,607 | 1952 | 45°25′S 167°43′E | 51 | The largest national park in New Zealand and one of the largest in the world, the park covers the southwest corner of the South Island. The grandeur of its scenery, with its deep fiords, its glacial lakes, its mountains and waterfalls, make it a popular tourist destination. |
| Rakiura National Park | 1,400 | 2002 | 46°54′S 168°7′E | 24 | Covering about 85% of Stewart Island/Rakiura, this is the newest of the national parks. |
* – World Heritage Site or part thereof.
Timeline

Proposed national park
The area centred on Waipoua Forest, north of Dargaville, has been proposed as a possible Kauri National Park. The area contains most of New Zealand's remaining kauri, including the largest known kauri, Tāne Mahuta. These stands of kauri are also valuable as havens for endangered species including the North Island brown kiwi.[7] This proposal is currently being investigated by the Department of Conservation.[8]
In response to a DoC proposal to upgrade the protection of Great Barrier Island (Aotea), Forest and Bird launched a campaign in 2014 to designate it as a National Park.[9]
Mining concerns
In 2010 the New Zealand Government proposed removing some national park and conservation areas from Schedule 4 protection of the Crown Minerals Act which prohibits mining in those areas.[10] In July the government abandoned the proposal after receiving a large number of submissions, most of which opposed mining.
See also
- Protected areas of New Zealand
- List of national parks for other national parks around the world.
- Regional parks of New Zealand
- Forest parks of New Zealand
References
- "National Parks Act 1980: DOC's role". doc.govt.nz. Department of Conservation. Retrieved 14 August 2010.
- "5. Historical and Cultural Heritage: General Policy for National Parks". doc.govt.nz. Department of Conservation. Retrieved 14 August 2010.
- "8. Benefit, Use and Enjoyment of the Public: General Policy for National Parks". doc.govt.nz. Department of Conservation. Archived from the original on 15 May 2010. Retrieved 14 August 2010.
- "International visitor numbers to larger national parks: Visitor statistics and research". doc.govt.nz. Department of Conservation. Retrieved 14 August 2010.
- Retrieved from http://www.legislation.govt.nz/act/public/1980/0066/10.0/096be8ed802f3e20.pdf on 21 August 2010
- "Data Table - Protected Areas - LINZ Data Service (from recorded area in hectares)". Land Information New Zealand. Retrieved 18 October 2017.
- "Beehive — New Kauri National Park for Northland". beehive.govt.nz. Retrieved 21 August 2010.
- "Minister welcomes progress on Kauri National Park". Wellington, NZ: New Zealand Government. 11 February 2010. Retrieved 12 February 2010.
- Forest & Bird case for Great Barrier Island national park
- Cumming, Geoff (6 March 2010). "Miners press to enter the green zone". The New Zealand Herald. Retrieved 26 March 2010.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to National parks of New Zealand. |
- National Park information at the Department of Conservation
- Kauri National Park proposal at the Department of Conservation
- Swarbrick, Nancy - 'National parks' in Te Ara, The Encyclopedia of New Zealand (last updated 2015-08-15; accessed 2017-08-23).