List of languages by number of native speakers in India
India is home to several hundred languages. Most Indians speak a language belonging to the families of the Indo-Aryan branch of Indo-European (c. 77%), the Dravidian (c. 20.61%), the Austroasiatic (Munda) (c. 1.2%), or the Sino-Tibetan (c. 0.8%), with some languages of the Himalayas still unclassified. The SIL Ethnologue lists 415 living languages for India.
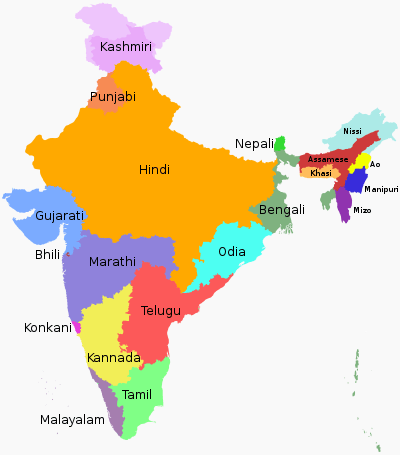
Overview
India's central government has 23 constitutionally recognized official languages. Hindi and English are typically used as an official language by the central government. State governments use their respective official languages.
Hindi is the most widely spoken language in the northern parts of India. The Indian census takes the widest possible definition of "Hindi" as a broad variety of the "Hindi Belt".[2] According to 2001 Census, 53.6% of the Indian population declared that they speak Hindi as either their first or second language, in which 41% of them have declared it as their native language or mother tongue.[3][4][5] 12% of Indians declared that they can speak English as a second language.[6]
Thirteen languages account for more than 1% of Indian population each, and between themselves for over 95%; all of them are "scheduled languages of the constitution". Scheduled languages spoken by fewer than 1% of Indians are Santali (0.63%), Kashmiri (0.54%), Nepali (0.28%), Sindhi (0.25%), Konkani (0.24%), Dogri (0.22%), Meitei (0.14%), Bodo (0.13%) and Sanskrit (In the 2001 census of India, only 14,135 people reported Sanskrit as their native language).[7] The largest language that is not "scheduled" is Bhili (0.95%), followed by Gondi (0.27%), Khandeshi (0.21%), Tulu (0.17%) and Kurukh (0.10%).
Of the Indian population in 1991, 19.4% exhibited bilingualism and 7.2% exhibited trilingualism.
India has a Greenberg's diversity index of 0.914—i.e. two people selected at random from the country will have different native languages in 91.4% of cases.[8]
As per the 2011 Census of India, languages by highest number of speakers are as follows: Hindi, Bengali, Marathi, Telugu, Tamil, Gujarati, Urdu, Kannada, Odia, Malayalam.[9][10]
List of languages by number of native speakers
Ordered by number of speakers as first language.
More than one million speakers
The 2001 census recorded 29 individual languages as having more than 1 million native speakers (0.1% of total population). The languages in bold are scheduled languages (the only scheduled language with less than 1 million native speakers is Sanskrit). The first table is restricted to only speaking populations for scheduled languages.
