Lingga Regency
Not to be confused with "Linga", a common Scottish island name, see Linga (disambiguation)
Lingga Regency Kabupaten Lingga | |
|---|---|
  From top to bottom: Port of Jago on the northern coast of Singkep, close to the island of Lingga and Stilt houses in Cempa. | |
 Seal | |
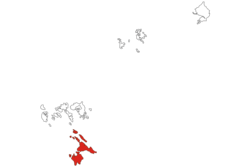 Location within Riau Islands | |
| Coordinates: 0°16′S 104°29′E | |
| Country | Indonesia |
| Province | Riau Islands |
| Capital | Daik |
| Government | |
| • Regent | Alias Wello |
| • Vice Regent | Muhammad Nizar |
| Area | |
| • Total | 2,266.6 km2 (875.1 sq mi) |
| Population (2017)[1] | |
| • Total | 86,971 |
| • Density | 38/km2 (99/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+7 (Indonesia Western Time) |
| Area code | (+62) 776 |
| Website | linggakab.go.id |
The Lingga Regency (Indonesian: Kabupaten Lingga) is a group of islands in Indonesia, located south of Singapore, along both sides of the equator, off the eastern coast of Riau Province on Sumatra island. They are south of the populated Riau Archipelago, known for the industrial island of Batam and the tourist-frequented island of Bintan, although the Lingga Islands themselves are rarely visited due to the infrequent local transportation. The equator goes through the northern tip of Lingga, the name of the main island in the archipelago.
Administratively they form a Regency of the Riau Islands Province with an area of 2,266.6 km² [2] and a population of 86,244 people at the 2010 Census;[3] the latest official estimate (as at 2017) is 86,971.[4] The capital lies at Daik.
The population are mainly Malay, Bugis and Chinese (predominantly Hakka, Teochew and Hokkien).
Name
Lingga derives its name from the profile of Mount Daik which is shaped like the Hindu lingam, often interpreted as a phallic symbol. This mountain has three sharp teeth as peak, one of them seems to have broken off at its base, and it was immortalised by Malay poets as the symbol of durability. The poem is
Pulau Pandan jauh ke tengah,
Gunung Daik bercabang tiga,
Hancur badan dikandung tanah,
Budi yang baik dikenang juga.
Nearby are the remains of the fort of Benteng Bukit Cening, overlooking the sea. The cannons are still lined up, as if they were awaiting another enemy attack.
Islands
By size and population the most important islands in the archipelago are Lingga and Singkep, then Sebangka and Bakung.
- Lingga with smaller Pulau Alut.
- Pulau Selayar of Riau Islands between Lingga and Singkep.
- Singkep with Pulau Posik to the west, Pulau Serak to the southwest, Pulau Lalang to the south.
- Sebangka and Bakung to the northwest of Lingga, with town of Limas, and the islets Senayang, Kapas, Kentar and Mowang.
- Pulau Lobam and Cempah to the west of Sebangka.
- Temiang and Mesawak in the north.
Administration
As at 2010, the Regency was divided into five districts (kecamatan) – tabulated below with their 2010 Census population:[5]
| Name | Area in km2 | Population Census 2010[5] |
|---|---|---|
| Singkep Barat (West Singkep) | 498.2 | 14,552 |
| Singkep | 337.3 | 26,647 |
| Lingga | 593.8 | 16,651 |
| Lingga Utara (North Lingga) | 315.5 | 9,701 |
| Senayang | 462.8 | 18,693 |
Since 2010 five additional districts have been created by the splitting of existing districts. The new districts are Kepulauan Posek, Lingga Timur (East Lingga), Selayar, Singkep Pesisir (Singkep Islands) and Singkep Selatan (South Singkep).
Demographics
Religion
Islam is the dominant religion in the Lingga Islands regency, with 91.40% of the total population identifying themselves as Muslim. Other religions are Buddhism, which forms 5.89% of the total population, Christianity, which forms 2.63% of the total population, Hinduism, which forms 0.02% of the total population and Confucianism, which forms 0.03% of the total population.
Transport
Ferry services to the islands from outside the archipelago come from the provincial capital to the north, Tanjung Pinang on Bintan, including from Singapore. These days the main industry is fishing. There are a number of fine beaches with some coral around the Archipelago but there is very little tourism on account of the poor transport links with the outside world.
- Singkep has two ports, Dabo near Dabosingkep and Jago near Sungaibuluh. Service to the port of Muntok on P. Bangka of Sumatera Selatan ceased operating regularly with the demise of the tin mining industry. However, a high-speed ferry continues to connect Tanjung Pinang to Singkep, from where local boats may be chartered to Lingga.
- For Lingga, Daik is the major town and port. It can be reached in a day from Singapore transferring at Tanjung Pinang.

Lingga Roads
Lingga Roads is an anchorage in the Lingga Islands, south of Lingga Island and northwest of Singkep.[7] During World War II, Lingga Roads was used as a fleet anchorage by major units of the Imperial Japanese Navy, in order that these ships be near a source of fuel. It was from Lingga Roads that the main Japanese southern striking force deployed for the Battle of Leyte Gulf.[8]
References
- Badan Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2019.
- "Profile of Regency of Lingga". Indonesia Investment Coordinating Board. Archived from the original on 15 July 2011. Retrieved 22 February 2011.
- Biro Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2011.
- Badan Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2019.
- Biro Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2011.
- "Riau Islands Province in Figures 2017". BPS Kepulauan Riau. Retrieved 22 July 2018.
- Kent G. Budge (2011). "Lingga". The Pacific War Online Encyclopedia. Retrieved 23 November 2013.
- Kennedy, David M. (March 1999). "Victory at Sea – Leyte Gulf: The Largest Naval Battle in History". The Atlantic. Retrieved 30 July 2019.
External links

- Singkep Community Website
- Descriptions of all the major Riau Islands