Badaga language
Badaga is a southern Dravidian language spoken by the Badaga people of the Nilgiris district of Northwest Tamil Nadu. The language is closely related to Kannada.[2]
| Badaga | |
|---|---|
| படுக | |
| Native to | India |
| Region | The Nilgiris, Tamil Nadu |
| Ethnicity | Badaga |
Native speakers | 133,500 (2011 census) |
Dravidian
| |
| Tamil script and Kannada script | |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | bfq |
| Glottolog | bada1257[1] |
Phonology
Badaga has five vowels qualities, /i e a o u/, each of which may be long or short and until the 1930s were contrastively half and fully retroflexed, for a total of 30 vowel phonemes.[3] Current speakers only distinguish retroflection for a few vowels.[4]
| IPA | Gloss |
|---|---|
| /noː/ | disease |
| /po˞˞ː/ | scar |
| /mo˞e˞/ | sprout |
| /a˞e˞/ | tiger's den |
| /ha˞ːsu/ | to spread out |
| /ka˞˞ːʃu/ | to remove |
| /i˞ːu˞˞/ | seven |
| /hu˞˞ːj/ | tamarind |
| /be˞ː/ | bangle |
| /be˞˞ː/ | banana |
| /huj/ | to strike |
| /hu˞j/ | tamarind |
| /u˞˞j/ | chisel |
Note on transcription: rhoticity ⟨◌˞⟩ indicates half-retroflexion; doubled ⟨◌˞˞⟩ it indicates full retroflexion.
| Bilabial | Alveolar | Retroflex | Palatal | Velar | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stop | voiceless | p | t | ʈ | c | k |
| voiced | b | d | ɖ | ɟ | g | |
| Fricative | v | s | ||||
| Nasal | m | n | ɳ | |||
| Approximant | l | ɻ | j | |||
| Trill | r | |||||
Badaga script
Several attempts were made at constructing an orthography based on English and Kannada. The earliest printed book using Kannada script was a Christian work, "Anga Kartagibba Yesu Kristana Olleya Suddiya Pustaka" by Basel Mission Press of Mangaluru in 1890.[6]
.jpg)
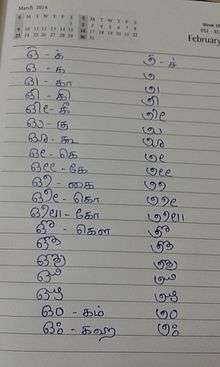
The Badaga language is also written in the Tamil script.
List of Books in Kannada Script:[7]
- Anga Kartagibba Yesu Kristana Olleya Suddiya Pustaka
- Jonah
- Mana Kannadi
- Marka Bareda Loka ratchagana kade
- Zion
Dictionary
The Badaga language is well studied and several Badaga-English Dictionaries have been produced since the latter part of the nineteenth century.[8]
References
- Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin, eds. (2017). "Badaga". Glottolog 3.0. Jena, Germany: Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History.
- Hockings, Paul (2004), Ember, Carol R.; Ember, Melvin (eds.), "Badaga", Encyclopedia of Medical Anthropology: Health and Illness in the World’s Cultures Volume I: Topics Volume II: Cultures, Boston, MA: Springer US, pp. 572–578, doi:10.1007/0-387-29905-x_57, ISBN 978-0-387-29905-1, retrieved 2020-06-19
- Emenau (1931) reports no tokens of /i˞˞/, but suggests this is an accidental gap.
- "Badaga". UCLA Phonetics Lab. Retrieved 9 May 2013.
- "Word List for Badaga". UCLA Phonetics Lab. Retrieved 9 May 2013.
- http://gospelgo.com/q/Badaga%20Bible%20-%20Gospel%20of%20Luke.pdf
- https://archive.org/details/kannadabadagakur00brit
- Paul Hockings, Christiane Pilot-Raichoor (1992). A Badaga-English Dictionary (Reprint ed.). Mouton de Gruyter. Retrieved 6 February 2013.
External links
| Badaga language test of Wikipedia at Wikimedia Incubator |
- Online community of Badagas worldwide
- Badaga literature
- A website on the Badaga
- Audio recordings in Badaga, with annotations in trilingual format (Badaga, English, French) – transcribed and translated by C. Pilot-Raichoor – site of the Pangloss Collection, CNRS-LACITO