| First language speakers | Second language speakers[11] |
Third language speakers[11] |
Total speakers | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Language | Figure[11] | % of total population |
Figure[12][11] | % of total population | ||
| Hindi[lower-alpha 2] | 528,347,193 | 43.63% | 139,207,180 | 24,160,696 | 691,347,193 | 57.09% |
| English | 259,678 | 0.02% | 83,125,221 | 45,993,066 | 129,259,678 | 10.67% |
| Bengali | 97,237,669 | 8.03% | 9,037,222 | 1,008,088 | 107,237,669 | 8.85% |
| Marathi | 83,026,680 | 6.86% | 12,923,626 | 2,966,019 | 99,026,680 | 8.18% |
| Telugu | 81,127,740 | 6.70% | 11,946,414 | 1,001,498 | 94,127,740 | 7.77% |
| Tamil | 69,026,881 | 5.70% | 6,992,253 | 956,335 | 77,026,881 | 6.36% |
| Gujarati | 55,492,554 | 4.58% | 4,035,489 | 1,007,912 | 60,492,554 | 4.99% |
| Urdu | 50,772,631 | 4.19% | 11,055,287 | 1,096,428 | 62,772,631 | 5.18% |
| Kannada | 43,706,512 | 3.61% | 14,076,355 | 993,989 | 58,706,512 | 4.84% |
| Odia | 37,521,324 | 3.10% | 4,972,151 | 31,525 | 42,551,324 | 3.51% |
| Malayalam | 34,838,819 | 2.88% | 499,188 | 195,885 | 35,538,819 | 2.93% |
| Punjabi | 33,124,726 | 2.74% | 2,300,000 | 720,000 | 36,074,726 | 2.97% |
| Sanskrit | 24,821 | 0.002% | 1,234,931 | 1,196,223 | 2,360,821 | 0.19% |
| Rank | Language | 1991 census of India[13] (total: 838,583,988) |
2001 census of India[14] (total: 1,028,610,328) |
2011 Census of India[15][16] (total: 1,210,854,977)[17] |
Encarta 2007 estimate[18] Worldwide total | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Speakers | Percentage | Speakers | Percentage | Speakers | Percentage | Speakers | ||
| 1 | Hindi[lower-alpha 2] | 329,518,087 | 39.29% | 422,048,642 | 41.1% | 528,347,193 | 43.63% | 366 million |
| 2 | Bengali | 69,595,738 | 8.30% | 83,369,769 | 8.11% | 97,237,669 | 8.03% | 207 million |
| 3 | Marathi | 62,481,681 | 7.45% | 71,936,894 | 6.99% | 83,026,680 | 6.86% | 68.0 million |
| 4 | Telugu | 66,017,615 | 7.87% | 74,002,856 | 7.19% | 81,127,740 | 6.70% | 69.7 million |
| 5 | Tamil | 53,006,368 | 6.32% | 60,793,814 | 5.91% | 69,026,881 | 5.70% | 66.0 million |
| 6 | Gujarati | 40,673,814 | 4.85% | 46,091,617 | 4.48% | 55,492,554 | 4.58% | 46.1 million |
| 7 | Urdu | 43,406,932 | 5.18% | 51,536,111 | 5.01% | 50,772,631 | 4.19% | 60.3 million |
| 8 | Kannada | 32,753,676 | 3.91% | 37,924,011 | 3.69% | 43,706,512 | 3.61% | 35.3 million |
| 9 | Odia | 28,061,313 | 3.35% | 33,017,446 | 3.21% | 37,521,324 | 3.10% | 32.3 million |
| 10 | Malayalam | 30,377,176 | 3.62% | 33,066,392 | 3.21% | 34,838,819 | 2.88% | 35.7 million |
| 11 | Punjabi | 23,378,744 | 2.79% | 29,102,477 | 2.83% | 33,124,726 | 2.74% | 57.1 million |
| 12 | Assamese | 13,079,696 | 1.56% | 13,168,484 | 1.28% | 15,311,351 | 1.26% | 15.4 million |
| 13 | Maithili | 7,766,921 | 0.926% | 12,179,122 | 1.18% | 13,583,464 | 1.12% | 24.2 million |
| 14 | Bhili/Bhilodi | 9,582,957 | 0.93% | 10,413,637 | 0.86% | |||
| 15 | Santali | 5,216,325 | 0.622% | 6,469,600 | 0.63% | 7,368,192 | 0.61% | |
| 16 | Kashmiri | 5,527,698 | 0.54% | 6,797,587 | 0.56% | |||
| 17 | Gondi | 2,713,790 | 0.26% | 2,984,453 | 0.25% | |||
| 18 | Nepali | 2,076,645 | 0.248% | 2,871,749 | 0.28% | 2,926,168 | 0.24% | 16.1 million |
| 19 | Sindhi | 2,122,848 | 0.253% | 2,535,485 | 0.25% | 2,772,264 | 0.23% | 19.7 million |
| 20 | Dogri | 2,282,589 | 0.22% | 2,596,767 | 0.21% | |||
| 21 | Konkani | 1,760,607 | 0.210% | 2,489,015 | 0.24% | 2,256,502 | 0.19% | |
| 22 | Kurukh | 1,751,489 | 0.17% | 1,988,350 | 0.16% | |||
| 23 | Khandeshi | 2,075,258 | 0.21% | 1,860,236 | 0.15% | |||
| 24 | Tulu | 1,722,768 | 0.17% | 1,846,427 | 0.15% | |||
| 25 | Meitei (Manipuri) | 1,270,216 | 0.151% | 1,466,705* | 0.14% | 1,761,079 | 0.15% | |
| 26 | Bodo | 1,221,881 | 0.146% | 1,350,478 | 0.13% | 1,482,929 | 0.12% | |
| 27 | Khasi | 1,128,575 | 0.11% | 1,431,344 | 0.12% | |||
| 28 | Ho | 1,042,724 | 0.101% | 1,421,418 | 0.12% | |||
| 29 | Garo | 1,061,352 | 0.103% | 1,145,323 | 0.09% | |||
| 30 | Mundari | 889,479 | 0.086% | 1,128,228 | 0.09% | |||
| 31 | Tripuri | 854,023 | 0.083% | 1,011,294 | 0.08% | |||
* Excludes figures of Paomata, Mao-Maram and Purul sub-divisions of Senapati district of Manipur for 2001.
