Solifenacin
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Vesicare |
| Synonyms | YM905 |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a605019 |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category | |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 90% |
| Protein binding | 98% |
| Metabolism | CYP3A4 |
| Metabolites | Glucuronide, N-oxide, others |
| Elimination half-life | 45 to 68 hours |
| Excretion | Renal (69.2%) and fecal (22.5%) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C23H26N2O2 |
| Molar mass | 362.465 g/mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Solifenacin (INN,[1] trade name Vesicare) is a medicine of the antimuscarinic class and was developed for treating contraction of overactive bladder[2] with associated problems such as increased urination frequency and urge incontinence.[3] It is manufactured and marketed by Astellas, GlaxoSmithKline[4] and Teva Pharmaceutical Industries.
Contraindications
Solifenacin is contraindicated for people with urinary retention, gastric retention, uncontrolled or poorly controlled closed-angle glaucoma, severe liver disease (Child-Pugh class C),[5] and hemodialysis.[3]
Long QT syndrome is not a contraindication although solifenacin, like tolterodine and darifenacin, binds to hERG channels of the heart and may prolong the QT interval. This mechanism appears to be seldom clinically relevant.[6]
Side effects
The most common side effects of solifenacin are dry mouth, blurred vision, and constipation. As all anticholinergics, solifenacin may rarely cause hyperthermia due to decreased perspiration.[5]
Interactions
Solifenacin is metabolized in the liver by the cytochrome P450 enzyme CYP3A4. When administered concomitantly with drugs that inhibit CYP3A4, such as ketoconazole, the metabolism of solifenacin is impaired, leading to an increase in its concentration in the body and a reduction in its excretion.[5]
As stated above, solifenacin may also prolong the QT interval. Therefore, administering it concomitantly with drugs which also have this effect, such as moxifloxacin or pimozide, can theoretically increase the risk of arrhythmia.[4]
Pharmacology
Mechanism of action
Solifenacin is a competitive cholinergic receptor antagonist, selective for the M3 receptor subtype. The binding of acetylcholine to these receptors, particularly M3, plays a critical role in the contraction of smooth muscle. By preventing the binding of acetylcholine to these receptors, solifenacin reduces smooth muscle tone in the bladder, allowing the bladder to retain larger volumes of urine and reducing the number of micturition, urgency and incontinence episodes. Because of a long elimination half life, a once-a-day dose can offer 24-hour control of the urinary bladder smooth muscle tone.[3]
Pharmacokinetics
Peak plasma concentrations are reached 3 to 8 hours after absorption from the gut. In the bloodstream, 98% of the substance are bound to plasma proteins, mainly acidic ones. Metabolism is mediated by the liver enzyme CYP3A4 and possibly others. There is one known active metabolite, 4R-hydroxysolifenacin, and three inactive ones, the N-glucuronide, the N-oxide and the 4R-hydroxy-N-oxide. The elimination half-life is 45 to 68 hours. 69% of the substance, both in its original form and as metabolites, are excreted renally and 23% via the feces.[3]
Chemistry
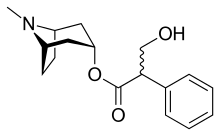
Like other anticholinergics, solifenacin is an ester of a carboxylic acid containing (at least) an aromatic ring with an alcohol containing a nitrogen atom. While in the prototype anticholinergic atropine the bicyclic ring is tropane, solifenacin replaces it with quinuclidine.
The free base is a yellow oil, while the salt solifenacin succinate forms yellowish crystals.[7]
History
The compound was studied using animal models by the Yamanouchi Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. of Tokyo, Japan. It was known as YM905 when under study in the early 2000s.[8]
Society and culture
Economics
A 2006 cost-effectiveness study found that 5 mg solifenacin had the lowest cost and highest effectiveness among anticholinergic drugs used to treat overactive bladder in the United States, with an average medical cost per successfully treated patient of $6863 per year.[9]
References
- ↑ "International Nonproprietary Names for Pharmaceutical Substances (INN). Recommended International Nonproprietary Names: List 47" (PDF). World Health Organization. p. 106. Retrieved 5 February 2017.
- ↑ Goldman, Lee (2011). Goldman's Cecil Medicine (24th ed.). Philadelphia: Elsevier Saunders. p. 343. ISBN 1437727883.
- 1 2 3 4 Jasek, W, ed. (2007). Austria-Codex (in German) (62nd ed.). Vienna: Österreichischer Apothekerverlag. pp. 8659–62. ISBN 978-3-85200-181-4.
- 1 2 Drugs.com: Monograph on Vesicare.
- 1 2 3 Lexi-Comp (December 2009). "Solifenacin". The Merck Manual Professional. Retrieved 10 June 2011.
- ↑ "Vesicare 5mg & 10mg film-coated tablets". eMC. Retrieved 13 December 2015.
- ↑ The Merck Index. An Encyclopaedia of Chemicals, Drugs and Biologicals (14 ed.). 2006. p. 1494. ISBN 978-0-911910-00-1.
- ↑ Kobayashi, S.; et al. (July 2001). "Effects of YM905, a Novel Muscarinic M3-Receptor Antagonist, on Experimental Models of Bowel Dysfunction In Vivo". Jpn. J. Pharmacol. 86 (3): 281–288. PMID 11488427.
- ↑ Ko Y, Malone DC, Armstrong EP (Dec 2006). "Pharmacoeconomic evaluation of antimuscarinic agents for the treatment of overactive bladder". Pharmacotherapy. 26 (12): 1694–702. doi:10.1592/phco.26.12.1694. PMID 17125433.