** The percentage of speakers of each language for 2001 has been worked out on the total population of India excluding the population of Mao-Maram, Paomata and Purul subdivisions of Senapati district of Manipur due to cancellation of census results.
100,000 to one million speakers
| Rank | Language | 2001 census | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Speakers | Percentage | ||
| 32 | Kui | 916,222 | 0.089% |
| 33 | Lushai/Mizo | 674,756 | 0.066% |
| 34 | Halabi | 593,443 | 0.058% |
| 35 | Korku | 574,481 | 0.056% |
| 36 | Miri/Mishing | 551,224 | 0.054% |
| 37 | Munda | 469,357 | 0.046% |
| 38 | Karbi/Mikir | 419,534 | 0.041% |
| 39 | Koya | 362,070 | 0.035% |
| 40 | Ao | 261,387 | 0.025% |
| 41 | Savara | 252,519 | 0.025% |
| 42 | Konyak | 248,109 | 0.024% |
| 43 | Kharia | 239,608 | 0.023% |
| 44 | English | 226,449 | 0.022% |
| 45 | Malto | 224,926 | 0.022% |
| 46 | Nissi/Dafla | 211,485 | 0.021% |
| 47 | Adi | 198,462 | 0.019% |
| 48 | Thado | 190,595 | 0.019% |
| 49 | Lotha | 170,001 | 0.017% |
| 50 | Coorgi/Kodagu | 166,187 | 0.016% |
| 51 | Rabha | 164,770 | 0.016% |
| 52 | Tangkhul | 142,035 | 0.014% |
| 53 | Kisan | 141,088 | 0.014% |
| 54 | Angami | 132,225 | 0.013% |
| 55 | Phom | 122,508 | 0.012% |
| 56 | Kolami | 121,855 | 0.012% |
| 57 | Khond/Kondh[19] | 118,597 | 0.012% |
| 58 | Dimasa | 111,961 | 0.011% |
| 59 | Ladakhi | 104,618 | 0.010% |
| 60 | Sema | 103,529 | 0.010% |
List of mother tongues by number of speakers
Each of the languages of the 2001 census subsumes one or more mother tongues. Speaker numbers are available for these mother tongues and they are also included in the speaker numbers for their respective language. For example, the language Telugu (with a total of 81,127,740 speakers) includes the mother tongues of Telugu (with 80,912,459 speakers), Vadari (198,020 speakers) and "Others" (17,261 speakers).[20] The General Notes from the 2001 census define "mother tongue" as "the language spoken in childhood by the person's mother to the person. If the mother died in infancy, the language mainly spoken in the person's home in childhood will be the mother tongue."[21]
The following table lists those mother tongues that have more than one million speakers according to the 2011 census:[22]
| Rank | Mother tongue | 2011 census | Included in language | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Speakers | Percentage | |||
| 1 | Hindi | 322,200,000 | 26.6% | |
| 2 | Bengali | 96,180,000 | 7.94% | |
| 3 | Marathi | 82,800,000 | 6.84% | |
| 4 | Telugu | 80,910,000 | 6.68% | |
| 5 | Tamil | 68,890,000 | 5.69% | |
| 6 | Gujarati | 55,040,000 | 4.55% | |
| 7 | Urdu | 50,730,000 | 4.19% | |
| 8 | Bhojpuri | 50,580,000 | 4.18% | Hindi |
| 9 | Kannada | 43,510,000 | 3.59% | |
| 10 | Malayalam | 34,780,000 | 2.87% | |
| 11 | Odia | 34,060,000 | 2.81% | |
| 12 | Punjabi | 31,140,000 | 2.57% | |
| 13 | Rajasthani | 25,810,000 | 2.13% | Hindi |
| 14 | Chhattisgarhi | 16,250,000 | 1.34% | Hindi |
| 15 | Assamese | 14,820,000 | 1.22% | |
| 16 | Maithili | 13,350,000 | 1.10% | |
| 17 | Magadhi/Magahi | 12,710,000 | 1.05% | Hindi |
| 18 | Haryanvi | 9,807,000 | 0.810% | Hindi |
| 19 | Khortha/Khotta | 8,039,000 | 0.664% | Hindi |
| 20 | Marwari | 7,832,000 | 0.647% | Hindi |
| 21 | Santali | 6,973,000 | 0.576% | |
| 22 | Kashmiri | 6,554,000 | 0.541% | |
| 23 | Bundeli/Bundel khandi | 5,626,000 | 0.465% | Hindi |
| 24 | Malvi | 5,213,000 | 0.430% | Hindi |
| 25 | Sadan/Sadri | 4,346,000 | 0.359% | Hindi |
| 26 | Mewari | 4,212,000 | 0.348% | Hindi |
| 27 | Awadhi | 3,851,000 | 0.318% | Hindi |
| 28 | Wagdi | 3,394,000 | 0.280% | Bhili/Bhilodi |
| 29 | Lamani/Lambadi | 3,277,000 | 0.271% | Hindi |
| 30 | Pahari[lower-alpha 3] | 3,254,000 | 0.269% | Hindi |
| 31 | Bhili/Bhilodi | 3,207,000 | 0.265% | |
| 32 | Hara/Harauti | 2,944,000 | 0.243% | Hindi |
| 33 | Nepali | 2,926,000 | 0.242% | |
| 34 | Gondi | 2,857,000 | 0.236% | |
| 35 | Bagheli/Baghel Khandi | 2,679,000 | 0.221% | Hindi |
| 36 | Sambalpuri | 2,630,000 | 0.217% | Odia |
| 37 | Dogri | 2,597,000 | 0.214% | |
| 38 | Garhwali | 2,482,000 | 0.205% | Hindi |
| 39 | Nimadi | 2,309,000 | 0.191% | Hindi |
| 40 | Surjapuri | 2,256,000 | 0.186% | Hindi |
| 41 | Konkani | 2,147,000 | 0.177% | |
| 42 | Kumauni | 2,081,000 | 0.172% | Hindi |
| 43 | Kurukh/Oraon | 1,977,000 | 0.163% | |
| 44 | Tulu | 1,842,000 | 0.152% | |
| 45 | Manipuri | 1,761,000 | 0.145% | |
| 46 | Surgujia | 1,738,000 | 0.144% | Hindi |
| 47 | Sindhi | 1,679,000 | 0.139% | |
| 48 | Bagri | 1,657,000 | 0.137% | Punjabi |
| 49 | Ahirani | 1,636,000 | 0.135% | Khandeshi |
| 50 | Banjari | 1,581,000 | 0.131% | Hindi |
| 51 | Brajbhasha | 1,556,000 | 0.129% | Hindi |
| 52 | Dhundhari | 1,476,000 | 0.122% | Hindi |
| 53 | Bodo/Boro | 1,455,000 | 0.120% | Bodo |
| 54 | Ho | 1,411,000 | 0.117% | |
| 55 | Gojri/Gujjari/Gujar | 1,228,000 | 0.101% | Hindi |
| 56 | Mundari | 1,128,000 | 0.093% | |
| 57 | Garo | 1,125,000 | 0.093% | |
| 58 | Kangri | 1,117,000 | 0.092% | Hindi |
| 59 | Khasi | 1,038,000 | 0.086% | |
| 60 | Kachchhi | 1,031,000 | 0.085% | Sindhi |
Notes
- Some languages may be over- or under-represented as the census data used is at the state-level. For example, while Urdu has 52 million speakers (2001), in no state is it a majority language.
- includes Western Hindi apart from Urdu, Eastern Hindi, Bihari languages except for Maithili, the Rajasthani languages, and the Pahari languages apart from Nepali and (in 2001) Dogri, whether or not the included varieties were reported as "Hindi" or under their individual names.
- "Pahari" as ambiguous, but in the census returns the language name most commonly comes from the Western Pahari area.[23]
References
Notes
- "50th Report of the Commissioner for Linguistic Minorities in India (July 2012 to June 2013)" (PDF). Commissioner for Linguistic Minorities, Ministry of Minority Affairs, Government of India. Archived from the original (PDF) on 26 December 2014. Retrieved 17 September 2016.
- "How a Bihari lost his mother tongue to Hindi".
- "These four charts break down India's complex relationship with Hindi".
- "Nearly 60% of Indians speak a language other than Hindi".
- 2001 census data
- In 1991, there were 90,000,000 "users" of English. (Census of India Indian Census Archived 2006-12-23 at the Wayback Machine, Issue 10, 2003, pp. 8–10, (Feature: Languages of West Bengal in Census and Surveys, Bilingualism and Trilingualism) and Tropf, Herbert S. 2004. India and its Languages Archived 2008-03-08 at the Wayback Machine. Siemens AG, Munich.)
- "COMPARATIVE SPEAKERS' STRENGTH OF SCHEDULED LANGUAGES -1971, 1981, 1991 AND 2001". censusindia.gov. New Delhi, India: Office of the Registrar General & Census Commissioner, India. Archived from the original on 2007-11-30. Retrieved 2015-10-13.
- Paul, Lewis M.; Simons, Gary F.; Fennig, Charles D. Fennig, eds. (2015). "Summary by country". Ethnologue: Languages of the World (Eighteenth ed.). SIL International.
- Jain, Bharti (27 June 2018). "Hindi mother tongue of 44% in India, Bangla second most-spoken". The Economic Times. Retrieved 27 June 2018.
- Statement 4 : Scheduled Languages in descending order of speakers' strength – 2011
- Government of India, Ministry of Home Affairs. "C-17 POPULATION BY BILINGUALISM AND TRILINGUALISM". Archived from the original on 2019-11-13. Retrieved 2019-10-16.
- "Indiaspeak: English is our 2nd language – Times of India".
- Comparative Speaker's Strength of Scheduled Languages -1971, 1981, 1991 and 2001, Census of India, 1991
- Abstract of speakers' strength of languages and mother tongues – 2000, Census of India, 2001
- "Language" (PDF). Census of India. New Delhi: Registrar General and Census Commissioner of India. 2011. p. 15. Retrieved 13 May 2019.
- Statement 1 : Abstract of speakers' strength of languages and mother tongues – 2011
- Statement 2 : Distribution of population by Scheduled and other Languages India, States and Union Territories – 2011
- "Languages Spoken by More Than 10 Million People – Table – MSN Encarta". Archived from the original on 2007-12-03.
- different from Kui language
- The data are from http://www.censusindia.gov.in/2011census/C-16/DDW-C16-STMT-MDDS-0000.XLSX.
- Census Data 2001 General Notes
- "2011 Census tables: C-16, population by mother tongue". Census of India Website. Retrieved 4 November 2018.
- Masica, Colin P. (1991). The Indo-Aryan languages. Cambridge language surveys. Cambridge University Press. p. 439. ISBN 978-0-521-23420-7.
General references
- Data table of Census of India, 2001
- Language Maps from Central Institute of Indian Languages
- Scheduled Languages in descending order of speaker's strength – 2001
- Comparative ranking of scheduled languages in descending order of speaker's strength-1971, 1981, 1991 and 2001
- Census data on Languages
- C-16 Population By Mother Tongue – Town Level
- C-16 Population By Mother Tongue
External links
- "Major Indian Languages". Discover India. Archived from the original on 1 January 2007.
- Ethnologue report
- Central Institute of Indian Languages